Summary
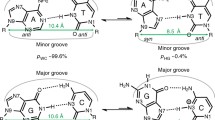
The actinomycin-D-d(A1-A2-A3-G4-C5-T6-T7-T8) complex (1 drug per duplex) has been generated in aqueous solution and its structure characterized by a combined application of two-dimensional NMR experiments and molecular dynamics calculations. We have assigned the exchangeable and nonexchangeable proton resonances of Act and d(A3GCT3) in the complex and identified the intermolecular proton-proton NOES that define the alignment of the antitumor agent at its binding site on duplex DNA. The molecular dynamics calculations were guided by 70 intermolecular distance constraints between Act and nucleic acid protons in the complex. The phenoxazone chromophore of Act intercalates at the (G-C)I·(G-C)II step in the d(A3GCT3) duplex with the phenoxazone ring stacking selectively with the G4I and G4II purine bases but not with C4I and C4II pyrimidine bases at the intercalation site. There is a pronounced unwinding between the A3·T6 and G4·C5 base pairs which are the next steps located in either direction from the intercalation site in the Act-d(A3GCT3) complex. The Act cyclic pentapeptide ring conformations in the complex are similar to those for free Act in the crystal except for a change in orientation of the ester linkage connecting meVal and Thr residues. The cyclic pentapeptide rings are positioned in the minor groove with the established G-C sequence specificity of binding associated with intermolecular hydrogen bonds between the Thr backbone CO and NH groups to the NH2-2 and N3 positions of guanosine, respectively. Complex formation is also stabilized by van der Waals interactions between nonpolar groups on the cyclic pentapeptide rings and the sugar residues and base pair edges lining the widened minor groove of the (A3-G4-C5-T6)I·(A3-G4-C5-T6)II binding site segment of the DNA helix.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, S.C., Shafer, R.H. and Mirau, P.A. (1982)J. Am. Chem. Soc.,104, 5504–5506.
Brown, S.C., Mullis, K., Levenson, C. and Shafer, R.H. (1984)Biochemistry,23, 403–408.
Cerami, A., Reich, E., Ward, D.C. and Goldberg, I.H. (1967)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,57, 1036–1042.
Creighton, S., Rudolph, B., Lybrand, T., Singh, U.C., Shafer, R., Brown, S., Kollman, P., Case, D.A. and Andrea, T. (1989)J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.,6, 929–969.
Delepierre, M., van Heijenoort, C., Igolen, J., Pothier, J., LeBret, M. and Roques, B.P. (1989)J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.,7, 557–589.
Dickerson, R.E. and Drew, H.R. (1981)J. Mol. Biol.,149,761–786.
Fox, K.R. and Waring, M.J. (1984)Nucl. Acids Res.,12, 9271–9285.
Gao, X. and Patel, D.J. (1988)Biochemistry,27, 1744–1751.
Gao, X. and Patel, D.J. (1989)Biochemistry,28, 751–762.
Gao, X., Mirau, P. and Patel, D.J. (1991)J. Mal. Biol., in press.
Ginell, S., Lessinger, L. and Berman, H.M. (1988)Biopolymers,27, 843–864.
Jain, S.C. and Sobell, H.M. (1972)J. Mol. Biol.,68, 1–20.
Jones, R.L., Scott, E.V., Zon, G., Marzilli, L.G. and Wilson, W.D. (1988)Biochemistry,27, 6021–6026.
Krugh, T.R. (1972)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,69, 1911–1914.
Krugh, T.R. and Chen, Y.C. (1975)Biochemistry,14, 4912–4922.
Krugh, T.R. and Neely, J.W. (1973)Biochemistry,12, 4418–4425.
Metzler, W.J., Wang, C., Kitchen, D., Levy, R.M. and Pardi, A. (1990)J. Mal. Biol.,214, 711–736.
Muller, W. and Crothers, D.M. (1968)J. Mol. Biol.,35, 251–290.
Patel, D.J. (1974a)Biochemistry,13, 2388–2396.
Patel, D.J. (1974b)Biochemistry,13, 2396–2402.
Patel, D.J. (1976a)Biochem. Biophys. Acta,442, 98–108.
Patel, D.J. (1976b)Biopolymers,15, 533–558.
Patel, D.J. and Canuel, L.L. (1977)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,74, 2624–2628.
Patel, D.J., Kozlowski, S.A., Rice, J.A., Broka, C. and Itakura, K. (1981)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,78, 7281–7284.
Petersheim, M., Mehdi, S. and Gerlt, J.A. (1984)J. Am. Chem. Soc.,106, 439–440.
Reich, E. and Goldberg, I.H. (1964)Progress in Nucleic Acids Research and Molecular Biology 3, 183–234.
Reid, D.G., Salisbury, S.A. and Williams, D.H. (1983)Biochemistry,22, 1377–1385.
Scott, E.V., Jones, R.L., Banville, D.L., Zon, G., Marzilli, L.G. and Wilson, W.D. (1988a)Biochemistry,27, 915–923.
Scott, E.V., Zon, G., Marzilli, L.G. and Wilson, W.D. (1988b)Biochemistry,27, 7940–7951.
Sobell, H.M. (1973)Progress in Nucleic Acids Research and Molecular Biology,13, 153–190.
Sobell, H.M. and Jain, S.C. (1972)J. Mol. Biol.,68, 21–34.
Sobell, H.M., Jain, S.C. and Sakore, T.D. (1971)Nature New Biology,231, 200–205.
Takusagawa, F., Dabrow, M., Neidle, S. and Berman, H.M. (1982)Nature,296, 466–469.
Van de Ven, F.J. and Hilbers, C.W. (1988)Eur. J. Biochem.,178, 1–38.
Van Dyke, M.W., Hertzberg, R.P. and Dervan, P.B. (1982)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.,79, 5470–5474.
Wang, A.H., Ughetto, G., Quigley, G. and Rich, A. (1987)Biochemistry,26, 1152–1163.
Waring, M. (1970)J. Mal. Biol.,54, 247–279.
Waring, M. (1981) InThe Molecular Basis of Antibiotic Action (Eds, Gale, F. et al.) Wiley, London, pp. 314–333.
Wells, R.D. and Larson, J.E. (1970)J. Mol. Biol.,49, 319–342.
Wilson, W.D., Jones, R.L., Zon, G., Scott, E.V., Banville, D.M. and Marzilli, L.G. (1986)J. Am. Chem. Soc.,108, 7113–7114.
Wüthrich, K. (1986)NMR of Proteins and Nucleic Acids, Wiley, New York.
Zhang, X. and Patel, D.J. (1990)Biochemistry,29, 9451–9466.
Zhang, X. and Patel, D.J. (1991)Biochemistry,30, 4026–4041.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to the memory of Professor V.F. Bystrov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Chen, H. & Patel, D.J. Solution structure of actinomycin-DNA complexes: Drug intercalation at isolated G-C sites. J Biomol NMR 1, 323–347 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02192858
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02192858