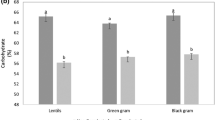
Abstract
During the germination of legume seeds, enzymes become active in order to degrade starch, storage-protein and proteinaceous antinutritional factors. The degradation of storage-protein is necessary to make peptides and amino acids available in order to stimulate seed growth and early plant growth. Proteinaceous antinutritional factors such as amylase inhibitors, lectins and trypsin inhibitors are present in legume seeds and protect them against predators. However, during germination, they degrade to a lower level by the action of several enzymes. The effect of germination on the content and activity of amylase inhibitors, lectins, tannins and trypsin inhibitors is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babar VS, Chavan JK, Kadam SS, (1988) Effects of heat treatments and germination on trypsin inhibitor activity and polyphenols in jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis L. DC). Plant Foods Hum Nutr 38:319–324
Bansal KK, Dhindsa KS, Batra VIP (1988) Trypsin inhibitor and hemagglutinin activities in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): effects of heat and germination. J Food Sci Technol 25(1): 46–48
Birk Y (1987) Proteinase inhibitors. In: A Neuberger & K Brocklehurst (Eds): Hydrolytic enzymes. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 257–305
Birk Y (1989) Protein protease inhibitors of plant origin and their significance in nutrition. In: Recent advances of research in antinutritional factors in legume seeds: J Huisman, AFB Van der Poel, IE Liener (Eds), PUDOC, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 83–94
Bond DA, Smith DB (1989) Possibilities for the reduction of antinutritional factors in grain legumes by breeding. In: Recent advances of research in antinutritional factors in legume seeds: J Huisman, AFB Van der Poel, IE Liener (Eds), PUDOC, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 285–296
Boyer RF (1977) A spectrofotometric assay of polyphenoloxidase activity. J Chem Educ 54: 585–586
Boylan MT, Sussex JM (1987) Purification of an endopeptidase involved with storage-protein degradation inPhaseolus vulgaris L., cotyledons. Planta 170: 343–352
Brandon DL, Bates AH, Friedman M (1988) Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay of soybean Kunitz Trypsin Inhibitor using monoclonal antibodies. J Food Sci 53: 102–106
Bressani R, Elias LG (1980) The nutritional role of polyphenols in beans. In: Hulse JH (ed) Polyphenols in cereals and legumes. Ottawa, Canada: IDRC 61-68
Chang KC, Harrold RL (1988) Changes in selected biochemical components, in vitro protein digestibility and amino acids in two bean cultivars during germination. J Food Sci 53: 783–787
Chen LH, Thacker RR, Pan SH (1977) Effect of germination on hemagglutinating activity of pea and bean seeds. J Food Sci 42: 1666–1668
Deshpande SS, Cheryan M, Salunkhe DK (1986) Tannin analysis of food products. CRC Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 24: 401–449
Erlanger BF, Kakowsky N, Cohen W (1961) The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates for trypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys 95: 271–278
Feller U (1979) Nitrogen mobilization and proteolytic activities in germinating and maturing bush beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Z Pflanzenphysiol 95: 413–422
Frels JM, Rupnow JH (1984) Purification and partial characterization of two α-amylases inhibitors from black bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). J Food Biochem 8: 281–301
Goldstein IJ, Poretz RD (1986) Isolation, physicochemical characterization, and carbohydrate-binding specificity of lectins. In: The lectins: IE Liener, N, Sharon, IJ Goldstein (Eds), Acad Press Inc, London 33: 247
Goldstein JL, Swain T (1963) Changes in tannins in ripening fruits. Phytochem 2: 371–383
Gupta YP (1987) Anti-nutritional and toxic factors in food legumes: a review. Plant Fds Hum Nutr 37: 201–228
Gupta RK, Haslam E (1979) Vegetable tannins: structure and biosynthesis. In: Polyphenols in cereals and legumes, Hulse JH (Ed), International Development Research Center, Ottawa, Canada, 15
Hartl PM, Tan-Wilson AL, Wilson KA (1986) Proteolysis of Kunitz soybean trypsin inhibitor during germination. Phyto 25: 23–26
Hoffman LM (1984) Structure of a chromosomalPhaseolus vulgaris lectin gene and its transcript. J Mol Appl Genet 2: 447–453
Hoffman LM, Ma Y, Barker BF (1982) Molecular cloning ofPhaseolus vulgaris lectin mRNA and use of cDNA as a probe to estimate lectin transcript levels in various tissues. Nucleic Acid Res 10(23): 7819–7828
Jacob RT, Pattabiraman TN (1986) Natural plant enzyme inhibitors: isolation and properties of a trypsin/chymotrypsin inhibitor from kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Ind J Biochem Biophys 23: 105–109
Jaffe WG, Moreno R, Wallis V (1973) Amylase inhibitors in legume seeds. Nutr Rep Int 7: 169–174
Kakade MD, Rackis JJ, McGhee JE, Puski G (1974) Determination of trypsin inhibitor activity of soy products: A collaborative analysis of an improved procedure. Cereal Chem 51: 376–382
Kakade ML, Simon N, Liener IE (1969) An evaluation of natural versus synthetic substrates for measuring the antitryptic activity of soybean samples. Cereal Chem 46: 518–526
Kik MJL, Rojer JM, Mouwen JMVM, Koninkx, JFJG, van Dijk JE, van der Hage MH (1989) The interaction between plant lectins and the small intestinal epithelium: a primary cause of intestinal disturbance. Vet Quart 11: 108–115
Koehler HH, Herrick HE, Burke DW (1986) Differentiating the lectin activity in twenty-four cultivars of dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Food Sci 51: 1471–1475
Kotaru M, Kimoto F, Yoshikawa, H, Ikeuchi T (1987) Changes of α-amylase inhibitor activity in kidney beans during heating and germination J Jpn Soc Nutr Food Sci 40: 240–243
Kotaru M, Yeh H-Y, Yoshikawa H, Ikeuchi T, Iwami K, Ibuki F (1989) Activity changes in cranberry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) α-amylase inhibitor by chemical modification and enzymatic digestion. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 35: 71–80
Kunitz M (1947) Crystalline soybean trypsin inhibitor. J Gen Physiol 30: 291–320
Lajolo FM, Filho FF (1985) Partial characterization of the amylase inhibitor of black beans (Phaseolus vulgaris), Variety Rico 23. J Agric Food Chem 33: 132–138
Liener IE (1986) Nutritional significance of lectins in the diet. In: The lectins, properties, functions, and applications in biology and medicine: Liener IE, Sharon N, Goldstein IJ (Eds), Acad Press, New York 527–552
Liener IE (1989) Antinutritional factors in legume seeds: state of the art. In: Recent advances of research in antinutritional factors in legume seeds: J Huisman, AFB Van der Poel and IE Liener (Eds), PUDOC, Wageningen, 6–14
Liener IE, Hill EG (1953) Measurement of hemagglutinating activity in raw and processed soybean. J Nutr 49: 609
Liener IE, Kakade ML (1980) Protease inhibitors: In: IE Liener (Ed): Toxic constituents of plant foodstuffs. Acad Press, New York, 7–71
Lis H, Sharon N (1981) Affinity chromatography for the purification of lectins (a review). J Chrom 215: 361–372
Mangan JL (1988) Nutritional effects of tannins in animal feeds Nutr Res Rev 1: 209–231
Marquardt RR (1989) Dietary effects of tannins, vicine and convicine. In: Recent advances of research in antinutritional factors in legume seeds: J. Huisman, AFB Van der Poel, IE Liener (Eds), Pudoc, Wageningen 141–155
Marquardt RR, Ward TT, Campbell LD, Cransfield PE (1977) Purification and characterization of a growth inhibitor in faba beans (Vicia faba L. var minor). J Nutr 107: 1313–1324
Marshall, JJ, Lauda CM (1975) Purification and properties of phaseolamin, an inhibitor of α-amylase from the kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). J Biol Chem 250: 8030–8037
Mikkonen A (1986) Activities of some peptidases and proteinases in germinating kidney bean,Phaseolus vulgaris. Physiol Plant 68: 282–286
Mikkonen A, Begbie R, Grant G, Pusztai A (1986) Intracellular localisation of some peptidases and-mannosidase in cotyledons of resting kidney bean,Phaseolus vulgaris. Physiol Plant 68: 75–80
Mikkonen A, Mikola J (1986) Separation and partial characterization of two alkaline peptidases from cotyledons of restin kidney beans,Phaseolus vulgaris. Physiol Plant 68: 81–85
Mikola J (1983) Proteinases, peptidases and inhibitors of endogeneous proteinases in germinating seeds. In: Seed proteins: J Daussant, J Mosse and J Vaughan (Eds), Acad Press, London, 35–52
Nielsen SS, Liener IE (1984) Degradation of the major storage protein ofPhaseolus vulgaris during germination. Plant Physiol 74: 494–498
Nielsen SS, Liener IE (1988) Effect of germination on trypsin inhibitor and hemagglutinating activities in (Phaseolus vulgaris). J Food Sci 53: 298–301
Pick K and Wöber G (1978) Proteinaceous α-amylase inhibitor from beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). Hoppe-Seyler's Z Physiol Chem 359: 1371–1377
Powers JH, Whitaker JR (1977) Purification and some physical and chemical properties of red kidney (Phaseolus vulgaris) α-amylase inhibitor. J Food Biochem 1: 217–238
Price ML, Strombery AM, Butler JL (1979) Tannin content as a function of grain maturity and drying conditions in several varieties ofSorghum bicolor (L.). J Agric Food Chem 27: 1270–1274
Prigent MJ, Bourillon R (1976) Purification and characterization of a lectin (plant hemagglutinin) with N blood group specificity fromVicia grammina seeds. Biochem Biophy Acta 420: 112
Pusztai A (1987) Plant lectins — biological functions. Acta Biochim Biophys Hungaria 22: 355–375
Pusztai A, Croy RRD, Grant G, Stewart JC (1983) Seed lectins: distribution, location and biological role. In: Seed proteins: J Daussant, J Mossé and J Vaughan (Eds), Acad Press, London, 53–81
Rahma EH, El-Bedawey AA, El-Adawy, TA, Goma MA (1987) Changes in chemical and antinutritional factors and functional properties of faba beans during germination. Lebensm-Wiss u-Technol 20: 271–276
Rao PU, Deosthale YG (1982) Tannin content of pulses: varietal differences and effects of germination and cooking. J Sci Food Agric 33: 1013–1016
Rao PU, Deosthale YG (1987) Polyphenoloxidase activity in germinated legume seeds. J Food Sci 52: 1549–1551
Reddy NR, Pierson MD, Sathe SK, Salunkhe DK (1985) Dry bean tannins: a review of nutritional implications. JAOCS 62: 541–549
Roberts DD, Goldstein IJ (1984) Isolation from Lima bean lectin of a peptide containing a cysteine residue essential for carbohydrate binding activity. J Biol Chem 259: 909–914
Roozen JP, Groot de J (1988) Bepaling van het trypsine gehalte in voedsel voor mens en dier. De Ware(n)-Chemicus 18, 125–132
Roozen JP, Groot de J (1987) Analysis of low levels of trypsin inhibitor activity in food. Lebensm- Wiss u- Technol 20: 305–308
Ryan CA (1973) Proteolytic enzymes and their inhibitors in plants. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 24: 173–196
Sathe SK, Deshapande SS, Reddy ND, Goll DE, Salunkhe DK (1983) Effects of germination on proteins, raffinose oligosaccharides, and antinutritional factors in the great northern beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Food Sci 48: 1796–1800
Sawathar PN, Kadam SS, Salunkhe DK (1981) Effects of germination and cooking on polyphenols and in vitro protein digestibility of horse gram and moth bean. Qual Plant Plant Foods Hum Nutr 31: 77–83
Sopanen T (1976) Purification and partial characterization of a dipeptidase from barley. Plant Physiol 57: 867–871
Sopanen T, Mikola J (1975) Purification and partial characterization of barley leucine aminopeptidase. Plant Physiol 55: 809–814
Strosberg AD, Buffard D, Lauwereys M, Foriers A. (1986) Legume lectins: a large family of homologous proteins. In: The lectins: IE Liener, N Sharon and IJ Goldstein (Eds), Acad Press Inc, London, 249–264
Subbulakshmi G, GaneshKumar K, Venkataraman LV (1976) Effect of germination on the carbohydrates, proteins, trypsin inhibitor, amylase inhibitor and hemagglutinin in horsegram and mothbean. Nutr Rep Int 13: 19–31
Tan-Wilson AL, Rightmire BR, Wilson KA (1982) Different rates of metabolism of soybean proteinase inhibitors during germination. Plant Physiol 70: 493–497
Tsukamoto I, Miyoshi M, Hamaguchi Y (1983) Purification and characterization of three trypsin inhibitors from beans,Phaseolus vulgaris ‘Kintoki’. Cer Chem 60: 281–286
Valdebouze P, Bergeron E, Gaborit T, Delort-Laval J (1980) Content and distribution of trypsin inhibitors and hemagglutinins in some legume seeds. Can J Plant Sci 60: 695–701
Van der Poel AFB (1989) Effects of processing on antinutritional factors (ANF) and nutritional value of legume seeds for non-ruminant feeding. In: Recent advances of research in antinutritional factors in legume seeds: J Huisman, AFB Van der Poel and IE Liener (Eds), PUDOC, Wageningen, 213–229
Van der Poel AFB (1990) Effects on processing on bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) protein quality. Ph D Thesis, Ponson & Looyen, Wageningen, 160 pp
Wilson KA, Laskowski M (1973) Isolation of three inhibitors of trypsin from garden bean,Phaseolus vulgaris, having either lysine or arginine at the reactive site. J Biol Chem 248: 756–762
Wilson KA, Papastoitsis G, Hartl P, Tan-Wilson AL (1988) Survey of the proteolytic activities degrading the Kunitz trypsin inhibitor and glycinin in germinating soybeans (Glycine max). Plant Physiol 88: 355–360
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savelkoul, F.H.M.G., Van Der Poel, A.F.B. & Tamminga, S. The presence and inactivation of trypsin inhibitors, tannins, lectins and amylase inhibitors in legume seeds during germination. A review. Plant Food Hum Nutr 42, 71–85 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02196074
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02196074