Abstract
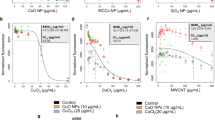
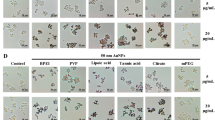
The unique properties of nanoparticles and biological systems are important factors affecting the biological response following nanoparticle exposure. Iron oxide nanoparticles are classified mainly as magnetite (M-FeNPs) and maghemite (NM-FeNPs). In our previous study, NM-FeNPs induced autophagic cell death in RAW264.7, a murine peritoneal macrophage cell line, which has excellent lysosomal activity. In this study, we compared the toxicity of M-FeNPs and NM-FeNPs in MH-S, a murine alveolar macrophage cell line, which has relatively low lysosomal activity. At 24 h post-exposure, M-FeNPs decreased cell viability and ATP production, and elevated the levels of reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide, and pro-inflammatory cytokines to a higher extent than NM-FeNPs. Damage of mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum and the down-regulation of mitochondrial function and transcription-related genes were also higher in cells exposed to M-FeNPs than in cells exposed to NM-FeNPs (50 μg/ml). In addition, cells exposed to M-FeNPs (50 μg/ml) showed an increase in the number of autophagosome-like vacuoles, whereas cells exposed to NM-FeNPs formed large vacuoles in the cytosol. However, an autophagy-related molecular response was not induced by exposure to either FeNPs, unlike the results seen in our previous study with RAW264.7 cells. We suggest that M-FeNPs induced higher toxicity compared to NM-FeNPs in MH-S cells, and lysosomal activity plays an important role in determining cell death pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altamura S, Muckenthaler MU (2009) Iron toxicity in diseases of aging: Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and atherosclerosis. J Alzheimers Dis 16(4):879–895
Andón FT, Fadeel B (2013) Programmed cell death: molecular mechanisms and implications for safety assessment of nanomaterials. Acc Chem Res 46(3):733–742
Beard J, Han O (2009) Systemic iron status. Biochim Biophys Acta 1790(7):584–588
Berberat PO, Katori M, Kaczmarek E, Anselmo D, Lassman C, Ke B, Shen X, Busuttil RW, Yamashita K, Csizmadia E, Tyagi S, Otterbein LE, Brouard S, Tobiasch E, Bach FH, Kupiec-Weglinski JW, Soares MP (2003) Heavy chain ferritin acts as an antiapoptotic gene that protects livers from ischemia reperfusion injury. FASEB J 17:1724–1726
Bonkovsky HL (1991) Iron and the liver. Am J Med Sci 301(1):32–43
Boya P, Reggiori F, Codogno P (2013) Emerging regulation and functions of autophagy. Nat Cell Biol 15(7):713–720
Cho SH, Ahn AK, Bhargava P, Lee CH, Eischen CM, McGuinness O, Boothby M (2011) Glycolytic rate and lymphomagenesis depend on PARP14, an ADP ribosyltransferase of the B aggressivelymphoma (BAL) family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(38):15972–15977
Crichton RR, Wilmet S, Legssyer R, Ward RJ (2002) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of iron homeostasis and toxicity in mammalian cells. J Inorg Biochem 91(1):9–18
Culcasi M, Benameur L, Mercier A, Lucchesi C, Rahmouni H, Asteian A, Casano G, Botta A, Kovacic H, Pietri S (2012) EPR spin trapping evaluation of ROS production in human fibroblasts exposed to cerium oxide nanoparticles: evidence for NADPH oxidase and mitochondrial stimulation. Chem Biol Interact 199(3):161–176
Dunai Z, Bauer PI, Mihalik R (2011) Necroptosis: biochemical, physiological and pathological aspects. Pathol Oncol Res 17:791–800
Dupont CL, Grass G, Rensing C (2011) Copper toxicity and the origin of bacterial resistance—new insights and applications. Metallomics 3:1109–1118
Duvigneau JC, Piskernik C, Haindl S, Kloesch B, Hartl RT, Hüttemann M, Lee I, Ebel T, Moldzio R, Gemeiner M, Redl H, Kozlov AV (2008) A novel endotoxin-induced pathway: upregulation of heme oxygenase 1, accumulation of free ion, and free iron-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction. Lab Invest 88:70–77
Feliu N, Fadeel B (2010) Nanotoxicology: no small matter. Nanoscale 2:2514–2520
Fong NM, Jensen TC, Shah AS, Parekh NN, Saltiel AR, Brady MJ (2000) Identification of binding sites on protein targeting to glycogen for enzymes of glycogen metabolism. J Biol Chem 275(45):35034–35039
Galleano M, Gimontacchi M, Puntarulo S (2004) Nitric oxide and iron: effect of iron overload on nitric oxide production in endotoxemia. Mol Aspects Med 25(1–2):141–154
Grau-Crespo R, Al-Baitai AY, Saadoune I, De Leeuw NH (2010) Vacancy ordering and electronic structure of γ-Fe2O3 (maghemite): a theoretical investigation. J Phys Condens Matter 22(25):255401
Hamilton RF, Wu N, Porter D, Buford M, Wolfarth M, Holian A (2009) Particle length-dependent titanium dioxide nanomaterials toxicity and bioactivity. Part Fibre Toxicol 6:35
Hegde ML, Hegde PM, Rao KS, Mitra S (2011) Oxidative genome damage and its repair in neurodegenerative diseases: function of transition metals as a double-edged sword. J Alzheimers Dis 24(Suppl 2):183–198
Jomova K, Vondrakova D, Lawson M, Valko M (2010) Metals, oxidative stress and neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Cell Biochem 345:91–104
Kang YS, Sisbud S, Rabolt JF, Stroeve P (1996) Synthesis and characterization of nanometer-size Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3 particles. Chem Mater 8:2209
Kimball SR (1999) Eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 31(1):25–29
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C, Vander Elst L, Muller RN (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev 108(6):2064–2110
Liu Q, Berchner-Pfannschmidt U, Möller U, Brecht M, Wotzlaw C, Acker H, Jungermann K, Kietzmann T (2004) A fenton reaction at the endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the redox control of hypoxia-inducible gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:4302–4307
Lu JV, Walsh CM (2012) Programmed necrosis and autophagy in immune function. Immunol Rev 249:205–217
Maurer-Jones MA, Lin YS, Haynes CL (2010) Functional assessment of metal oxide nanoparticle toxicity in immune cells. ACS Nano 4:3363–3373
Núñez MT, Urrutia P, Mena N, Aguirre P, Tapia V, Salazar J (2012) Iron toxicity in neurodegeneration. Biomaterials 25(4):761–776
Orrenius S, Nicotera P, Zhivotovsky B (2011) Cell death mechanisms and their implications in toxicology. Toxicol Sci 119:3–19
Park J, An K, Hwang Y, Park JG, Noh HJ, Kim JY, Park JH, Hwang NM, Hyeon T (2004) Ultra-large-sacle syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat Mater 3:891–895
Park EJ, Shim HW, Lee GH, Kim JH, Kim DW (2013) Comparison of toxicity between the different-type TiO2 nanowires in vivo and in vitro. Arch Toxicol 87(7):1219–1230
Park EJ, Umh HN, Kim SW, Cho MH, Kim JH, Kim Y (2014) ERK pathway is activated in bare-FeNps-induced autophagy. Arch Toxicol 88(2):323–336
Platt N, Haworth R, Darley L, Gordon S (2002) The many roles of the class A macrophage scavenger receptor. Int Rev Cytol 212:1–40
Sasidharan A, Panchakarla LS, Chandran P, Menon D, Nair S, Rao CN, Koyakutty M (2011) Differential nano-bio interactions and toxicity effects of pristine versus functionalized graphene. Nanoscale 3(6):2461–2464
Sperandio S, Poksay KS, Schilling B, Crippen D, Gibson BW, Bredesen DE (2010) Identification of new modulators and protein alteration in non-apoptotic programmed cell death. J Cell Biochem 111(6):1401–1412
The National Academy of Sciences (2007) Toxicity testing in the 21st century: a vision and a strategy. http://nationalacacemies.org/best
Trump BF, Berezesky IK (1995) Calcium-mediated cell injury and cell death. FASEB J 9:219–228
Voinov MA, Sosa Pagán JO, Morrison E, Smirnova TI, Smirnov AI (2011) Surface-mediated production of hydroxyl radicals as a mechanism of iron oxide nanoparticle biotoxicity. J Am Chem Soc 133:35–41
Warheit DB, Webb TR, Sayes CM, Colvin VL, Reed KL (2006) Pulmonary instillation studies with nanoscale TiO2 rods and dots in rats: toxicity is not dependent upon particle size and surface area. Toxicol Sci 91:227–236
Warheit DB, Webb TR, Reed KL, Frerichs S, Sayes CM (2007) Pulmonary toxicity study in rats with three forms of ultrafine-TiO2 particles: differential responses related to surface properties. Toxicology 230:90–104
Winterbourn CC (1995) Toxicity of iron and hydrogen peroxide: the Fenton reaction. Toxicol Lett 82–83:969–974
Wu W, Liu P, Li J (2012) Necroptosis: an emerging form of programmed cell death. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 82:249–258
Yorimitsu T, Klionsky DJ (2005) Autophagy: molecular machinery for self-eating. Cell Death Differ 12(Suppl 2):1542–1552
Zhang R, Piao MJ, Kim KC, Kim AD, Choi JY, Choi J, Hyun JW (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling is involved in silver nanoparticles-induced apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44(1):224–232
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (2011-35B-E00011).
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, EJ., Umh, H.N., Choi, DH. et al. Magnetite- and maghemite-induced different toxicity in murine alveolar macrophage cells. Arch Toxicol 88, 1607–1618 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1210-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1210-1