Abstract
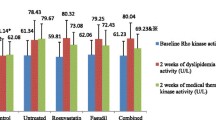
The current study was designed to investigate the potential beneficial therapeutic outcome of Rho kinase inhibitor (fasudil) against hypercholesterolemia-induced myocardial and vascular injury in rabbits together with diet modification. Sixteen male rabbits were randomly divided into four groups: normal control group which received standard rabbit chow, hypercholesterolemic control group, and treated groups which received cholesterol-rich rabbit chow (1.5% cholesterol) for 8 weeks. Treated groups received either fasudil (100 mg/kg/day) or rosuvastatin (2.5 mg/kg/day) starting from the ninth week for further 4 weeks with interruption of the cholesterol-rich chow. Biochemical assessment of serum cholesterol, triglyceride, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and myocardial oxidative/antioxidant biomarkers malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and reduced glutathione (GSH), besides biochemical assessment of serum nitric oxide (NO), creatine kinase (CK), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activities and serum total antioxidant capacity (TAC), was conducted. Serum vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) and serum Rho-associated protein kinase 1 (ROCK-1) were also evaluated along with histopathological examination of aorta specimens. Fasudil administration significantly decreased serum cholesterol, triglyceride (TG), and LDL and significantly increased serum HDL, with concomitant decrease in serum CK and LDH activities, NO, and restoration of serum TAC. Myocardial MDA significantly declined; SOD activity and GSH contents were restored. Serum ROCK-1 and VCAM-1 levels significantly declined as well. Vascular improvement was confirmed with histopathological examination, which revealed normal aortic intema with the absence of atheromas. Fasudil has promising anti-atherogenic activity mediated primarily via alleviation of hypercholesterolemia-induced oxidative stress and modulation of inflammatory response.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, L.B. 2005. “Hyperlipidemia” in Stang, J. and Story, M.: Guidelines for Adolescent Nutrition Services, The University of Minnesota, USA, pp.109–124
Amano M, Nakayama M, Kaibuchi K (2010) Rho-kinase/ROCK: a key regulator of the cytoskeleton and cell polarity. Cytoskeleton 67:545–554. doi:10.1002/cm.20472
Amin E, Dubey BN, Zhang S, Gremer L, Dvorsky R, Moll JM, Taha MS, Nagel-Steger L, Piekorz RP, Somlyo AV, Ahmadian MR (2013) Rho-kinase: regulation, dysfunction, and inhibition. Bio Chem J 394(11):1399–1410. doi:10.1515/hsz-2013-0181
Anila L, Vijayalakshmi NR (2003) Antioxidant action of flavonoids from Mangifera indica and Emblica officinalis in hypercholesterolemic rats. Food Chem 83:569–574
Ankur R, Nidhi D, Seema R, Amarjeet D, Ashok K (2012) Hyperlipidemia—a deadly pathological condition. Int J Curr Pharm Res 4(2):15–18
Avogaro A, Albiero M, Menegazzo L, de Kreutzenberg S, Fadini GP (2011) Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes the role of reparatory mechanisms. Diabetes Care 34(2):s285–s290. doi:10.2337/dc11-s239
Bjorkbacka H, Fredrikson GN, Nilsson J (2012) Emerging biomarkers and intervention targets for immune-modulation of atherosclerosis—a review of the experimental evidence. Atherosclerosis 227:9–17
Calderon RM, Cubeddu LX, Goldberg RB, Schiff ER (2010) Statins in the treatment of dyslipidemia in the presence of elevated liver aminotransferase levels: a therapeuticdilemma. Mayo Clin Proc 85(4):349–356. doi:10.4065/mcp.2009.0365
Covington MB (2004) Omega-3 fatty acids. Am Fam Physician 70:133–140
Deeb RS, Lamon BD, Hajjar DP (2009) Silent partner in blood vessel homeostasis? Pervasive role of nitric oxide in vascular disease. Curr Hypertens Rev 5:273–282
Ding J, Yu JZ, Li QY, Wang X, Lu CZ, Xiao BG (2009) Rho kinase inhibitor fasudil induces neuroprotection and neurogenesis partially through astrocyte derived G-CSF. Brain Behav Immun 23:1083–1088. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2009.05.002
El-Agamy DS, Said E, Abo-Haded HM (2015) Diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis: a review article. Prensa Med Argent 101:1–4. doi:10.4172/lpma.1000161
Elkind MS, Rundek T, Sciacca RR, Ramas R, Chen HJ et al (2005) Interleukin-2 levels are associated with carotid artery intima-media thickness. Atherosclerosis 180:181–187
Gillies PJ, Rathgeb KA, Robinson CS (1986) Regulation of acyl Co A: cholesterol acyl transferase activity in normal and atherosclerotic rabbit aortas: role of a cholesterol substrate pool. Exp Mol Pathol 44:320–339. doi:10.1016/0014-4800(86)90046-8
Gojo A, Utsunomiya K, Taniguchi K, Yokota T, Ishizawa S, Kanazawa Y, Kurata H, Tajima N (2007) The Rho-kinase inhibitor, fasudil, attenuates diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 568(1–3):242–247
Hakonarson H, Thorvaldsson S, Helgadottir A, Gudbjartsson D, Zink F et al (2005) Effects of a 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein inhibitor on biomarkers associated with risk of myocardial infarction: a randomized trial. JAMA 293:2245–2256
Hansson GK, Hermansson A (2011) The immune system in atherosclerosis. Nat Immunol 12:204–212
Hirooka Y, Shimokawa H (2005) Therapeutic potential of rho-kinase inhibitors in cardiovascular diseases. American journal of cardiovascular drugs 5:31–39. doi:10.2165/00129784-200505010-00005
Hsueh TP, Sheen JM, Pang JHS, Bi KW, Huang CC, Wu HT, Huang ST (2016) The anti-atherosclerotic effect of naringin is associated with reduced expressions of cell adhesion molecules and chemokines through NF-kB pathway. Molecules 21:195. doi:10.3390/molecules21020195
Huang Y, Xiao S, Jiang Q (2015) Role of Rho kinase signal pathway in inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Clin Exper Med 8(3):3089–3097
Ikeda S, Satoh K, Kikuchi N, Miyata S, Suzuki K, Omura J, Shimizu T, Kobayashi K, Kobayashi K, Fukumoto Y, Sakata Y, Shimokawa H (2014) Crucial role of rho-kinase in pressure overload-induced right ventricular hypertrophy and dysfunction in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 34(6):1260–1271. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303320
ILAR (Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources) 1996. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Published by National Academy Press, 2101 Constitution Ave. NW, Washington, DC 20055.
Ishizaki T, Uehata M, Tamechika I, Keel J, Nonomura K, Maekawa M, Narumiya S (2000) Pharmacological properties of Y-27632, a specific inhibitor of rho-associated kinases. Mol Pharmacol 57:976–983
Itabe, H., Obama, T. and Kato, R. 2011. The dynamics of oxidized LDL during atherogenesis. Journal of Lipids, 1–9. doi: 10.1155/2011/418313.
Jacobson MS (1998) Heart healthy diets for all children: no longer controversial. J Pediatr 133(1):1–2. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(98)70167-2
Kandabashi T, Shimokawa H, Miyata K, Kunihiro I, Kawano Y, Fukata Y, Higo T, Egashira K, Takahashi S, Kaibuchi K, Takeshita A (2000) Inhibition of myosin phosphatase by upregulated rho-kinase plays a key role for coronary artery spasm in a porcine model with interleukin-1beta. Circulation 101:1319–1323
Kandabashi T, Shimokawa H, Mukai Y, Matoba T, Kunihiro I, Morikawa K, Ito M, Takahashi S, Kaibuchi K, Takeshita A (2002) Involvement of rho-kinase in agonists-induced contractions of arteriosclerotic human arteries. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:243–248
Karantonis HC, Antonopoulou S, Perrea DN, Sokolis DP, Theocharis SE, Kavantzas N (2006) In vivo antiatherogenic properties of olive oil and its constituents lipid classic in hyperlipidemic rabbits. Nutr. Metabolism Cardiovasc. Dis 16:174–185
Kawanami D, Matoba K, Okada R, Tsukamoto M, Kinoshita J, Ishizawa S, Kanazawa Y, Yokota T, Utsunomiya K (2013) Fasudil inhibits ER stress-induced VCAM-1 expression by modulating unfolded protein response in endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 435(2):171–175
Kikuchi Y, Yamada M, Imakiire T, Kushiyama T, Higashi K, Hyodo N, Yamamoto K, Oda T, Suzuki S, Miura S (2007) A Rho-kinase inhibitor, fasudil, prevents development of diabetes and nephropathy in insulin-resistant diabetic rats. J Endocrinol 192(3):595–603
Landmesser U, Hornig B, Drexler H (2004) Endothelial function: a critical determinant in atherosclerosis? Circulation 109:II27–II33
Lappas M, Yee Ks, Permezel M, Rice GE (2005) Sulfasalazine and BAY 11-7082 interfere with the nuclear factor-kappa B and I kappa B kinase pathway to regulate the release of proinflammatory cytokines from human adipose tissue and skeletal muscle in vitro. Endocrinology 46:1491–1497
Li D, Mehta JL (2000) Antisense to LOX-1 inhibits oxidized LDL-mediated upregulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and monocyte adhesion to human coronary artery endothelial cells. Circulation 101(25):2889–2895. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.101.25.2889
Liao JK (2006) Rho-kinase a potential link between hypercholesterolemia and abnormal vascular smooth muscle contraction. Circ Res 99:238–239
Libby P, Okamoto Y, Rocha VZ, Folco E (2010) Inflammation in atherosclerosis: transition from theory to practice. Circ J 74:213–220
Ma Z, Zhang J, Du R, Ji E, Chu L (2011a) Rho kinase inhibition by fasudil has anti-inflammatory effects in hypercholesterolemic rats. Biol Pharm Bull 34(11):1684–1689
Ma Z, Zhang J, Ji E, Cao G, Li G, Chu L (2011b) Rho kinase inhibition by fasudil exerts antioxidant effects in hypercholesterolemic rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 38(10):688–694. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05561.x
Markus HS, Labrum R, Bevan S, Reindl M, Egger G et al (2006) Genetic and acquired inflammatory conditions are synergistically associated with early carotid atherosclerosis. Stroke 37:2253–2259
Maron R, Sukhova G, Faria AM, Hoffmann E, Mach F (2002) Mucosal administration of heat shock protein-65 decreases atherosclerosis and inflammation in aortic arch of low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Circulation 106:1708–1715
Masseau I, Bowles DK (2015) Carotid endothelial VCAM-1 is an early marker of carotid atherosclerosis and predicts coronary artery disease in swine. J Biomed Sci Eng 8:767–779. doi:10.4236/jbise.2015.811075
Naci H, Brugts JJ, Fleurence R, Tsoi B, Toor H, Ades AE (2013) Comparative benefits of statins in the primary and secondary prevention of major coronary events and all-cause mortality: a network meta-analysis of placebo-controlled and active-comparator trials. Eur J Prev Cardiol 20(4):641–657. doi:10.1177/2047487313480435
Napoli C, de Nigris F, Williams-Ignarro S, Pignalosa O, Sica V, Ignarro LJ (2006) Nitric oxide and atherosclerosis: an update. Nitric Oxide 15:265–279
Nathan C (2002) Points of control in inflammation. Nature 420:846–852
Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Nishida M, Matsuyama A et al (2001) Adipocyte-derived plasma protein, adiponectin, suppresses lipid accumulation and class A scavenger receptor expression in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Circulation 103:1057–1063
Rajendran P, Rengarajan T, Thangavel J, Nishigaki Y, Sakthisekaran D, Sethi G, Nishigaki I (2013) The vascular endothelium and human diseases. Int J Biol Sci 9(10):1057–1069. doi:10.7150/ijbs.7502
Register TC (2009) Primate models in women’s health: inflammation and atherogenesis in female cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fascicularis). Am J Primatol 71:766–775
Riento K, Ridley AJ (2003) Rocks: multifunctional kinases in cell behaviour. Natural Reviews Molecular Cell Biological 4:446–456
Smolen JS, Beaulieu A, Rubbert-Roth A, Ramos-Remus C, Rovensky J et al (2008) Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet 371:987–997
Stapleton PA, Adam GG, James ME, Brock RW, Frisbee JC (2010) Hypercholesterolemia and microvascular dysfunction: interventional strategies. J Inflamm 7:54
Steinberg D (2009) The LDL modification hypothesis of atherogenesis: an update. J Lipid Res 50(l):S376–S381
Sun X, Minoharab M, Kikuchi H, Ishizu T, Tanaka M, Piao H, Osoegawa M, Ohyagi Y, Shimokawa H, Kira J (2006) The selective Rho-kinase inhibitor fasudil is protective and therapeutic in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 180(1–2):126–134. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.06.027
Taylor, A.J. and Villines, T.C. (eds.) 2013. Atherosclerosis: clinical perspectives through imaging. Springer-Verlag London. DOI 10.1007/978–1–4471-4288-1
Tian J, Hu S, Sun Y, Ban X, Yu H, Dong N, Wu J, Yu B (2012) A novel model of atherosclerosis in rabbits using injury to arterial walls induced by ferric chloride as evaluated by optical coherence tomography as well as intravascular ultrasound and histology. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:2. doi:10.1155/2012/121867
Wang L, Qiu X-M, Li DJ (2013) Anti-inflammatory effects of a Chinese herbal medicine in atherosclerosis via estrogen receptor b mediating nitric oxide production and NF-jB suppression in endothelial cells. Cell Death and Disease 4:551. doi:10.1038/cddis.2013.66
Wang W, Zhang Y, Gao M, Wang J, Hou Y (2014) Effect of rosuvastatin on atrial structural remodeling in rabbits with myocardial infarction. Biomedical Reports 3(1):78–82. doi:10.3892/br.2014.366
Wirth A (2010) Rho kinase and hypertension. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802(12):1276–1284. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.05.002
Wu DJ, Xu JZ, Wu YJ, Jean-Charles L, Xiao B, Gao PJ, Zhu DL (2009) Effects of fasudil on early atherosclerotic plaque formation and established lesion progression in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. Atherosclerosis 207(1):68–73
Zhang X, Wu C, Wu H, Sheng L, Su Y, Zhang X (2013) Antihyperlipidemic effects and potential mechanisms of action of the caffeoyl quinic acid-rich Pandanus tectorius fruit extract in hamsters fed a high fat-diet. PLoS One 8(4):e61922
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure 1
(DOCX 53 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
(DOCX 54 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdali, N.T., Yaseen, A.H., Said, E. et al. Rho kinase inhibitor fasudil mitigates high-cholesterol diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and vascular damage. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 390, 409–422 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1343-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1343-x