Abstract
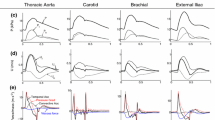
A forward mathematical model of the human arterial system, based on an electrical transmission line analogy, has been developed, using a new method for the calculation of peripheral impedance. Simulations of the human arterial system under normal and stenotic arterial conditions were compared with other published simulations, as well as measured clinical data and known clinical quantitative and qualitative characteristics: the harmonic arterial input impedance spectrum demonstrated a mean error of 0.07–0.1 mmHg.s.cm−1, compared with equivalent simulation and physiological data, respectively; qualitative and quantitative variation of blood pressure and flow waveforms along the arterial tree followed clinical trends; arterial pulse wave velocities compared favourably with physiological data close to the aortic root (−50–20 cm s−1 difference), but there were larger differences in the periphery (149–1192 cm s−1 difference); qualitative as well as quantitative variation of blood flow waveforms with progressive stenotic arterial disease, as measured by the pulsatility index, demonstrated an error between 2 and 16% in comparison with mean clinical data for critical stenosis. Under the given test conditions, the forward model was found closely to represent clinically observed haemodynamic characteristics of the human arterial system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avolio, A. P. (1980): ‘Multi-branched model of the human arterial system’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,18, pp. 709–718
Cavalcanti, S., Belardinelli, E., andSeveri, S., (1995): ‘Numerical simulation of the short-term heart regulation’, inPower, H., andHart, R. T. (Eds): ‘Computer simulations in biomedicine’ (Computational Mechanics Publications Southampton, 1995), pp. 115–122
Chen, C.-W., Shau, Y.-W. R., andWu, C.-P. (1997): ‘Analog transmission line model for simulation of systemic circulation’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,44, pp. 90–94
Clifford, P. C., Skidmore, R., Bird, D. R., Woodcock, J. P., andBaird, R. N. (1981): ‘The role of pulsatility index in the clinical assessment of lower limb ischaemia’,J. Med. Eng. Tech.,5, pp. 237–240
Corey, P. D., andWemple, R. R. (1975): ‘A combined left ventricle systemic arterial model’,J. Biomech.,8, pp. 9–15
Einav, S., Aharoni, S., andManoach, M. (1988): ‘Exponentially tapered transmission line model of the arterial system’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,35, pp. 333–339
Einav, S., Aharoni, S., andManoach, M. (1992): ‘Pulse transmission and impedance characteristics of a non-uniform circulatory model’,J. Biomed. Eng.,14, pp. 390–396
Guha, S. K. (1970): ‘Haemodynamics of the small arterial region in the femoral vascular bed’,Med. Biol. Eng.,8, pp. 291–299
Guyton, A. C. (1981): ‘Physiology of the human body’, 6th edn (Saunders College Publishing, London, 1981)
Helal, M. A., Watts, K. C., Marble, A. E., andSarwal, S. N. (1990): ‘Theoretical model for assessing hemodynamics in arterial networks which include bypass grafts’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,28, pp. 465–473
Helal, M. A. (1994): ‘Derivation of closed-form expression for the cerebral circulation models’,Comput. Biol. Med.,24, pp. 103–118
Jager, G. N., Westerhof, N., andNoordegraaf, A. (1965): ‘Oscillatory flow impedance in electrical analog of arterial system’,Circ. Res.,16, pp. 121–133
John, L. R. (2000): ‘An inverse transmission line model of the lower limb arterial system’. PhD thesis, University of Cape Town, South Africa
Kapal, E., Martini, F., andWetterer, E. (1951): ‘Uber die zuverlassigkeit der bisherigen bestimmungsart der pulswellengeschwindigkeit’,Z. Biol.,104, pp. 75–86
Karamanoglu, M., Gallagher, D. E., Avolio, A. P., andO'Rourke, M. F. (1994): ‘Functional origin of reflected pressure waves in a multibranched model of the human arterial system’,Am. J. Physiol.,267 (Heart Circ. Physiol.,36), pp. H1681-H1688
Karamanoglu, M., Gallagher, D. E., Avolio, A. P., andO'Rourke, M. F. (1995): ‘Pressure wave propagation in a multibranched model of the human upper limb’,Am. J. Physiol.,269 (Heart Circ. Physiol.,38), pp. H1363-H1369
Karamanoglu, M. (1997): ‘A system for analysis of arterial blood pressure waveforms in humans’,Comput. Biomed. Res.,30, pp. 244–255
LaCourse, J. R., Mohanakrishnan, G., andSivaprasad, K. (1986): ‘Simulations of arterial pressure pulses using a transmission line model’,J. Biomech.,19, pp. 771–780
Latham, R. D., Westerhof, N., Sipkema, P., Rubal, B. J., Reuderink, P., andMurgo, J. P. (1985): ‘Regional wave travel and reflections along the human aorta: a study with six simultaneousmicromanometric pressures’,Circulation,72, pp. 1257–1269
Learoyd, B. M., andTaylor, M. G. (1966): ‘Alterations with age in the viscoelastic properties of human arterial walls’,Circ. Res.,18, pp. 278–292
Luchsinger, P. C., Snell, R. E., andPatel, D. J. (1964): ‘Instantaneous pressure distribution along the human aorta’,Circ. Res.,11, pp. 885–888
McIlroy, M. B., Seitz, W. S., andTargett, R. C. (1986): ‘A transmission line model of the normal aorta and its branches’,Cardiovasc. Res.,20, pp. 81–587
McIlroy, M. B., andTargett, R. C. (1988): ‘A model of the systemic arterial bed showing ventricular-systemic arterial coupling’,Am. J. Physiol.,254, pp. 609–616
Miller, M. A., Drakontides, A. B., andLeavell, L. C. (1977): ‘Kimber-Gray-Stackpoles anatomy and physiology’, 17th edn (Macmillan Publishing Co. Ltd, New York, 1977)
Mills, C. J., Gabe, I. T., Gault, J. H., Mason, D. T., Ross, J., Braunwald, E., andShillingford, J. P. (1970): ‘Pressure-flow relationships and vascular impedance in man’,Cardiovasc. Res.,4, pp. 405–417
Milnor, W. R. (1989): ‘Hemodynamics’, 2nd edn (Williams & Wilkinson, Baltimore, 1989)
Nichols, W. W., andO'Rourke, M. F. (Eds) (1990): ‘McDonald's blood flow in arteries’, 3rd edn (Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, 1990)
O'Rourke, M. F., andAvolio, A. P. (1980): ‘Pulsatile flow and pressure in human systemic arteries, Studies in man and in a multibranched model of the human systemic arterial tree’,Circ. Res.,46, pp. 363–372
Raines, J. K., Jafrin, M. Y., andShapiro, A. H. (1974): ‘A computer simulation of arterial dynamics in the human leg’,J. Biomech.,7, pp. 77–91
Ramo, S., Whinnery, J. R., andVan Duzer, T. (1965): ‘Fields and waves in communication electronics’ (John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York, 1965)
Remington, R. B., andO'Brien, L. J. (1970): ‘Construction of aortic flow pulse from pressure pulse’,Am. J. Physiol.,218, pp. 437–447
Roller, M. L., andClarke, M. E. (1969): ‘Precusor cerebral circulation models’,J. Biomech.,2, pp. 241–250
Snyder, M. F., Rideout, V. C., andHillestad, R. J. (1968): ‘Computer modelling of the human systemic arterial tree’,J. Biomech.,1, pp. 341–353.
Strandness, D. E. Jr (1986): ‘Ultrasound in the study of atherosclerosis’,Ultrasound Med. Biol. 12, pp. 453–464
Strandness, D. E. Jr (1991): ‘Noninvasive vascular laboratory and vascular imaging’, inYoung, J. R., Graor, R. A. Olin, J. W., andBartholomew, J. R. (Eds): ‘Peripheral vascular diseases’ (osby Year Book, London, 1991), chap. 3, pp. 39–69
Taylor, M. G. (1966): ‘Wave transmission though an assembly of randomly branching elastic tubes’,Biophys. J.,6, pp. 697–716
Ursino, M. (1995): ‘A mathematical model of the interaction between arterial and cardiopulmonary baroreceptors during acute cardiovascular stress’ inPower, H., Hart, R. T. (Eds): ‘Computer simulations in biomedicine’ (Computational Mechanics Publications, Southampton, 1995), pp. 139–146
Westerhof, N., Bosman, F., Devries, C. J., andNoordegraaf, A. (1969): ‘Analog studies of the human systemic arterial tree’,J. Biomech.,2, pp. 121–143
Wezler, K., andBoger, A. (1939): ‘Die dynamik des arteriellen systems. Der arterielle blutdruck und seine komponenten’,Ergebn. Physiol.,41, pp. 292–306
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
John, L.R. Forward electrical transmission line model of the human arterial system. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 42, 312–321 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344705
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344705