Abstract
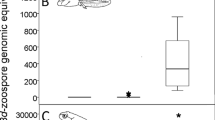
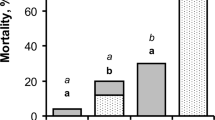
The blowfly Lucilia bufonivora shows high host specificity for toads despite the host’s toxic skin secretion, which consists mainly of bufadienolides. These toxins are effective blockers of the Na+, K+-ATPase, an enzyme that is essential for many physiological processes in animals. Whereas common toad (Bufo bufo) toxins were identified in the larvae of the fly, few toxins were found in the pupae and empty puparia as trace amounts, while adult flies were entirely free of these toxic compounds. Similar results were obtained when larvae of generalist necrophagous blowflies (L. sericata, Calliphora vicina) fed on toad carcasses. Analysis of the Na+, K+-ATPase gene revealed no amino acid substitution at positions known to mediate resistance to bufadienolides in other systems. Alternative mechanisms of resistance such as efficient excretion of the compounds may enable the flies to use this poisonous food source.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal AA, Petschenka G, Bingham RA, Weber MG, Rasmann S (2012) Toxic cardenolides: chemical ecology and coevolution of specialized plant–herbivore interactions. New Phytol 194:28–45
Blackith RE, Blackith RM (1990) Insect infestation of small corpses. J Nat Hist 24:699–709
Boehme P, Spahn P, Amendt J, Zehner R (2013) Differential gene expression during metamorphosis: a promising approach for age estimation of forensically important Calliphora vicina pupae (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Int J Legal Med 127:243–249
Croyle ML, Woo AL, Lingrel JB (1997) Extensive random mutagenesis analysis of the Na+/K+-ATPase α subunit identifies known and previously unidentified amino acid residues that alter ouabain binding. Eur J Biochem 248:488–495
Dalla S, Swarts HG, Koenderink JB, Dobler S (2013) Amino acid substitutions of Na, K-ATPase conferring decreased sensitivity to cardenolides in insects compared to mammals. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 43:1109–1115
Deulofeu V, Ruveda EA (1971) The constituents of toad venoms. In: Bücherl W, Buckley EE (eds) Venomous animals and their venoms, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 475–495
Dobler S, Petschenka G, Pankoke HC (2011) Coping with toxic plant compounds—the insect’s perspective on iridoid glycosides and cardenolides. Phytochemistry 72:1593–1604
Dobler S, Dalla S, Wagschal V, Agrawal AA (2012) Community-wide convergent evolution in insect adaptation to toxic cardenolides by substitutions in the Na, K-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:13040–13045
Dvela M, Rosen H, Feldmann T, Nesher M, Lichtstein D (2007) Diverse biological responses to different cardiotonic steroids. Pathophysiology 14:150–166
Eaton BR, Moenting AE, Paszkowski CA, Shpeley D (2008) Myiasis by Lucilia silvarum (Calliphoridae) in amphibian species in boreal Alberta, Canada. J Parasitology 94:949–952
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 3:294–299
Fremdt H, Szpila K, Huijbregts J, Lindström A, Zehner R, Amendt J (2012) Lucilia silvarum Meigen, 1826 (Diptera: Calliphoridae)—a new species of interest for forensic entomology in Europe. Forensic Sci Intern 222:335–339
Glaw F, Morinière J, Glaw K, Doczkal D (2014) Myiasis bei der Erdkröte (Bufo bufo) verursacht durch die Schmeißfliege Lucilia ampullacea. Z Feldherpetologie 21:83–95
Groth U, Reissmüller H (1973) Beziehungen synanthroper Fliegen zu Kleintierleichen, Teil I: Methodik, Vor- und Hauptversuche. Angew Parasitol 14:83–100
Hinaidy HK, Frey H (1990) Neue Myiasis-Fälle bei Tieren in Österreich. Mitt Öster Ges Tropenmed Parasitol 12:111–120
Holzinger F, Wink M (1996) Mediation of cardiac glycoside insensitivity in the monarch butterfly (Danaus plexippus): role of an amino acid substitution in the ouabain binding site of Na+, K+-ATPase. J Chem Ecol 22:1921–1937
Horisberger JD (2004) Recent insights into the structure and mechanism of the sodium pump. Physiology 19:377–387
Krenn L, Kopp B (1998) Bufadienolides from animal and plant sources. Phytochemistry 48:1–29
Labeyrie E, Dobler S (2004) Molecular adaptation of Chrysochus leaf beetles to toxic compounds in their food plants. Mol Biol Evol 21:218–221
Lazarus LH, Attila M (1993) The toad, ugly and venomous, wears yet a precious jewel in his skin. Prog Neurobiol 41:473–507
Lebovitz RM, Takeyasu K, Fambrough DM (1989) Molecular characterization and expression of the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase alpha-subunit in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J 8:193–202
Lingrel JB, Orlowski J, Shull MM, Price EM (1990) Molecular genetics of Na, K-ATPase. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 38:37–89
Malcolm SB (1991) Cardenolide-mediated interactions between plants and herbivores. In: Rosenthal GA, Berenbaum MR (eds) Herbivores: their interactions with secondary plant metabolites, vol 1. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 251–295
Mebs D, Zehner R, Schneider M (2000) Molecular studies on the ouabain binding site of the Na+, K+-ATPase in milkweed butterflies. Chemoecology 10:201–203
Meyer K, Linde H (1971) Collection of toad venom and chemistry of the toad venom steroids. In: Bücherl W, Buckley EE (eds) Venomous animals and their venoms, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 521–556
Petschenka G, Offe JK, Dobler S (2012) Physiological screening for target site insensitivity and localization of Na+/K+-ATPase in cardenolide-adapted Lepidoptera. J Insect Physiol 58:607–612
Petschenka G, Fandrich S, Sander N, Wagschal V, Boppré M, Dobler S (2013a) Stepwise evolution of resistance to toxic cardenolides via genetic substitutions in the Na+/K+-ATPase of milkweed butterflies (Lepidoptera: Danaini). Evolution 67:2753–2761
Petschenka G, Pick C, Wagschal V, Dobler S (2013b) Functional evidence for physiological mechanisms to circumvent neurotoxicity of cardenolides in an adapted and a non-adapted hawk–moth species. Proc R Soc B: Biol Sci 280:20123089. doi:10.1098/rspb.2012.3089
Qiu LY, Swarts HG, Tonk EC, Willems PH, Koenderink JB, De Pont JJ (2006) Conversion of the low affinity ouabain-binding site of non-gastric H, K-ATPase into a high affinity binding site by substitution of only five amino acids. J Biol Chem 281:13533–13539
Rognes K (1991) Blowflies (Diptera, Calliphoridae) of fennoscandia and Denmark. Fauna Entomol Scand, 24th edn. EJ Brill/Scandinavian Sci Press Ltd, Leiden
Schatzmann HJ (1953) Herzglykoside als Hemmstoffe für den aktiven Kalium und Natriumtransport durch die Erythrocytenmembran. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta 11:346–354
Scudder GGE, Meredith J (1982) The permeability of the midgut of three insects to cardiac glycosides. J Insect Physiol 28:689–694
Shimada K, Ohishi K, Fukunaga H, Ro JS, Nambara T (1985) Structure-activity relationship of bufotoxins and related compounds for the inhibition of Na+, K+ -adenosine triphosphatase. J Pharmacobiodyn 8:1054–1059
Stevens J, Wall R (1997) The evolution of ectoparasitism in the genus Lucilia (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Proc Roy Soc London Ser B 263:1335–1341
Steyn PS, van Heerden FR (1998) Bufadienolides of plant and animal origin. Nat Prod Rep 15:397–413
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Torrie LS, Radford JC, Southall TD, Kean L, Dinsmore AJ, Davies SA, Dow JA (2004) Resolution of the insect ouabain paradox. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:13689–13693
Weddeling K, Kordges T (2008) Lucilia bufonivora-Befall (Myiasis) bei Amphibien in Nordrhein-Westfalen—Verbreitung, Wirtsarten, Ökologie und Phänologie. Z Feldherpetologie 15:183–202
Yatime L, Laursen M, Morth JP, Esmann M, Nissen P, Fedosova NU (2011) Structural insights into the high affinity binding of cardiotonic steroids to the Na+, K+-ATPase. J Struct Biol 174:296–306
Zhen Y, Aardema ML, Medina EM, Schumer M, Andolfatto P (2012) Parallel molecular evolution in an herbivore community. Science 337:1634–1637
Zumpt F (1965) Myiasis in man and animals in the old world. Butterworth, London
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Vera Wagschal for her help in sequencing the Na+, K+-ATPase gene and to Dr. Sara DeLeon, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, for improving the English language of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Michael Heethoff.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mebs, D., Petschenka, G., Pogoda, W. et al. Amphibian myiasis. Blowfly larvae (Lucilia bufonivora, Diptera: Calliphoridae) coping with the poisonous skin secretion of the common toad (Bufo bufo). Chemoecology 24, 159–164 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00049-014-0157-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00049-014-0157-2