Abstract
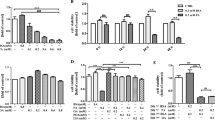
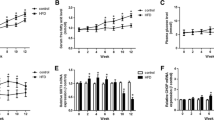
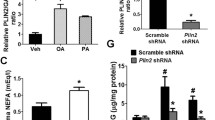
Pancreatic β-cells are particularly susceptible to fatty-acid-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and apoptosis. To understand how β-cells sense fatty acid stimuli and translate into a long-term adaptive response, we investigated whether palmitic acid (PA) regulates early growth response-1 (Egr-1), an immediate-early transcription factor, which is induced by many environmental stimuli and implicated in cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. We found that Egr-1 was rapidly and transiently induced by PA in MIN6 insulinoma cells, which was accompanied by calcium influx and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Calcium chelation and MEK1/2 inhibition blocked PA-induced Egr-1 upregulation, suggesting that PA induces Egr-1 expression through a calcium influx-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 cascade. Knockdown of Egr-1 increased PA-induced caspase-3 activation and ER stress markers and decreased PA-induced Akt phosphorylation and insulin secretion and signaling. Akt replenishment and insulin supplementation rescued PA-induced apoptosis in Egr-1 knockdown cells. These results suggest that the absence of Egr-1 loses its ability to couple the short-term insulin/Akt pathway to long-term survival adaptation. Finally, Egr-1-deficient mouse islets are more susceptible to ex vivo stimuli of apoptosis. In human pancreatic tissues, EGR1 expression correlated with expression of ER stress markers and anti-apoptotic gene. In conclusion, Egr-1 is induced by PA and further attempts to rescue β-cells from ER stress and apoptosis through improving insulin/Akt signaling. Our study underscores Egr-1 as a critical early sensor in pancreatic β-cells to translate fatty acid stimuli into a cellular adaptation mechanism.
Key Message
-
PA stimulates Egr-1 expression via a calcium influx-MEK1/2-ERK1/2-Elk-1 cascade.
-
Egr-1 attenuates PA-induced ER stress and apoptosis.
-
Egr-1 maintains Akt survival pathway to protect β-cells from PA-induced apoptosis.
-
Egr-1-deficient islets are prone to ex vivo stimuli of apoptosis.
-
Human EGR1 expression correlates with genes for ER stress and anti-apoptosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Randle PJ, Garland PB, Hales CN, Newsholme EA (1963) The glucose fatty-acid cycle. its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1:785–789
Hirose H, Lee YH, Inman LR, Nagasawa Y, Johnson JH, Unger RH (1996) Defective fatty acid-mediated beta-cell compensation in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. pathogenic implications for obesity-dependent diabetes. J Biol Chem 271:5633–5637
Shimabukuro M, Zhou YT, Levi M, Unger RH (1998) Fatty acid-induced beta cell apoptosis: a link between obesity and diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:2498–2502
Cousin SP, Hugl SR, Wrede CE, Kajio H, Myers MG Jr, Rhodes CJ (2001) Free fatty acid-induced inhibition of glucose and insulin-like growth factor I-induced deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in the pancreatic beta-cell line INS-1. Endocrinology 142:229–240
Pap M, Cooper GM (1998) Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in the phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt cell survival pathway. J Biol Chem 273:19929–19932
Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME (1999) Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev 13:2905–2927
Eizirik DL, Cardozo AK, Cnop M (2008) The role for endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetes mellitus. Endocr Rev 29:42–61
Kaneto H, Matsuoka TA, Nakatani Y, Kawamori D, Matsuhisa M, Yamasaki Y (2005) Oxidative stress and the JNK pathway in diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rev 1:65–72
Hirosumi J, Tuncman G, Chang L, Gorgun CZ, Uysal KT, Maeda K, Karin M, Hotamisligil GS (2002) A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 420:333–336
Kawamori D, Kajimoto Y, Kaneto H, Umayahara Y, Fujitani Y, Miyatsuka T, Watada H, Leibiger IB, Yamasaki Y, Hori M (2003) Oxidative stress induces nucleo-cytoplasmic translocation of pancreatic transcription factor PDX-1 through activation of c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase. Diabetes 52:2896–2904
Thiel G, Cibelli G (2002) Regulation of life and death by the zinc finger transcription factor Egr-1. J Cell Physiol 193:287–292
Mayer SI, Rossler OG, Endo T, Charnay P, Thiel G (2009) Epidermal-growth-factor-induced proliferation of astrocytes requires Egr transcription factors. J Cell Sci 122:3340–3350
Gitenay D, Baron VT (2009) Is EGR1 a potential target for prostate cancer therapy? Future Oncol 5:993–1003
Baron V, Adamson ED, Calogero A, Ragona G, Mercola D (2006) The transcription factor Egr1 is a direct regulator of multiple tumor suppressors including TGFbeta1, PTEN, p53, and fibronectin. Cancer Gene Ther 13:115–124
Garnett KE, Chapman P, Chambers JA, Waddell ID, Boam DS (2005) Differential gene expression between Zucker Fatty rats and Zucker Diabetic Fatty rats: a potential role for the immediate-early gene Egr-1 in regulation of beta cell proliferation. J Mol Endocrinol 35:13–25
Josefsen K, Sorensen LR, Buschard K, Birkenbach M (1999) Glucose induces early growth response gene (Egr-1) expression in pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 42:195–203
Frodin M, Sekine N, Roche E, Filloux C, Prentki M, Wollheim CB, Van Obberghen E (1995) Glucose, other secretagogues, and nerve growth factor stimulate mitogen-activated protein kinase in the insulin-secreting beta-cell line, INS-1. J Biol Chem 270:7882–7889
Eto K, Kaur V, Thomas MK (2006) Regulation of insulin gene transcription by the immediate-early growth response gene Egr-1. Endocrinology 147:2923–2935
Muller I, Rossler OG, Wittig C, Menger MD, Thiel G (2012) Critical role of Egr transcription factors in regulating insulin biosynthesis, blood glucose homeostasis, and islet size. Endocrinology 153:3040–3053
Lee SL, Tourtellotte LC, Wesselschmidt RL, Milbrandt J (1995) Growth and differentiation proceeds normally in cells deficient in the immediate early gene NGFI-A. J Biol Chem 270:9971–9977
Schnell S, Schaefer M, Schofl C (2007) Free fatty acids increase cytosolic free calcium and stimulate insulin secretion from beta-cells through activation of GPR40. Mol Cell Endocrinol 263:173–180
Hodge C, Liao J, Stofega M, Guan K, Carter-Su C, Schwartz J (1998) Growth hormone stimulates phosphorylation and activation of elk-1 and expression of c-fos, egr-1, and junB through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2. J Biol Chem 273:31327–31336
Storling J, Binzer J, Andersson AK, Zullig RA, Tonnesen M, Lehmann R, Spinas GA, Sandler S, Billestrup N, Mandrup-Poulsen T (2005) Nitric oxide contributes to cytokine-induced apoptosis in pancreatic beta cells via potentiation of JNK activity and inhibition of Akt. Diabetologia 48:2039–2050
Wrede CE, Dickson LM, Lingohr MK, Briaud I, Rhodes CJ (2002) Protein kinase B/Akt prevents fatty acid-induced apoptosis in pancreatic beta-cells (INS-1). J Biol Chem 277:49676–49684
Assmann A, Ueki K, Winnay JN, Kadowaki T, Kulkarni RN (2009) Glucose effects on beta-cell growth and survival require activation of insulin receptors and insulin receptor substrate 2. Mol Cell Biol 29:3219–3228
Aikin R, Hanley S, Maysinger D, Lipsett M, Castellarin M, Paraskevas S, Rosenberg L (2006) Autocrine insulin action activates Akt and increases survival of isolated human islets. Diabetologia 49:2900–2909
Klein S, Wolfe RR (1992) Carbohydrate restriction regulates the adaptive response to fasting. Am J Physiol 262:E631–E636
Fraser DA, Thoen J, Rustan AC, Forre O, Kjeldsen-Kragh J (1999) Changes in plasma free fatty acid concentrations in rheumatoid arthritis patients during fasting and their effects upon T-lymphocyte proliferation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 38:948–952
Poitout V, Amyot J, Semache M, Zarrouki B, Hagman D, Fontes G (2010) Glucolipotoxicity of the pancreatic beta cell. Biochim Biophys Acta 1801:289–298
Itoh Y, Kawamata Y, Harada M, Kobayashi M, Fujii R, Fukusumi S, Ogi K, Hosoya M, Tanaka Y, Uejima H et al (2003) Free fatty acids regulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells through GPR40. Nature 422:173–176
Brissova M, Shiota M, Nicholson WE, Gannon M, Knobel SM, Piston DW, Wright CV, Powers AC (2002) Reduction in pancreatic transcription factor PDX-1 impairs glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. J Biol Chem 277:11225–11232
Johnson JD, Ahmed NT, Luciani DS, Han Z, Tran H, Fujita J, Misler S, Edlund H, Polonsky KS (2003) Increased islet apoptosis in Pdx1+/- mice. J Clin Invest 111:1147–1160
Yu X, Shen N, Zhang ML, Pan FY, Wang C, Jia WP, Liu C, Gao Q, Gao X, Xue B et al (2011) Egr-1 decreases adipocyte insulin sensitivity by tilting PI3K/Akt and MAPK signal balance in mice. EMBO J 30:3754–3765
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Sun T, Guo F, Huang S, Chandalia M, Abate N, Fan D, Xin HB, Chen YE et al (2013) Dietary obesity-induced Egr-1 in adipocytes facilitates energy storage via suppression of FOXC2. Sci Rep 3:1476
Ritchie MF, Zhou Y, Soboloff J (2011) Transcriptional mechanisms regulating Ca(2+) homeostasis. Cell Calcium 49:314–321
Pacini L, Suffredini S, Ponti D, Coppini R, Frati G, Ragona G, Cerbai E, Calogero A (2013) Altered calcium regulation in isolated cardiomyocytes from Egr-1 knock-out mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 91:1135–1142
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Meng-Ru Shen at Department of Pharmacology of National Cheng Kung University for critical suggestions and Dr. Huei-Fen Jheng for technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from National Science Council (NSC-102-2321-B-006-007 and NSC-101-2320-B-006-036), National Health Research Institutes (NHRI-EX104-10231SI), and National Cheng Kung University Top-Notch Project.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no duality of interest associated with this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mun-Wai Cheong, Li-Hua Kuo and Yi-Ning Cheng contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 703 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheong, MW., Kuo, LH., Cheng, YN. et al. Loss of Egr-1 sensitizes pancreatic β-cells to palmitate-induced ER stress and apoptosis. J Mol Med 93, 807–818 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-015-1272-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-015-1272-4