Abstract
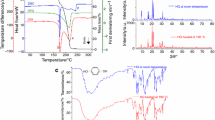
The objective of this study was to formulate itraconazole semisolid dosage forms and characterize their physicochemical properties. Itraconazole and excipients such as polysorbate 80, fatty acids, fatty alcohols, oils and organic acids were melted at 160°C. The fused solution was then cooled immediately at-10°C to make wax-like semisolid preparations. Their physicochemical attributes were first characterized using differential scanning calorimetry, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry. The solubility of itraconazole in semisolid preparations and their dispersability in the simulated gastric fluid were also determined. Our semisolid preparations did not show any distinct endothermic peak of a crystalline form of itraconazole around 160–163°C. This suggested that it was changed into amorphous one, when it was formulated into semisolid preparations. In addition, the distinctive functional peaks and chemical shifts of itraconazole were well retained after processing into semisolid preparations. It could be inferred from the data that itraconazole was stable during incorporation into semisolid preparations by the hot melt technique. In particular, itraconazole semisolid preparations composed of polysorbate 80, fatty acids and organic acids showed good solubility and dissolution when dispersed in an aqueous medium. It was anticipated that the semisolid dosage forms would be industrially applicable to improving the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amidon, G. L., Lennernas, H., Shah, V. P., and Crison, J. R., A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutics drug classification: the correlation ofin vitro drug product dissolution andin vivo bioavailability.Pharm Res., 12, 413–420 (1995).
Cao, Q.-R., Kim, T.-W., Choi, C.-Y., Kwon, K. A., and Lee, B.-J., Preparation and dissolution of PVP-based solid dispersion capsules containing solubilizers.J. Kor. Pharm. Sci., 33, 7–14 (2003).
Charman, S. S., Charman, W. N., Rogg, M. C., Wilson, T. D., Dutko, F. J., and Pouton, C. W., Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: formulation and biopharmaceutics evaluation of an investigational lipophilic compound.Pharm Res., 9, 87–93 (1992).
Heo, M.-Y., Piao, Z.-Z., Kim, T.-W., Cao, Q.-R., Kim, A., and Lee, B.-J.., Effect of solubilizing and microemulsifying excipients in polyethylene glycol 6000 solid dispersion on enhanced dissolution and bioavailability of ketoconazole.Arch. Pharm. Res., 28, 604–611 (2005).
Kim, T.-W., Choi, C.-Y., Cao, Q.-R., Kwon, K. A., and Lee, B.-J., Dissolution profiles of solid dispersions containing poorly water-soluble drugs and solubilizing compositions.J. Kor. Pharm. Sci., 32, 191–197 (2002).
Koks, C. H. W., Meenhorst, P. L., Bult, A., and Beijnen, J. H., Itraconazole solution: summary of Pharmacokinetic features and review of activity in the treatment of fluconazole-resistant oral candidosis in HIV-infected persons.Pharmacol. Res., 46, 195–201 (2002).
Nazzal, S., Smalyukh, I. I., Lavrentovich, O. D., and Khan, M. A., Preparation and in vitro characterization of a eutetic based smisolid self — nanoemulsified drug delivery system (SNEDDS) of ubiquinone: mechanism and progress of emulsion formation.Int. J. Pharm., 235, 247–265 (2002).
Peeters, J., Neeskens, P., Tollenaere, J. P.,, Van Remoortere, P., and Brewster, M., Characterization of the interaction of 2-hydroxypropyl-b-cyclodextrin with itraconazole at pH 2, 4 and 7.J. Pharm. Sci., 91, 1414–1422 (2002).
Rambali, B., Verreck, G., Baert, L., and Massart, D. L., Itraconazole formulation studies of the melt-extrusion process with mixture design.Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 29, 641–652 (2003).
Serajuddin, A. T. M., Solid dispersion of poorly water-soluble drugs: Early promises, subsequent problems, and recent breakthroughs.,J. Pharm. Sci., 88, 1058–1066 (1999).
Six, K., Daems, T., de Hoon, J., Hecken, A. V., Depre, M., Bouche, M.-P., Prinsen, P., Verreck, G., Peeters, J., Brewster, M. E., and den Mooter, G. V., Clinical study of solid dispersions of itraconazole prepared by hot-stage extrusion.Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 24, 179–186 (2005).
Wang, X., Michoel, A., and den Mooter, G. V., Solid state characteristics of ternary solid dispersions composed of PVP VA64, Myrj, 52 and itraconazole.Int. J. Pharm., 303, 54–61 (2005).
Woo, J.-S. and Yi, H.-G, Antifungal oral composition containing itraconazole and process for preparing same.US Patent, 6,039,981, March (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shim, SY., Ji, CW., Sah, H. et al. Characterization of itraconazole semisolid dosage forms prepared by hot melt technique. Arch Pharm Res 29, 1055–1060 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02969291
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02969291