Abstract
Rationale
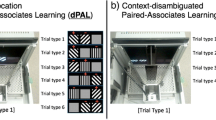
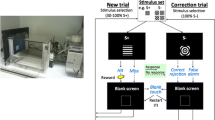
Cognitive testing with touchscreen-equipped operant boxes (‘touchscreens’) is becoming increasingly popular. Tasks, such as paired associate learning or reversal learning of visual stimuli, have the discrimination of visual stimuli as a fundamental component. However, the effect of drugs commonly used in the study of cognitive mechanisms has yet to be described in a visual discrimination.
Objective
The objective of the study was to profile a range of psychoactive agents (glutamatergic, dopaminergic, and cholinergic agonists and antagonists) known to be important in cognitive processing on visual discrimination performance using a touch sensitive computer monitor.
Methods
Male Lister Hooded rats were trained to a stable level of performance in a simple visual discrimination. In Experiment 1, the effect of MK-801, phencyclidine, memantine, dextroamphetamine sulphate (d-amphetamine) and scopolamine was assessed. In Experiment 2, the stimuli were blended together resulting in a perceptually more demanding discrimination and a reduction in accuracy. The rats used in Experiment 1 were then retested with these ‘morphed’ stimuli under the influence of the above compounds.
Results
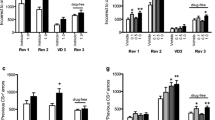
MK-801, PCP, and d-amphetamine induced selective deficits in accuracy in both versions of the task. In contrast, scopolamine and memantine produced non-selective deficits in accuracy. Morphing the stimuli reduced accuracy, but did not alter the observed behavioural profile after compound administration.
Conclusion
These data improve our understanding of the basic neuropharmacology of a visual discrimination in cognitive tests employing touchscreens and will aid in the interpretation of pharmacological studies with more cognitively demanding methodologies.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews JS, Grutzner M, Stephens DN (1992) Effects of cholinergic and non-cholinergic drugs on visual discrimination and delayed visual discrimination performance in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 106:523–530
Barkus C, Feyder M, Graybeal C, Wright T, Wiedholz L, Izquierdo A, Kiselycznyk C, Schmitt W, Sanderson DJ, Rawlins JN, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ, Sprengel R, Bannerman D, Holmes A (2011) Do GluA1 knockout mice exhibit behavioral abnormalities relevant to the negative or cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder? Neuropharmacology. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.06.005
Bartko SJ, Romberg C, White B, Wess J, Bussey TJ, Saksida LM (2011a) Intact attentional processing but abnormal responding in M(1) muscarinic receptor-deficient mice using an automated touchscreen method. Neuropharmacology 61:1366–1378
Bartko SJ, Vendrell I, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ (2011b) A computer-automated touchscreen paired-associates learning (PAL) task for mice: impairments following administration of scopolamine or dicyclomine and improvements following donepezil. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 214:537–548
Blackwell AD, Sahakian BJ, Vesey R, Semple JM, Robbins TW, Hodges JR (2004) Detecting dementia: novel neuropsychological markers of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 17:42–48
Brigman JL, Ihne J, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ, Holmes A (2009) Effects of subchronic phencyclidine (PCP) treatment on social behaviors, and operant discrimination and reversal learning in C57BL/6J mice. Front Behav Neurosci 3:2
Broadbent NJ, Squire LR, Clark RE (2007) Rats depend on habit memory for discrimination learning and retention. Learn Mem 14:145–151
Bussey TJ, Muir JL, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1996) Dissociable effects of anterior and posterior cingulate cortex lesions on the acquisition of a conditional visual discrimination: facilitation of early learning vs. impairment of late learning. Behav. Brain Res 82:45–56
Bussey TJ, Muir JL, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1997) Triple dissociation of anterior cingulate, posterior cingulate, and medial frontal cortices on visual discrimination tasks using a touchscreen testing procedure for the rat. Behav Neurosci 111:920–936
Bussey TJ, Clea WE, Aggleton JP, Muir JL (1998) Fornix lesions can facilitate acquisition of the transverse patterning task: a challenge for “configural” theories of hippocampal function. J Neurosci 18:1622–1631
Bussey TJ, Saksida LM, Rothblat LA (2001) Discrimination of computer-graphic stimuli by mice: a method for the behavioral characterization of transgenic and gene-knockout models. Behav Neurosci 115:957–960
Bussey TJ, Saksida LM, Murray EA (2002) Perirhinal cortex resolves feature ambiguity in complex visual discriminations. Eur J Neurosci 15:365–374
Bussey TJ, Saksida LM (2002) The organization of visual object representations: a connectionist model of effects of lesions in perirhinal cortex. Eur J Neurosci 15:355–364
Bussey TJ, Holmes A, Lyon L, Mar AC, McAllister KA, Nithianantharajah J, Oomen CA, Saksida LM (2011) New translational assays for preclinical modelling of cognition in schizophrenia: the touchscreen testing method for mice and rats. Neuropharmacology
Chen WS, Wong FK, Chapman PF, Pemberton DJ (2009) Effect of donepezil on reversal learning in a touchscreen-based operant task. Behav Pharmacol 20:653–656
Clelland CD, Choi M, Romberg C, Clemenson GD Jr, Fragniere A, Tyers P, Jessberger S, Saksida LM, Barker RA, Gage FH, Bussey TJ (2009) A functional role for adult hippocampal neurogenesis in spatial pattern separation. Science 325:210–213
Danysz W, Parsons CG (2003) The NMDA receptor antagonist memantine as a symptomatological and neuroprotective treatment for Alzheimer’s disease: preclinical evidence. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 18:S23–S32
Dix S, Gilmour G, Potts S, Smith JW, Tricklebank M (2010) A within-subject cognitive battery in the rat: differential effects of NMDA receptor antagonists. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 212:227–242
Ebert U, Kirch W (1998) Scopolamine model of dementia: electroencephalogram findings and cognitive performance. Eur J Clin Invest 28:944–949
Ennaceur A, Aggleton JP (1997) The effects of neurotoxic lesions of the perirhinal cortex combined to fornix transection on object recognition memory in the rat. Behav Brain Res 88:181–193
Gilmour G, Pioli EY, Dix SL, Smith JW, Conway MW, Jones WT, Loomis S, Mason R, Shahabi S, Tricklebank MD (2009) Diverse and often opposite behavioural effects of NMDA receptor antagonists in rats: implications for “NMDA antagonist modelling” of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 205:203–216
Gilmour G, Dix S, Fellini L, Gastambide F, Plath N, Steckler T, Talpos J, Tricklebank M (2011) NMDA receptors, cognition and schizophrenia—testing the validity of the NMDA receptor hypofunction hypothesis. Neuropharmacology
Grilly DM, Loveland A (2001) What is a “low dose” of d-amphetamine for inducing behavioral effects in laboratory rats? Psychopharmacology 153:155–69
Hampson CL, Body S, den Boon FS, Cheung TH, Bezzina G, Langley RW, Fone KC, Bradshaw CM, Szabadi E (2010) Comparison of the effects of 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine and d-amphetamine on the ability of rats to discriminate the durations and intensities of light stimuli. Behav Pharmacol 21:11–20
Hijzen TH, Broersen LM, Slangen JL (1991) Effects of subchronic d-amphetamine on prepulse and gap inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex in rats. Biol Psychiatry 29:1119–1128
Hutton SB, Ettinger U (2006) The antisaccade task as a research tool in psychopathology: a critical review. Psychophysiology 43:302–313
Johnson JW, Kotermanski SE (2006) Mechanism of action of memantine. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6:61–67
Jones DN, Higgins GA (1995) Effect of scopolamine on visual attention in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 120:142–149
Kalkstein S, Hurford I, Gur RC (2010) Neurocognition in schizophrenia. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 4:373–390
Karlsson RM, Tanaka K, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ, Heilig M, Holmes A (2009) Assessment of glutamate transporter GLAST (EAAT1)-deficient mice for phenotypes relevant to the negative and executive/cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:1578–1589
Klinkenberg I, Blokland A (2010) The validity of scopolamine as a pharmacological model for cognitive impairment: a review of animal behavioral studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34:1307–1350
McCarthy AD, Owens IJ, Bansal AT, McTighe SM, Bussey TJ, Saksida LM (2011) FK962 and donepezil act synergistically to improve cognition in rats: potential as an add-on therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 98:76–80
McDonald RJ, White NM (1993) A triple dissociation of memory systems: hippocampus, amygdala, and dorsal striatum. Behav Neurosci 107:3–22
McDonald RJ, King AL, Wasiak TD, Zelinski EL, Hong NS (2007) A complex associative structure formed in the mammalian brain during acquisition of a simple visual discrimination task: dorsolateral striatum, amygdala, and hippocampus. Hippocampus 17:759–774
McKeage K (2010) Spotlight on memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease. Drugs Aging 27:177–179
McTighe SM, Mar AC, Romberg C, Bussey TJ, Saksida LM (2009) A new touchscreen test of pattern separation: effect of hippocampal lesions. Neuroreport 20:881–885
Morgan CJ, Mofeez A, Brandner B, Bromley L, Curran HV (2004) Acute effects of ketamine on memory systems and psychotic symptoms in healthy volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:208–218
Morgan CJ, Muetzelfeldt L, Curran HV (2009a) Ketamine use, cognition and psychological wellbeing: a comparison of frequent, infrequent and ex-users with polydrug and non-using controls. Addiction 104:77–87
Morgan CJ, Huddy V, Lipton M, Curran HV, Joyce EM (2009b) Is persistent ketamine use a valid model of the cognitive and oculomotor deficits in schizophrenia? Biol. Psychiatry 65:1099–1102
Morgan CJ, Muetzelfeldt L, Curran HV (2010) Consequences of chronic ketamine self-administration upon neurocognitive function and psychological wellbeing: a 1-year longitudinal study. Addiction 105:121–133
Niemegeers CJ, Awouters F, Lenaerts FM, Vermeire J, Janssen PA (1982) Prevention of physostigmine-induced lethality in rats. A pharmacological analysis. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 259:153–165
Packard MG, Hirsh R, White NM (1989) Differential effects of fornix and caudate nucleus lesions on two radial maze tasks: evidence for multiple memory systems. J Neurosci 9:1465–1472
Pietrzak RH, Snyder PJ, Maruff P (2010) Use of an acute challenge with d-amphetamine to model cognitive improvement in chronic schizophrenia. Hum Psychopharmacol 25:353–358
Reading PJ, Dunnett SB, Robbins TW (1991) Dissociable roles of the ventral, medial and lateral striatum on the acquisition and performance of a complex visual stimulus–response habit. Behav Brain Res 45:147–161
Robbins TW (1978) The acquisition of responding with conditioned reinforcement: effects of pipradrol, methylphenidate, d-amphetamine, and nomifensine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 58:79–87
Sarter M, Martinez V, Kozak R (2009) A neurocognitive animal model dissociating between acute illness and remission periods of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 202:237–258
Smith JW, Gastambide F, Gilmour G, Dix S, Foss J, Lloyd K, Malik N, Tricklebank M (2011) A comparison of the effects of ketamine and phencyclidine with other antagonists of the NMDA receptor in rodent assays of attention and working memory. Psychopharmacology (Berl)
Squire LR (1994) Memory and forgetting: long-term and gradual changes in memory storage. Int Rev Neurobiol 37:243–269
Steckler T, Sahgal A (1995) Psychopharmacological studies in rats responding at touch-sensitive devices. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 118:226–229
Taffe MA, Weed MR, Gutierrez T, Davis SA, Gold LH (2004) Modeling a task that is sensitive to dementia of the Alzheimer’s type: individual differences in acquisition of a visuo-spatial paired-associate learning task in rhesus monkeys. Behav Brain Res 149:123–133
Talpos JC, Dias R, Bussey TJ, Saksida LM (2008) Hippocampal lesions in rats impair learning and memory for locations on a touch-sensitive computer screen: the “ASAT” task. Behav Brain Res 192:216–225
Talpos JC, Winters BD, Dias R, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ (2009) A novel touchscreen-automated paired-associate learning (PAL) task sensitive to pharmacological manipulation of the hippocampus: a translational rodent model of cognitive impairments in neurodegenerative disease. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 205:157–168
Talpos JC, McTighe SM, Dias R, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ (2010) Trial-unique, delayed nonmatching-to-location (TUNL): a novel, highly hippocampus-dependent automated touchscreen test of location memory and pattern separation. Neurobiol Learn Mem 94:341–352
Winters BD, Forwood SE, Cowell RA, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ (2004) Double dissociation between the effects of peri-postrhinal cortex and hippocampal lesions on tests of object recognition and spatial memory: heterogeneity of function within the temporal lobe. J Neurosci 24:5901–5908
Winters BD, Bartko SJ, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ (2010) Muscimol, AP5, or scopolamine infused into perirhinal cortex impairs two-choice visual discrimination learning in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 93:221–228
Zeeuws I, Deroost N, Soetens E (2010) Verbal memory improved by d-amphetamine: influence of the testing effect. Hum Psychopharmacol 25:377–387
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the valuable contribution of Lilly Research Laboratory Research and Development, IT Innovations, and Solution Delivery teams who were invaluable in the development of our testing system, specially Sam Delaney, Christos Konstantinou, Filip Lukaszewski, and Marek Grabarz.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talpos, J.C., Fletcher, A.C., Circelli, C. et al. The pharmacological sensitivity of a touchscreen-based visual discrimination task in the rat using simple and perceptually challenging stimuli. Psychopharmacology 221, 437–449 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2590-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2590-z