Abstract
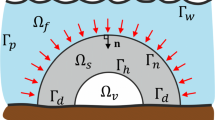
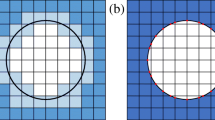
This paper presents a technique for imposing maximum length scale on features in continuum topology optimization. The design domain is searched and local constraints prevent the formation of features that are larger than the prescribed maximum length scale. The technique is demonstrated in the context of structural and fluid topology optimization. Specifically, maximum length scale criterion is applied to (a) the solid phase in minimum compliance design to restrict the size of structural (load-carrying) members, and (b) the fluid (void) phase in minimum dissipated power problems to limit the size of flow channels. Solutions are shown to be near 0/1 (void/solid) topologies that satisfy the maximum length scale criterion. When combined with an existing minimum length scale methodology, the designer gains complete control over member sizes that can influence cost and manufacturability. Further, results suggest restricting maximum length scale may provide a means for influencing performance characteristics, such as redundancy in structural design.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendsøe MP (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Optim 1:193–202
Benson HY, Vanderbei RJ, Shanno DF (2002) Interior-point methods for nonconvex nonlinear programming: Filter methods and merit functions. Comput Optim Appl 23:257–272
Borrvall T, Petersson J (2003) Topology optimization of fluids in stokes flow. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 41:77–107
Duysinx P, Sigmund O (1998) New developments in handling stress constraints in optimal material distributions. In: 7th Symposium on multidisciplinary analysis and optimization (AIAA/USAF/NASA/ISSMO held in St. Louis, MO), AIAA-98-4906, pp 1501–1509
Evgrafov A (2005) The limits of porous materials in topology optimization of stokes flows. Appl Math Optim 52:263–277
Gersborg-Hansen A, Sigmund O, Haber RB (2005) Topology optimization of channel flow problems. Struct Multidisc Optim 30:181–192
Guest JK, Prévost JH, Belytschko T (2004) Achieving minimum length scale in topology optimization using nodal design variables and projection functions. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61:238–254
Guest JK, Prévost JH (2006a) A penalty function for enforcing maximum length scale criterion in topology optimization. In: 11th AIAA/ISSMO multidisciplinary analysis and optimization conference proceedings (AIAA/ISSMO held in Portsmouth, VA), AIAA 2006-6938
Guest JK, Prévost JH (2006b) Topology optimization of creeping fluid flows using a Darcy–Stokes finite element. Int J Numer Methods Eng 66:461–484
Guest JK, Prévost JH (2007) Design of maximum permeability material structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196:1006–1017
Petersson J, Sigmund O (1998) Slope constrained topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 41:1417–1434
Poulsen TA (2003) A new scheme for imposing minimum length scale in topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 57:741–760
Rozvany GIN, Zhou M, Birker T (1992) Generalized shape optimization without homogenization. Struct Optim 4:250–252
Sigmund O (1997) On the design of compliant mechanisms using topology optimization. Mech Struct Mach 25:495–526
Sigmund O (2007) Morphology-based black and white filters for topology optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 33:401–424
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24:359–373
Svanberg K (1995) A globally convergent version of MMA without linesearch. In: Rozvany GIN, Olhoff N (eds) Proceedings of the first world congress of structural and multidisciplinary optimization. Pergamon, Goslar, pp 9–16
Wiker N, Klarbring A, Borrvall T (2007) Topology optimization of regions of Darcy and Stokes flow. Int J Numer Methods Eng 69:1374–1404
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guest, J.K. Imposing maximum length scale in topology optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 37, 463–473 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-008-0250-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-008-0250-7