Abstract
Rationale
Opioid neurotransmission has been implicated in reinforcement-related processes for several drugs of abuse, including opiates, stimulants, and alcohol. However, less is known about its role in the motivational effects of nicotine and nicotine-associated environmental cues.
Objective
This study investigated whether pretreatment with naltrexone, an opioid receptor antagonist, alters conditioned incentive salience of nicotine cues under two conditions: cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking after extinction and cue-maintained responding during extinction. The effect of naltrexone on nicotine self-administration during the maintenance phase was also examined.
Materials and methods
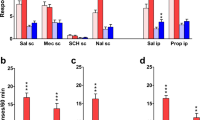
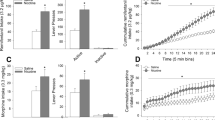
Male Sprague–Dawley rats were trained in daily 1-h sessions to self-administer nicotine (0.03 mg/kg/infusion, i.v.) on a fixed-ratio 5 schedule and associate a conditioned stimulus (CS) with each nicotine delivery. Once responding was extinguished by saline substitution for nicotine and omission of the CS, the reinstatement tests were conducted following subcutaneous administration of naltrexone (0, 0.25, 1, 2 mg/kg). In separate groups of rats, naltrexone (0, 2 mg/kg) was chronically given before each extinction sessions, where responses on the active lever resulted in presentations of the CS without nicotine infusion (saline substitution). Self-administration/naltrexone tests were conducted in different groups of rats receiving similar nicotine self-administration training.
Results
Naltrexone significantly attenuated the CS-reinstated responding on the active, previously nicotine-reinforced lever in the reinstatement tests and the CS-maintained active lever responding during the extinction tests. In contrast, neither acute nor chronic naltrexone produced an effect on nicotine self-administration behavior.
Conclusions
These results indicate that activation of opioid receptors is implicated in mediation of the conditioned incentive properties of nicotine cues but not in the maintenance of nicotine self-administration. Therefore, these findings suggest that opioid receptor antagonists might have clinical potential for prevention of smoking relapse associated with exposure to environmental cues.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams DB, Monti PM, Carey KB, Pinto RP, Jacobus SI (1988) Reactivity to smoking cues and relapse: two studies of discriminant validity. Behav Res Ther 26:225–233
Anggadiredja K, Sakimura K, Hiranita T, Yamamoto T (2004) Naltrexone attenuates cue- but not drug-induced methamphetamine seeking: a possible mechanism for the dissociation of primary and secondary reward. Brain Res 1021:272–276
Aubin HJ, Bobak A, Britton JR, Oncken C, Billing CB, Jr., Gong J, Williams KE, Reeves KR (2008) Varenicline versus transdermal nicotine patch for smoking cessation: Results from a randomised, open-label trial. Thorax 63:717–724 8 Feb 2008. doi:10.1136/thx.2007.090647
Backstrom P, Hyytia P (2004) Ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists modulate cue-induced reinstatement of ethanol-seeking behavior. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28:558–565
Bala MM, Lesniak W, Strzeszynski L (2008) Efficacy of pharmacological methods used for treating tobacco dependence: meta-analysis. Pol Arch Med Wewn 118:20–28
Baptista MA, Martin-Fardon R, Weiss F (2004) Preferential effects of the metabotropic glutamate 2/3 receptor agonist LY379268 on conditioned reinstatement versus primary reinforcement: comparison between cocaine and a potent conventional reinforcer. J Neurosci 24:4723–4727
Benedetti F, Mayberg HS, Wager TD, Stohler CS, Zubieta JK (2005) Neurobiological mechanisms of the placebo effect. J Neurosci 25:10390–10402
Berrendero F, Mendizabal V, Robledo P, Galeote L, Bilkei-Gorzo A, Zimmer A, Maldonado R (2005) Nicotine-induced antinociception, rewarding effects, and physical dependence are decreased in mice lacking the preproenkephalin gene. J Neurosci 25:1103–1112
Bienkowski P, Kostowski W, Koros E (1999) Ethanol-reinforced behaviour in the rat: effects of naltrexone. Eur J Pharmacol 374:321–327
Blendy JA, Strasser A, Walters CL, Perkins KA, Patterson F, Berkowitz R, Lerman C (2005) Reduced nicotine reward in obesity: cross-comparison in human and mouse. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 180:306–315
Boyadjieva NI, Sarkar DK (1997) The secretory response of hypothalamic beta-endorphin neurons to acute and chronic nicotine treatments and following nicotine withdrawal. Life Sci 61:PL59–PL66
Brauer LH, Behm FM, Westman EC, Patel P, Rose JE (1999) Naltrexone blockade of nicotine effects in cigarette smokers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 143:339–346
Burattini C, Gill TM, Aicardi G, Janak PH (2006) The ethanol self-administration context as a reinstatement cue: acute effects of naltrexone. Neuroscience 139:877–887
Burattini C, Burbassi S, Aicardi G, Cervo L (2008) Effects of naltrexone on cocaine- and sucrose-seeking behaviour in response to associated stimuli in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:103–109
Butschky MF, Bailey D, Henningfield JE, Pickworth WB (1995) Smoking without nicotine delivery decreases withdrawal in 12-hour abstinent smokers. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 50:91–96
Ciccocioppo R, Martin-Fardon R, Weiss F (2002) Effect of selective blockade of mu(1) or delta opioid receptors on reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior by drug-associated stimuli in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:391–399
Cohen C, Perrault G, Griebel G, Soubrie P (2005) Nicotine-associated cues maintain nicotine-seeking behavior in rats several weeks after nicotine withdrawal: reversal by the cannabinoid (CB1) receptor antagonist, rimonabant (SR141716). Neuropsychopharmacology 30:145–155
Corrigall WA, Coen KM (1991) Opiate antagonists reduce cocaine but not nicotine self-administration. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 104:167–170
David S, Lancaster T, Stead LF, Evins AE (2006) Opioid antagonists for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD003086
Dayas CV, Liu X, Simms JA, Weiss F (2007) Distinct patterns of neural activation associated with ethanol seeking: effects of naltrexone. Biol Psychiatry 61:979–989
DeNoble VJ, Mele PC (2006) Intravenous nicotine self-administration in rats: effects of mecamylamine, hexamethonium and naloxone. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 184:266–272
Donny EC, Caggiula AR, Mielke MM, Jacobs KS, Rose C, Sved AF (1998) Acquisition of nicotine self-administration in rats: the effects of dose, feeding schedule, and drug contingency. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 136:83–90
Donny EC, Houtsmuller E, Stitzer ML (2007) Smoking in the absence of nicotine: behavioral, subjective and physiological effects over 11 days. Addiction 102:324–334
Drobes DJ, Tiffany ST (1997) Induction of smoking urge through imaginal and in vivo procedures: physiological and self-report manifestations. J Abnorm Psychol 106:15–25
Droungas A, Ehrman RN, Childress AR, O’Brien CP (1995) Effect of smoking cues and cigarette availability on craving and smoking behavior. Addict Behav 20:657–673
Due DL, Huettel SA, Hall WG, Rubin DC (2002) Activation in mesolimbic and visuospatial neural circuits elicited by smoking cues: evidence from functional magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Psychiatry 159:954–960
Epstein AM, King AC (2004) Naltrexone attenuates acute cigarette smoking behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 77:29–37
Everitt BJ, Parkinson JA, Olmstead MC, Arroyo M, Robledo P, Robbins TW (1999) Associative processes in addiction and reward. The role of amygdala–ventral striatal subsystems. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877:412–438
Filliol D, Ghozland S, Chluba J, Martin M, Matthes HW, Simonin F, Befort K, Gaveriaux-Ruff C, Dierich A, LeMeur M, Valverde O, Maldonado R, Kieffer BL (2000) Mice deficient for delta- and mu-opioid receptors exhibit opposing alterations of emotional responses. Nat Genet 25:195–200
Gerrits MA, Wiegant VM, Van Ree JM (1999) Endogenous opioids implicated in the dynamics of experimental drug addiction: an in vivo autoradiographic analysis. Neuroscience 89:1219–1227
Gerrits MA, Kuzmin AV, van Ree JM (2005) Reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats is attenuated following repeated treatment with the opioid receptor antagonist naltrexone. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 15:297–303
Gianoulakis C (2004) Endogenous opioids and addiction to alcohol and other drugs of abuse. Curr Top Med Chem 4:39–50
Gonzales D, Rennard SI, Nides M, Oncken C, Azoulay S, Billing CB, Watsky EJ, Gong J, Williams KE, Reeves KR (2006) Varenicline, an alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, vs sustained-release bupropion and placebo for smoking cessation: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 296:47–55
Grimm JW, See RE (2000) Dissociation of primary and secondary reward-relevant limbic nuclei in an animal model of relapse. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:473–479
Gross J, Lee J, Stitzer ML (1997) Nicotine-containing versus de-nicotinized cigarettes: effects on craving and withdrawal. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 57:159–165
Houdi AA, Pierzchala K, Marson L, Palkovits M, Van Loon GR (1991) Nicotine-induced alteration in Tyr-Gly-Gly and Met-enkephalin in discrete brain nuclei reflects altered enkephalin neuron activity. Peptides 12:161–166
Houdi AA, Dasgupta R, Kindy MS (1998) Effect of nicotine use and withdrawal on brain preproenkephalin A mRNA. Brain Res 799:257–263
Hutchison KE, Monti PM, Rohsenow DJ, Swift RM, Colby SM, Gnys M, Niaura RS, Sirota AD (1999) Effects of naltrexone with nicotine replacement on smoking cue reactivity: preliminary results. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 142:139–143
Jorenby DE, Hays JT, Rigotti NA, Azoulay S, Watsky EJ, Williams KE, Billing CB, Gong J, Reeves KR (2006) Efficacy of varenicline, an alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, vs placebo or sustained-release bupropion for smoking cessation: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 296:56–63
Kalin NH, Shelton SE, Barksdale CM (1988) Opiate modulation of separation-induced distress in non-human primates. Brain Res 440:285–292
Katner SN, Magalong JG, Weiss F (1999) Reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior by drug-associated discriminative stimuli after prolonged extinction in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:471–479
King AC, Meyer PJ (2000) Naltrexone alteration of acute smoking response in nicotine-dependent subjects. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66:563–572
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2001) Drug addiction, dysregulation of reward, and allostasis. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:97–129
Lazev AB, Herzog TA, Brandon TH (1999) Classical conditions of environmental cues to cigarette smoking. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 7:56–63
Lee YS, Joe KH, Sohn IK, Na C, Kee BS, Chae SL (2005) Changes of smoking behavior and serum adrenocorticotropic hormone, cortisol, prolactin, and endogenous opioids levels in nicotine dependence after naltrexone treatment. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29:639–647
Leri F, Burns LH (2005) Ultra-low-dose naltrexone reduces the rewarding potency of oxycodone and relapse vulnerability in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 82:252–262
LeSage MG, Burroughs D, Dufek M, Keyler DE, Pentel PR (2004) Reinstatement of nicotine self-administration in rats by presentation of nicotine-paired stimuli, but not nicotine priming. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 79:507–513
Liu X, Weiss F (2002) Additive effect of stress and drug cues on reinstatement of ethanol seeking: exacerbation by history of dependence and role of concurrent activation of corticotropin-releasing factor and opioid mechanisms. J Neurosci 22:7856–7861
Liu X, Weiss F (2004) Nitric oxide synthesis inhibition attenuates conditioned reinstatement of ethanol-seeking, but not the primary reinforcing effects of ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28:1194–1199
Liu X, Caggiula AR, Yee SK, Nobuta H, Poland RE, Pechnick RN (2006) Reinstatement of nicotine-seeking behavior by drug-associated stimuli after extinction in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 184:417–425
Liu X, Caggiula AR, Yee SK, Nobuta H, Sved AF, Pechnick RN, Poland RE (2007) Mecamylamine attenuates cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking behavior in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:710–718
Liu X, Caggiula AR, Palmatier MI, Donny EC, Sved AF (2008) Cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking behavior in rats: effect of bupropion, persistence over repeated tests, and its dependence on training dose. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 196:365–375
Maldonado R (2003) The neurobiology of addiction. J Neural Transm Suppl 66:1–14
Malin DH, Lake JR, Carter VA, Cunningham JS, Wilson OB (1993) Naloxone precipitates nicotine abstinence syndrome in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 112:339–342
Martin-Fardon R, Maurice T, Aujla H, Bowen WD, Weiss F (2007) Differential effects of sigma1 receptor blockade on self-administration and conditioned reinstatement motivated by cocaine vs natural reward. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1967–1973
McDermut W, Haaga DA (1998) Effect of stage of change on cue reactivity in continuing smokers. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 6:316–324
Meil WM, See RE (1997) Lesions of the basolateral amygdala abolish the ability of drug associated cues to reinstate responding during withdrawal from self-administered cocaine. Behav Brain Res 87:139–148
Moles A, Kieffer BL, D’Amato FR (2004) Deficit in attachment behavior in mice lacking the mu-opioid receptor gene. Science 304:1983–1986
Monti PM, Rohsenow DJ, Hutchison KE, Swift RM, Mueller TI, Colby SM, Brown RA, Gulliver SB, Gordon A, Abrams DB (1999) Naltrexone’s effect on cue-elicited craving among alcoholics in treatment. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:1386–1394
Mucha RF, Pauli P, Angrilli A (1998) Conditioned responses elicited by experimentally produced cues for smoking. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 76:259–268
Nelson EE, Panksepp J (1998) Brain substrates of infant–mother attachment: contributions of opioids, oxytocin, and norepinephrine. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 22:437–452
Nemeth-Coslett R, Griffiths RR (1986) Naloxone does not affect cigarette smoking. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 89:261–264
Newman JL, Beardsley PM (2006) Effects of memantine, haloperidol, and cocaine on primary and conditioned reinforcement associated with cocaine in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 185:142–149
Niaura R, Abrams D, Demuth B, Pinto R, Monti P (1989) Responses to smoking-related stimuli and early relapse to smoking. Addict Behav 14:419–428
Niaura R, Abrams DB, Pedraza M, Monti PM, Rohsenow DJ (1992) Smokers’ reactions to interpersonal interaction and presentation of smoking cues. Addict Behav 17:557–566
Oncken C, Gonzales D, Nides M, Rennard S, Watsky E, Billing CB, Anziano R, Reeves K (2006) Efficacy and safety of the novel selective nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, varenicline, for smoking cessation. Arch Intern Med 166:1571–1577
Paterson NE, Markou A (2004) Prolonged nicotine dependence associated with extended access to nicotine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 173:64–72
Paterson NE, Froestl W, Markou A (2005) Repeated administration of the GABAB receptor agonist CGP44532 decreased nicotine self-administration, and acute administration decreased cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:119–128
Perkins KA, Grobe JE, Fonte C, Goettler J, Caggiula AR, Reynolds WA, Stiller RL, Scierka A, Jacob RG (1994) Chronic and acute tolerance to subjective, behavioral and cardiovascular effects of nicotine in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:628–638
Pomerleau OF (1998) Endogenous opioids and smoking: a review of progress and problems. Psychoneuroendocrinology 23:115–130
Ray R, Jepson C, Patterson F, Strasser A, Rukstalis M, Perkins K, Lynch KG, O’Malley S, Berrettini WH, Lerman C (2006) Association of OPRM1 A118G variant with the relative reinforcing value of nicotine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 188:355–363
Robinson ML, Houtsmuller EJ, Moolchan ET, Pickworth WB (2000) Placebo cigarettes in smoking research. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 8:326–332
Rohsenow DJ, Monti PM, Hutchison KE, Swift RM, Colby SM, Kaplan GB (2000) Naltrexone’s effects on reactivity to alcohol cues among alcoholic men. J Abnorm Psychol 109:738–7342
Rohsenow DJ, Monti PM, Colby SM, Gulliver SB, Swift RM, Abrams DB (2003) Naltrexone treatment for alcoholics: effect on cigarette smoking rates. Nicotine Tob Res 5:231–236
Rose JE, Behm FM, Westman EC, Johnson M (2000) Dissociating nicotine and nonnicotine components of cigarette smoking. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:71–81
Rusted JM, Graupner L, Greenwood K (1996) Methodological considerations in nicotine research: the use of “denicotinised” cigarettes as the control condition in smoking studies. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 125:176–178
Saumet JL, Dittmar A (1985) Heat loss and anticipatory finger vasoconstriction induced by a smoking of a single cigarette. Physiol Behav 35:229–232
Schiltz CA, Kelley AE, Landry CF (2005) Contextual cues associated with nicotine administration increase arc mRNA expression in corticolimbic areas of the rat brain. Eur J Neurosci 21:1703–1711
Scott DJ, Domino EF, Heitzeg MM, Koeppe RA, Ni L, Guthrie S, Zubieta JK (2007) Smoking modulation of mu-opioid and dopamine D2 receptor-mediated neurotransmission in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:450–457
Shaham Y, Stewart J (1996) Effects of opioid and dopamine receptor antagonists on relapse induced by stress and re-exposure to heroin in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 125:385–391
Stewart J (1983) Conditioned and unconditioned drug effects in relapse to opiate and stimulant drug self-administration. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 7:591–597
Stewart J, Wise RA (1992) Reinstatement of heroin self-administration habits: morphine prompts and naltrexone discourages renewed responding after extinction. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 108:79–84
Surawy C, Stepney R, Cox T (1985) Does watching others smoke increase smoking? Br J Addict 80:207–210
Sutherland G, Stapleton JA, Russell MA, Feyerabend C (1995) Naltrexone, smoking behaviour and cigarette withdrawal. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 120:418–425
Tanda G, Di Chiara G (1998) A dopamine-mu1 opioid link in the rat ventral tegmentum shared by palatable food (Fonzies) and non-psychostimulant drugs of abuse. Eur J Neurosci 10:1179–1187
Walters CL, Cleck JN, Kuo YC, Blendy JA (2005) Mu-opioid receptor and CREB activation are required for nicotine reward. Neuron 46:933–943
Watkins SS, Koob GF, Markou A (2000) Neural mechanisms underlying nicotine addiction: acute positive reinforcement and withdrawal. Nicotine Tob Res 2:19–37
Wewers ME, Dhatt R, Tejwani GA (1998) Naltrexone administration affects ad libitum smoking behavior. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 140:185–190
Wewers ME, Dhatt RK, Snively TA, Tejwani GA (1999) The effect of chronic administration of nicotine on antinociception, opioid receptor binding and met-enkelphalin levels in rats. Brain Res 822:107–113
Wilson DI, Bowman EM (2004) Nucleus accumbens neurons in the rat exhibit differential activity to conditioned reinforcers and primary reinforcers within a second-order schedule of saccharin reinforcement. Eur J Neurosci 20:2777–2788
Wong GY, Wolter TD, Croghan GA, Croghan IT, Offord KP, Hurt RD (1999) A randomized trial of naltrexone for smoking cessation. Addiction 94:1227–1237
Zarrindast MR, Faraji N, Rostami P, Sahraei H, Ghoshouni H (2003) Cross-tolerance between morphine- and nicotine-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74:363–369
Zubieta JK, Ketter TA, Bueller JA, Xu Y, Kilbourn MR, Young EA, Koeppe RA (2003) Regulation of human affective responses by anterior cingulate and limbic mu-opioid neurotransmission. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:1145–1153
Zubieta JK, Bueller JA, Jackson LR, Scott DJ, Xu Y, Koeppe RA, Nichols TE, Stohler CS (2005) Placebo effects mediated by endogenous opioid activity on mu-opioid receptors. J Neurosci 25:7754–7762
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by NIH grant DA017288 (X. Liu) from the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Palmatier, M.I., Caggiula, A.R. et al. Naltrexone attenuation of conditioned but not primary reinforcement of nicotine in rats. Psychopharmacology 202, 589–598 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1335-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1335-0