Summary
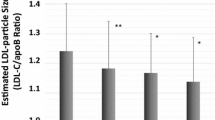
The Erfurt study is concerned with the follow-up of all the 208 long-term diabetics out of the closed area of the Erfurt district with an at least 20 years’ diabetes survival in 1970. In 1980 risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) were assessed in 71 (85% type I diabetes) out of 76 patients still alive. Progression of CHD within the subsequent five years (death due to CHD in 8 cases and progression of the ECG findings according to the Minnesota code in 3 cases) was associated with older age, lower body mass index, higher triglycerides, and a higher total cholesterol/HDL cholesterol ratio in comparison with the surviving patients without progression (n=41). No significant differences could be found with regard to sex distribution, age at diabetes onset, duration of diabetes, percentage of type I diabetes, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, smoking behavior, prevalence of nephropathy, glycemic control, and serum levels of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and HDL cholesterol. The subsequent reinvestigation in 1985 also included the determination of apolipoproteins. Since type II diabetes was not equally distributed, only type I diabetics were considered for the comparison of patients with ECG findings suggestive of CHD (n=5) with the remaining subjects (n=35). In addition to the above mentioned differences, CHD in long-term type I diabetes was also accompanied by lower HDL cholesterol, lower apolipoprotein A-I, and a higher apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A-I ratio. Substantially similar differences could be observed when type II diabetics were not excluded (10 patients with and 37 patients without CHD). It is concluded that the lipoprotein pattern is important for the survival in long-term diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackburn H.: Epidemiologic evidence for the causes and prevention of atherosclerosis. In:Steinberg D., Olefsky J. M. (Eds): Hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. Pathogenesis and prevention. Churchill Livingstone, New York, Edinburgh, London, Melbourne, 1987; p. 53.
Demaker P. N., Hijmans A. G., Brenninkeijer B. J., Jansen A. P., van-t Laar A.: Five methods for determining low-density lipoprotein cholesterol compared — Clin. Chem.30, 1797, 1984.
Eckel R. H., Albers J. J., Cheung M. C., Wahl P. W., Lindgren F. T., Bierman E. L.: High density lipoprotein composition in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Diabetes30, 132, 1981.
Friedewald W. T., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S.: Estimation of the concentration of low density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge — Clin. Chem.18, 499, 1972.
Laakso M., Pyörälä K., Sarlund H., Voutilainen E.: Lipid and lipoprotein abnormalities associated with coronary heart disease in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Arteriosclerosis6, 679, 1986.
Lopez-Virella M. F., Stone P., Ellis S., Colwell J. A.: Cholesterol determination in high density lipoproteins separated by three different methods — Clin. Chem.23, 882, 1977.
Nikkilä E. A.: Are plasma lipoproteins responsible for the excess atherosclerosis in diabetes? — Acta endocrinol. (Kbh.)110, (Suppl. 272), 27, 1985.
Panzram G., Pissarek D.: Long-term diabetes — associated factors in survivorship and mortality — Hormone metabol. Res. (Suppl. 15),10, 1985.
Panzram G., Pissarek D., Lundershausen R., Schauer U. J. W.: Prospektive Verlaufsbeobachtungen beim Langzeitdiabetes — Ergebnisse der Erfurt-Studie — Dtsch. med. Wschr.112, 1283, 1987.
Pense G., Panzram G., Pissarek D., Meinhold J., Müller W., Leder H., Kaselow D., Adolph W.: Qualität der Stoffwechselführung und Angiopathie bei 180 Langzeitdiabetikern mit mindestens 20jähriger Krankheitsdauer — Schweiz. med. Wschr.103, 1125, 1973.
Pontiroli A. E., Calderara A., Bonisolli L., Maffi P., De Pasqua A., Margonato A., Radaelli G., Gallus G., Pozza G.: Genetic and metabolic risk factors for the development of late complications in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes — Acta diabetol. lat.23, 351, 1986.
Pyörälä K., Laakso M., Uusitupa M.: Diabetes and atherosclerosis: an epidemiologic view — Diabet. metabol. Rev.3, 463, 1987.
Rose G. A., Blackburn N.: Cardiovascular survey methods. WHO Monographic Series No. 56, Geneva, 1968; p. 137.
Trivelli L. A., Ranney H. M., Lai H.-T.: Hemoglobin components in patients with diabetes mellitus — New Engl. J. Med.284, 353, 1971.
Wallbraun Q., Fiedler H., Gottschling H.-D.: Photometrische Mikromethode zur Bestimmung der glykosylierten Hämoglobine (HbAg) — Z. med. Lab. — Diagnost.23, 219, 1982.
Webber L. S., Cresanta J. L., Croft J. B., Srinivasan S. R., Berenson G. S.: Transitions of cardiovascular risk from adolescence to young adulthood — the Bogalusa Heart Study. II. Alterations in anthropometric blood pressure and serum lipoprotein variables — J. chron. Dis.39, 91, 1986.
Winkler L., Schlag B., Rüger H. J., Dargel R.: Eine Methodenvariante zur immunturbidimetrischen Bestimmung der Apolipoproteine AI und B im Serum — Z. med. Lab. — Diagnost.27, 372, 1986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schauer, U.J.W., Pissarek, D. & Panzram, G. Association of coronary heart disease with serum lipid and apolipoprotein concentrations in long-term diabetes. Results of the erfurt study. Acta diabet. lat 26, 35–42 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02581194
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02581194