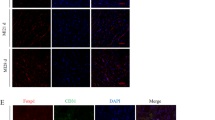
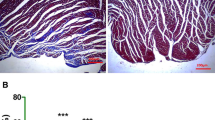
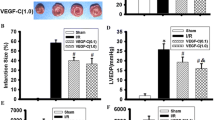
Abstract
Ginsenoside-Rg1 (Rg1) has been used in the traditional Chinese medicine for over 2,000 years. The present study was performed to test our hypothesis that Rg1 provides pro-angiogenic and anti-fibrotic benefits in the ischemic myocardium in a rat model of myocardial infarction. The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and phosphorylation/activation of PI3K, Akt, and p38 MAPK signaling pathways were examined in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and in the myocardial samples of rats. In addition, the expression levels of TNF-α and collagen I level, the number of newly formed blood vessels, the extent of myocardial fibrosis, and left ventricular function were measured in vivo. Our results demonstrated that administration of Rg1 increased VEGF expression levels, activated PI3K/Akt, and inhibited p38 MAPK in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, Rg1 increased the density of newly formed vessels, decreased TNF-α and collagen I expression levels and area of myocardial fibrosis, and improved left ventricle function in vivo. PI3K inhibitor LY294002 significantly attenuated Rg1-enhanced VEGF expression and capillary density. As well, inhibition of p38 MAPK slightly increased VEGF expression in vitro and in vivo, increased capillary density, and decreased TNF-α and collagen I expression levels and area of myocardial fibrosis in vivo. Rg1-induced activation of PI3K/Akt also contributed to the downregulation of p38 MAPK. Thus, Rg1 is effective in promoting angiogenesis and attenuating myocardial fibrosis, resulting in ameliorated left ventricular function. The possible mechanisms may involve activation of PI3K/Akt, inhibition of p38 MAPK, and cross talk between the two signaling pathways.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engel FB, Hsieh PC, Lee RT, Keating MT (2006) FGF1/p38 MAP kinase inhibitor therapy induces cardiomyocyte mitosis, reduces scarring, and rescues function after myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15546–15551
Swynghedauw B (1999) Molecular mechanisms of myocardial remodeling. Physiol Rev 79:215–262
Urabe A, Izumi T, Abe Y, Taniguchi I, Mochizuki S (2006) Effects of eplerenone and salt intake on left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in rats. Hypertens Res 29:627–634
Leung KW, Pon YL, Wong RN, Wong AS (2006) Ginsenoside-Rg1 induces vascular endothelial growth factor expression through the glucocorticoid receptor-related phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and beta-catenin/T-cell factor-dependent pathway in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 281:36280–36288
Chan LS, Yue PY, Mak NK, Wong RN (2009) Role of microRNA-214 in ginsenoside-Rg1-induced angiogenesis. Eur J Pharm Sci 38:370–377
Cheung LW, Leung KW, Wong CK, Wong RN, Wong AS (2011) Ginsenoside-Rg1 induces angiogenesis via non-genomic crosstalk of glucocorticoid receptor and fibroblast growth factor receptor-1. Cardiovasc Res 89: 419-425
Lu MC, Lai TY, Hwang JM, Chen HT, Chang SH, Tsai FJ, Wang HL, Lin CC, Kuo WW, Huang CY (2009) Proliferation- and migration-enhancing effects of ginseng and ginsenoside Rg1 through IGF-I- and FGF-2-signaling pathways on RSC96 Schwann cells. Cell Biochem Funct 27:186–192
Jia L, Zhao Y (2009) Current evaluation of the millennium phytomedicine—ginseng (I): etymology, pharmacognosy, phytochemistry, market and regulations. Curr Med Chem 16:2475–2484
Lu H, Xu X, Zhang M, Cao R, Brakenhielm E, Li C, Lin H, Yao G, Sun H, Qi L, Tang M, Dai H, Zhang Y, Su R, Bi Y, Zhang Y, Cao Y (2007) Combinatorial protein therapy of angiogenic and arteriogenic factors remarkably improves collaterogenesis and cardiac function in pigs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:12140–12145
Blazquez C, Gonzalez-Feria L, Alvarez L, Haro A, Casanova ML, Guzman M (2004) Cannabinoids inhibit the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in gliomas. Cancer Res 64:5617–5623
Mottet D, Michel G, Renard P, Ninane N, Raes M, Michiels C (2003) Role of ERK and calcium in the hypoxia-induced activation of HIF-1. J Cell Physiol 194:30–44
Issbrucker K, Marti HH, Hippenstiel S, Springmann G, Voswinckel R, Gaumann A, Breier G, Drexler HC, Suttorp N, Clauss M (2003) p38 MAP kinase—a molecular switch between VEGF-induced angiogenesis and vascular hyperpermeability. FASEB J 17:262–264
Wu CF, Bi XL, Yang JY, Zhan JY, Dong YX, Wang JH, Wang JM, Zhang R, Li X (2007) Differential effects of ginsenosides on NO and TNF-alpha production by LPS-activated N9 microglia. Int Immunopharmacol 7:313–320
Sivasubramanian N, Coker ML, Kurrelmeyer KM, MacLellan WR, DeMayo FJ, Spinale FG, Mann DL (2001) Left ventricular remodeling in transgenic mice with cardiac restricted overexpression of tumor necrosis factor. Circulation 104:826–831
Manning AM, Davis RJ (2003) Targeting JNK for therapeutic benefit: from junk to gold? Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:554–565
Karin M, Greten FR (2005) NF-kappaB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Immunol 5:749–759
Li M, Georgakopoulos D, Lu G, Hester L, Kass DA, Hasday J, Wang Y (2005) p38 MAP kinase mediates inflammatory cytokine induction in cardiomyocytes and extracellular matrix remodeling in heart. Circulation 111:2494–2502
Kanda S, Kanetake H, Miyata Y (2007) Role of Src in angiopoietin 1-induced capillary morphogenesis of endothelial cells: Effect of chronic hypoxia on Src inhibition by PP2. Cell Signal 19:472–480
Ravingerova T, Matejikova J, Neckar J, Andelova E, Kolar F (2007) Differential role of PI3K/Akt pathway in the infarct size limitation and antiarrhythmic protection in the rat heart. Mol Cell Biochem 297:111–120
Yamaguchi Y, Higashi M, Kobayashi H (1997) Effects of ginsenosides on maze performance and brain choline acetyltransferase activity in scopolamine-treated young rats and aged rats. Eur J Pharmacol 329:37–41
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Yin H, Zhang J, Lin H, Wang R, Qiao Y, Wang B, Liu F (2008) p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibition decreases TNFalpha secretion and protects against left ventricular remodeling in rats with myocardial ischemia. Inflammation 31:65–73
Wei HJ, Yang HH, Chen CH, Lin WW, Chen SC, Lai PH, Chang Y, Sung HW (2007) Gelatin microspheres encapsulated with a nonpeptide angiogenic agent, ginsenoside Rg1, for intramyocardial injection in a rat model with infarcted myocardium. J Control Release 120:27–34
Bozkurt B, Kribbs SB, Clubb FJ Jr, Michael LH, Didenko VV, Hornsby PJ, Seta Y, Oral H, Spinale FG, Mann DL (1998) Pathophysiologically relevant concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-alpha promote progressive left ventricular dysfunction and remodeling in rats. Circulation 97:1382–1391
Wallach D, Varfolomeev EE, Malinin NL, Goltsev YV, Kovalenko AV, Boldin MP (1999) Tumor necrosis factor receptor and Fas signaling mechanisms. Annu Rev Immunol 17:331–367
Chang YS, Seo EK, Gyllenhaal C, Block KI (2003) Panax ginseng: a role in cancer therapy? Integr Cancer Ther 2:13–33
Attele AS, Zhou YP, Xie JT, Wu JA, Zhang L, Dey L, Pugh W, Rue PA, Polonsky KS, Yuan CS (2002) Antidiabetic effects of Panax ginseng berry extract and the identification of an effective component. Diabetes 51:1851–1858
Sengupta S, Toh SA, Sellers LA, Skepper JN, Koolwijk P, Leung HW, Yeung HW, Wong RN, Sasisekharan R, Fan TP (2004) Modulating angiogenesis: the yin and the yang in ginseng. Circulation 110:1219–1225
Risau W (1997) Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 386:671–674
Gratton JP, Morales-Ruiz M, Kureishi Y, Fulton D, Walsh K, Sessa WC (2001) Akt down-regulation of p38 signaling provides a novel mechanism of vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated cytoprotection in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 276:30359–30365
Bondeson J (1997) The mechanisms of action of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: a review with emphasis on macrophage signal transduction and the induction of proinflammatory cytokines. Gen Pharmacol 29:127–150
Monden Y, Kubota T, Inoue T, Tsutsumi T, Kawano S, Ide T, Tsutsui H, Sunagawa K (2007) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha is toxic via receptor 1 and protective via receptor 2 in a murine model of myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H743–H753
Heeneman S, Cleutjens JP, Faber BC, Creemers EE, van Suylen RJ, Lutgens E, Cleutjens KB, Daemen MJ (2003) The dynamic extracellular matrix: intervention strategies during heart failure and atherosclerosis. J Pathol 200:516–525
Ingber DE (2002) Mechanical signaling and the cellular response to extracellular matrix in angiogenesis and cardiovascular physiology. Circ Res 91:877–887
Rundhaug JE (2005) Matrix metalloproteinases and angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med 9:267–285
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National 973 Basic Research Program of China (no. 2010CB732605). the National High-tech Research and Development Program of China (no. 2006AA02A406), the State Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China for Innovative Research Group (81021001), the State Key Program of National Natural Science of China (no. 60831003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 30700301, 30971096, and 30972809), the Major Project of Fujian Medical University (09ZD019), the Foundation for Excellent Young Scientists of Shandong Province (BS2009SW026, 2008BS03017), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2010HQ012, ZR2009CZ003, and Q2006C12).
Disclosures
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This article has been retracted upon request of the authors. The retraction has been made due to duplication of blots in Figure 1a and Figure 3 in this paper. The authors deeply apologize for any inconvenience this may have caused to the readers.
The retraction note to this article can be found online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00109-013-1018-0.
Huiqiu Yin and Zhaoqiang Liu contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, H., Liu, Z., Li, F. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Ginsenoside-Rg1 enhances angiogenesis and ameliorates ventricular remodeling in a rat model of myocardial infarction. J Mol Med 89, 363–375 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0723-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0723-9