Abstract
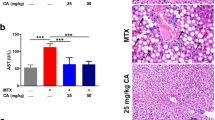
Methotrexate (MTX) is a widely used drug for treatment of rheumatic and autoimmune diseases as well as different types of cancer. One of the major side effects of MTX is hepatotoxicity. Retinoid receptors, including retinoid X receptor (RXR), and retinoic acid receptor (RAR) are vitamin A receptors that are highly expressed in the liver and regulate important physiological processes through regulation of different genes. In this study, we investigated the effect of MTX on RXR-α and RAR-α expression in the liver and the potential protective effects of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) in MTX-induced hepatotoxicity. Rats were randomly divided into five groups: The rates were treated with saline, DMSO, MTX (20 mg/kg/IP; single dose), ATRA (7.5 mg/kg/day, I.P), or MTX and ATRA. Rats were killed 24 h after the last ATRA injection. The liver tissues were dissected out, weighed, and subjected to histological, immunohistochemical, and biochemical examinations. Our results demonstrated that treatment with MTX resulted in significant decrease in reduced glutathione (GSH) content and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, with concomitant increase in ALT, AST, and MDA levels. In addition, MTX markedly downregulated the expression of both RXR-α and RAR-α, and changed the appearance of RXR-α to be very small speckled droplets. Treatment with ATRA significantly ameliorated MTX-induced effects on GSH, ALT, and MDA. Moreover, ATRA administration increased the expression and nuclear translocation of RXR-α in rat hepatocytes. In conclusion, our study revealed, for the first time, that retinoid receptors may play an important role in the MTX-induced hepatotoxicity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Bakky MS, Hammad MA, Walker LA, Ashfaq MK (2010) Loss of retinoic Acid receptor (RAR) and retinoid X receptor (RXR) contribute to liver toxicity in MCT/LPS co-treated mice model. Planta Med 76:100
Abdel-Bakky MS, Hammad MA, Walker LA, Ashfaq MK (2011) Tissue factor dependent liver injury causes release of retinoid receptors (RXR-alpha and RAR-alpha) as lipid droplets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 410:146–151
Akbulut S, Elbe H, Eris C, Dogan Z, Toprak G, Otan E, Erdemli E, Turkoz Y (2014) Cytoprotective effects of amifostine, ascorbic acid and N-acetylcysteine against methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. World J Gastroenterol 20:10158–10165. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10158
Balmer JE, Blomhoff R (2002) Gene expression regulation by retinoic acid. J Lipid Res 43:1773–1808
Beigneux AP, Moser AH, Shigenaga JK, Grunfeld C, Feingold KR (2000) The acute phase response is associated with retinoid X receptor repression in rodent liver. J Biol Chem 275:16390–16399. doi:10.1074/jbc.M000953200
BEUTLER E, DURON O, KELLY BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Bode JG, Peters-Regehr T, Gressner AM, Haussinger D (1998) De novo expression of glutamine synthetase during transformation of hepatic stellate cells into myofibroblast-like cells. Biochem J 335(Pt 3):697–700
Dalaklioglu S, Genc GE, Aksoy NH, Akcit F, Gumuslu S (2013) Resveratrol ameliorates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats via inhibition of lipid peroxidation. Hum Exp Toxicol 32:662–671. doi:10.1177/0960327112468178
Gilani ST, Khan DA, Khan FA, Ahmed M (2012) Adverse effects of low dose methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Coll Phys Surg Pak 22:101–104
Gudas LJ (2012) Emerging roles for retinoids in regeneration and differentiation in normal and disease states. Biochim Biophys Acta 1821:213–221. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.08.002
Gudas LJ, Sporn MB, Roberts AB (1994) Cellular biology and biochemistry of the retinoids. The retinoids: biology, chemistry, and medicine 1994:443-520
Hadi NR, Al-Amran FG, Swadi A (2012) Metformin ameliorates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity. J Pharmacol Pharmacother 3:248–253. doi:10.4103/0976-500X.99426
Jaskiewicz K, Voigt H, Blakolmer K (1996) Increased matrix proteins, collagen and transforming growth factor are early markers of hepatotoxicity in patients on long-term methotrexate therapy. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 34:301–305
Lee WM (2003) Drug-induced hepatotoxicity. N Engl J Med 349:474–485. doi:10.1056/NEJMra021844
Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM (1995) The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell 83:841–850
Mezaki Y, Yamaguchi N, Yoshikawa K, Miura M, Imai K, Itoh H, Senoo H (2009) Insoluble, speckled cytosolic distribution of retinoic acid receptor alpha protein as a marker of hepatic stellate cell activation in vitro. J Histochem Cytochem 57:687–699. doi:10.1369/jhc.2009.953208
Mezaki Y, Yoshikawa K, Yamaguchi N, Miura M, Imai K, Kato S, Senoo H (2007) Rat hepatic stellate cells acquire retinoid responsiveness after activation in vitro by post-transcriptional regulation of retinoic acid receptor alpha gene expression. Arch Biochem Biophys 465:370–379. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2007.06.024
Mukherjee R, Davies PJ, Crombie DL, Bischoff ED, Cesario RM, Jow L, Hamann LG, Boehm MF, Mondon CE, Nadzan AM, Paterniti JR Jr, Heyman RA (1997) Sensitization of diabetic and obese mice to insulin by retinoid X receptor agonists. Nature 386:407–410. doi:10.1038/386407a0
Nishikimi M, Appaji N, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46:849–854
Noy N (2010) Between death and survival: retinoic acid in regulation of apoptosis. Annu Rev Nutr 30:201–217. doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.28.061807.155509
Ohata M, Lin M, Satre M, Tsukamoto H (1997) Diminished retinoic acid signaling in hepatic stellate cells in cholestatic liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol 272:G589–G596
Radaeva S, Wang L, Radaev S, Jeong WI, Park O, Gao B (2007) Retinoic acid signaling sensitizes hepatic stellate cells to NK cell killing via upregulation of NK cell activating ligand RAE1. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 293:G809–G816. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00212.2007
Rao J, Zhang C, Wang P, Lu L, Zhang F (2010) All-trans retinoic acid alleviates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by enhancing manganese superoxide dismutase in rats. Biol Pharm Bull 33:869–875
REITMAN S, FRANKEL S (1957) A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol 28:56–63
Salbert G, Fanjul A, Piedrafita FJ, Lu XP, Kim SJ, Tran P, Pfahl M (1993) Retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptor-alpha down-regulate the transforming growth factor-beta 1 promoter by antagonizing AP-1 activity. Mol Endocrinol 7:1347–1356
Satoh K (1978) Serum lipid peroxide in cerebrovascular disorders determined by a new colorimetric method. Clin Chim Acta 90:37–43
Sener G, Eksioglu-Demiralp E, Cetiner M, Ercan F, Sirvanci S, Gedik N, Yegen BC (2006a) L-Carnitine ameliorates methotrexate-induced oxidative organ injury and inhibits leukocyte death. Cell Biol Toxicol 22:47–60. doi:10.1007/s10565-006-0025-0
Sener G, Eksioglu-Demiralp E, Cetiner M, Ercan F, Yegen BC (2006b) Beta-glucan ameliorates methotrexate-induced oxidative organ injury via its antioxidant and immunomodulatory effects. Eur J Pharmacol 542:170–178. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.02.056
Ulven SM, Natarajan V, Holven KB, Lovdal T, Berg T, Blomhoff R (1998) Expression of retinoic acid receptor and retinoid X receptor subtypes in rat liver cells: implications for retinoid signalling in parenchymal, endothelial, Kupffer and stellate cells. Eur J Cell Biol 77:111–116
Uraz S, Tahan V, Aygun C, Eren F, Unluguzel G, Yuksel M, Senturk O, Avsar E, Haklar G, Celikel C, Hulagu S, Tozun N (2008) Role of ursodeoxycholic acid in prevention of methotrexate-induced liver toxicity. Dig Dis Sci 53:1071–1077. doi:10.1007/s10620-007-9949-3
Vogel S, Piantedosi R, Frank J, Lalazar A, Rockey DC, Friedman SL, Blaner WS (2000) An immortalized rat liver stellate cell line (HSC-T6): a new cell model for the study of retinoid metabolism in vitro. J Lipid Res 41:882–893
Vonen B, Morland J (1984) Isolated rat hepatocytes in suspension: potential hepatotoxic effects of six different drugs. Arch Toxicol 56:33–37
Wang H, Dan Z, Jiang H (2008) Effect of all-trans retinoic acid on liver fibrosis induced by common bile duct ligation in rats. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci 28:553–557. doi:10.1007/s11596-008-0514-x
Wu JJ, Schiff KR (2004) Sarcoidosis. Am Fam Physician 70:312–322
Xiao JH, Durand B, Chambon P, Voorhees JJ (1995) Endogenous retinoic acid receptor (RAR)-retinoid X receptor (RXR) heterodimers are the major functional forms regulating retinoid-responsive elements in adult human keratinocytes. Binding of ligands to RAR only is sufficient for RAR-RXR heterodimers to confer ligand-dependent activation of hRAR beta 2/RARE (DR5). J Biol Chem 270:3001–3011
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ewees, M.G., Abdelghany, T.M., Abdel-Aziz, AA.H. et al. All-trans retinoic acid mitigates methotrexate-induced liver injury in rats; relevance of retinoic acid signaling pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 388, 931–938 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1130-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1130-5