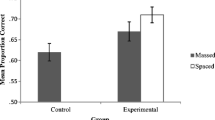
Abstract
There is considerable evidence, gathered in a variety of settings and across many different types of materials and procedures, that spaced repetitions—regardless of whether they are in the form of additional study opportunities or successful tests—are a highly effective means of promoting learning. Research on spacing effects is reviewed and its theoretical and educational implications are examined. It is concluded that spacing effects can best be understood in terms of the “accessibility” hypothesis, and that spaced repetitions have considerable potential for improving classroom learning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, G. A., Mahler, W. A., and Estes, W. K. (1969). Effects of recall tests on long-term retention of paired associates.J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 8: 463–470.
Anderson, R. C., and Biddle, W. B. (1975). On asking people questions about what they are reading. In Bower, G. H. (ed.),The Psychology of Language and Motivation (Vol. 9), New York, Academic Press, pp. 90–132.
Armbruster, B. B., and Anderson, T. H. (1984). Structures of explanation in history textbooks or so what if Governor Stanford missed the spike and hit the rail?J. Curric. Studies 16: 181–194.
Austin, S. D. M. (1921). A study in logical memory.Am. J. Psychol. 32: 370–403.
Ausubel, D. P. (1966). Early versus delayed review in meaningful learning.Psychol. Schools 3: 195–198.
Baddeley, A. D. (1976).The Psychology of Memory. New York, Basic Books.
Bahrick, H. P., and Phelps, E. (1987). Retention of Spanish vocabulary over 8 years.J. Exper. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cognit. 13: 344–349.
Bjork, R. A. (1979). Information-processing analysis of college teaching.Educat. Psychol. 14: 15–23.
Bjork, R. A., and Allen, T. W. (1970). The spacing effect: Consolidation or differential encoding?J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 9: 567–572.
Bower, G. H. (1972). Stimulus-sampling theory of encoding variability. In Melton, A. W., and Martin, E. (Eds.),Coding in Human Memory New York, Winston & Sons, pp. 85–124.
Brainerd, C. J., Kingma, J., and Howe, M. L. (1985). On the development of forgetting.Child Devel. 56: 1103–1119.
Bruning, R. H. (1968). Effects of review and testlike events within the learning of prose material.J. Educat. Psychol. 59: 16–19.
Burns, P. C. (1970). Intensive review as a procedure in teaching arithmetic.Elem. School J. 60: 205–211.
Burry, J., Catteral, J., Choppin, B., and Dorr-Bremme, D. (1982). Testing in the nation's schools and districts: How much? What kinds? To what ends? At what costs? (CSE report no. 194). Los Angeles, Center for the Study of Evaluation, University of California.
Cornell, E. H. (1980). Distributed study facilitates infants' delayed recognition memory.Mem. Cognit. 8: 539–542.
Dearborn, W. F. (1910). Experiments in learning.J. Educat. Psychol. 1: 373–388.
Dellarosa, D., and Bourne, L. E. (1985). Surface form and the spacing effect.Mem. Cognit. 13: 529–537.
Dempster, F. N. (1986). Spacing effects in text recall: An extrapolation from the laboratory to the classroom (submitted for publication).
Dempster, F. N. (1987). Effects of variable encoding and spaced presentations on vocabulary learning.J. Educat. Psychol. 79: 162–170.
Dempster, F. N. (1988). The spacing effect: A case study in the failure to apply the results of psychological research.Am. Psychol. 43: 627–634.
Dempster, F. N. (1989). Do sentence contexts facilitate vocabulary learning? Additional comparisons (submitted for publication).
Donaldson, W. (1970). Output effects in multitrial free recall.J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 10: 577–585.
Ebbinghaus, H. (1885).Memory (translated by H. A. Ruger and C. E. Bussenius). New York, Teachers College, 1913. Paperback ed., New York, Dover, 1964.
Elmes, D. G., Dye, C. J., and Herdelin, N. J. (1983). What is the role of affect in the spacing effect?Mem. Cognit. 11: 144–151.
Elmes, D. G., Greener, W. I., and Wilkinson, W. C. (1972). Free recall of items presented after massed- and distributed-practice items.Am. J. Psychol. 85: 237–240.
English, H. B., Wellborn, E. L., and Killian, C. D. (1934). Studies in substance memorization.J. Gen. Psychol. 11: 233–260.
Gates, A. I. (1917). Recitation as a factor in memorizing.Arch. Psychol. 6: 1–104.
Gay, L. R. (1973). Temporal position of reviews and its effect on the retention of mathematical rules.J. Educat. Psychol. 64: 171–182.
Glanzer, M., and Duarte, A. (1971). Repetition between and within languages in free recall.J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 10: 625–630.
Glenberg, A. M. (1979). Component-levels theory of the effects of spacing of repetitions on recall and recognition.Mem. Cognit. 7: 95–112.
Glenberg, A. M., and Lehmann, T. S. (1980). Spacing repetitions over 1 week.Mem. Cognit. 8: 528–538.
Glenberg, A. M., and Smith, S. M. (1981). Spacing repetitions and solving problems are not the same.J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 20: 110–119.
Glover, J. A., and Corkill, A. J. (1987). Influence of paraphrased repetitions on the spacing effect.J. Educat. Psychol. 79: 198–199.
Goldstein, A. G., Chance, J. E., and Otto, J. (1987). Enhanced face recognition memory after distributed viewing. Presented at the annual meeting of the Psychonomic Society, Seattle, Washington.
Good, T. L., and Brophy, J. E. (1986).Educational Psychology (3rd ed.). New York, Longman.
Good, T. L., and Grouws, D. A. (1979). The Missouri mathematics effectiveness project.J. Educat. Psychol. 71: 355–362.
Gordon, K. (1925). Class results with spaced and unspaced memorizing.J. Exper. Psychol. 8: 337–343.
Greeno, J. G. (1970). Conservation of information-processing capacity in paired-associate memorizing.J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 9: 581–586.
Halff, H. M. (1977). The role of opportunities for recall in learning to retrieve.Am. J. Psychol. 90: 383–406.
Hilgard, E. R., and Bower, G. H. (1975).Theories of Learning (4th ed.). Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, Prentice-Hall.
Hintzman, D. L. (1974). Theoretical implications of the spacing effect. In Solso, R. L. (ed.).Theories in Cognitive Psychology: The Loyola Symposium Potomac, Maryland, Erlbaum, pp. 77–99.
Hintzman, D. L. (1976). Repetition and memory. In Bower, G. H. (ed.),The Psychology of Learning and Motivation (Vol. 10), New York, Academic Press, pp. 47–91.
Hintzman, D. L., and Rogers, M. K. (1973). Spacing effects in picture memory.Mem. Cognit. 1: 430–434.
Hintzman, D. L., Summers, J. J., and Block, R. A. (1975). What causes the spacing effect? Some effects of repetition, duration, and spacing on memory for pictures.Mem. Cognit. xx: 287–294.
Hogan, R. M., and Kintsch, W. (1971). Differential effects of study and test trials on long-term recognition and recall.J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 10: 562–567.
Izawa, C. (1971). The test trial potentiating model.J. Math. Psychol. 8: 200–224.
Jacoby, L. L. (1978). On interpreting the effects of repetition: Solving a problem versus remembering a solution.J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 17: 649–667.
Jones, H. E. (1923–1924). The effects of examination on permanence of learning.Arch. Psychol. 10: 21–70.
Kim, E. C., and Kellough, R. D. (1987).A Resource Guide for Secondary School Teaching (4th ed.). New York, Macmillan.
Kraft, R. M., and Jenkins, J. J. (1981). The lag effect with aurally presented passages.Bull. Psychonom. Soc. 17: 132–134.
Kuhs, T., Porter, A., Floden, R., Freeman, D., Schmidt, W., and Schwille, J. (1985). Differences among teachers in their use of curriculum-embedded tests.Elem. School J. 86: 141–152.
Lachman, R., and Laughery, K. L. (1968). Is a test trial a training trial in free recall learning?J. Exper. Psychol. 76: 40–50.
Landauer, T. K. (1969). Reinforcement as consolidation.Psychol. Rev. 76: 82–96.
Landauer, T. K., and Bjork, R. A. (1978). Optimum rehearsal patterns and name learning. In Gruneberg, M. M., Morris, P. E., and Sykes, R. N. (eds.),Practical Aspects of Memory New York, Academic Press, pp. 625–632.
Lyon, D. O. (1914). The relation of length of material to time taken for learning and the optimum distribution of time.J. Educat. Psychol. 5: 85–91, 155–163.
Magliero, A. (1983). Pupil dilations following pairs of identical words and related to-be-remembered words.Mem. Cognit. 11: 609–615.
Martin, E. (1972). Stimulus encoding in learning and transfer. In Meltin, A. W., and Martin, E. (eds.),Coding Processes in Human Memory Washington, D.C., Winston, pp. 59–84.
MasKarinec, A. S., and Thompson, C. P. (1976). The within list distributed practice effect: Tests of the varied context and varied encoding hypotheses.Mem. Cognit. 4: 741–746.
Mayer, R. E. (1987).Educational Psychology: A Cognitive Approach. Boston, Little, Brown.
McDaniel, M. A., and Masson, M. E. J. (1985). Altering memory representation through retrieval.J. Exper. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cognit. 11: 371–385.
McDermott, P. A., and Watkins, M. W. (1983). Computerized vs. conventional remedial instruction for learning disabled pupils.J. Special Ed. 17: 81–88.
McGaw, B., and Grotelueschen, A. (1972). Direction of the effect of questions in prose material.J. Educat. Psychol. 63: 586–588.
McGeoch, J. A. (1943).The Psychology of Human Learning. New York, Longmans Green.
Melton, A. W. (1970). The situation with respect to the spacing of repetitions and memory.J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 9: 596–606.
Modigliani, V. (1976). Effects on a later recall by delaying initial recall.J. Exper. Psychol. Hum. Learn. Mem. 2: 609–622.
Moscovitch, M. (1984).Infant Memory. New York, Plenum Press.
Murdock, B. B., Jr., and Babick, A. J. (1961). The effect of repetition on the retention of individual words.J. Psychol. 74: 596–601.
Nungester, R. J., and Duchastel, P. C. (1982). Testing versus review: Effects on retention.J. Educat. Psychol. 74: 18–22.
Ornstein, P. A., and Naus, M. J. (1978). Rehearsal processes in children's memory. In Ornstein, P. A. (ed.),Memory Development in Children Hillsdale, New Jersey, Erlbaum, pp. 69–99.
Perkins, N. L. (1914). The value of distributed repetitions in rote learning.Brit. J. Psychol. 1: 253–261.
Peterson, H. A., Ellis, M., Toohill, N., and Kloess, P. (1935). Some measurements of the effects of reviews.J. Educat. Psychol. 26: 65–72.
Petros, T., and Hoving, K. (1980). The effects of review on young children's memory for prose.J. Exper. Child Psychol. 30: 33–43.
Postman, L., and Knecht, K. (1983). Encoding variability and retention.J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 22: 133–152.
Pyle, W. H. (1913). Economical learning.J. Educat. Psychol. 3: 148–158.
Rea, C. P., and Modigliani, V. (1985). The effect of expanded versus massed practice on the retention of multiplication facts and spelling lists.Hum. Learn. 4: 11–18.
Rea, C. P., and Modigliani, V. (1987). The spacing effect in 4- to 9-year-old children.Mem. Cognit. 15: 436–443.
Rescorla, R. A., and Wagner, A. R. (1972). A theory of Pavlovian conditioning: Variations in the effectiveness of reinforcement and nonreinforcement. In Black, A. H., and Prokasy, W. F. (eds.),Classical Conditioning II: Current Research and Theory New York, Appleton-Century-Crofts, pp. 64–99.
Reynolds, J. H., and Glaser, R. (1964). Effects of repetition and spaced review upon retention of a complex learning task.J. Educat. Psychol. 55: 297–308.
Rose, A. J. (1980). Encoding variability, levels of processing, and the effects of spacing of repetitions upon judgments of frequency.Mem. Cognit. 8: 84–93.
Rose, A. J. (1984). Processing time for repetitions and the spacing effect.Canad. J. Psychol. 38: 537–550.
Rosenshine, B., and Stevens, R. (1986). Teaching functions. In Wittrock, M. C. (ed.),Handbook of Research on Teaching (3rd. ed.), New York, Macmillan, pp. 376–391.
Rothkopf, E. Z. (1963). Some observations on predicting instructional effectiveness by simple inspection.J. Prog. Instruct. 3: 19–20.
Rothkopf, E. Z. (1966). Learning from written instructive materials: An exploration of the control of inspection behavior by test-like events.Am. Educat. Res. J. 3: 241–249.
Rothkopf, E. Z., and Coke, E. V. (1966). Variations in phrasing and repetition interval and the recall of sentence materials.J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 5: 86–89.
Rowe, E. J., and Rose, R. J. (1977). Effects of orienting task, spacing of repetitions, and list context on judgments of frequency.Mem. Cognit. 5: 505–512.
Ruch, T. C. (1928). Factors influencing the relative economy of massed and distributed practice in learning.Psychol. Rev. 35: 19–45.
Rundus, D. (1971). Analysis of rehearsal processes in free recall.J. Exper. Psychol. 89: 63–77.
Runquist, W. N. (1983). Some effects of remembering on forgetting.Mem. Cognit. 11: 641–650.
Runquist, W. N. (1986). The effect of testing on the forgetting of related and unrelated associates.Canad. J. Psychol. 40: 65–76.
Saxon, J. (1982). Incremental development: A breakthrough in mathematics.Phi Delta Kappan 63: 482–484.
Shaughnessy, J. J. (1976). Persistence of the spacing effect in free recall under varying incidental learning conditions.Mem. Cognit. 4: 369–377.
Siegel, M. A., and Misselt, A. L. (1984). Adaptive feedback and review paradigm for computer-based drills.J. Educat. Psychol. 76: 310–317.
Slamecka, N. J., and Katsaiti, L. T. (1988). Normal forgetting of verbal lists as a function of prior testing.J. Exper. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cognit. 14: 716–727.
Slavin, R. (1988).Educational Psychology: Theory into Practice (2nd ed.). Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, Prentice-Hall.
Sones, A. M., and Stroud, J. B. (1940). Review with special reference to temporal position.J. Educat. Psychol. 31: 665–676.
Spitzer, H. F. (1939). Studies in retention.J. Educat. Psychol. 30: 641–656.
Stigler, J. W., Fuson, K. C., Ham, M., and Kim, M. S. (1986). An analysis of addition and subtraction word problems in American and Soviet elementary mathematics textbooks.Cognit. Instruct. 3: 153–171.
Thorndike, E. L. (1916). Notes on practice, improvability and the curve of work.Am. J. Psychol. 27: 550–565.
Toppino, T. C., and DeMesquita, M. (1984). Effects of spacing repetitions on children's memory.J. Exper. Child Psychol. 37: 637–648.
Toppino, T. C., and DiGeorge, W. (1984). The spacing effect in free recall emerges with development.Mem. Cognit. 12: 118–122.
Toppino, T. C., and Gracen, T. F. (1985). The lag effect and differential organization theory.J. Exper. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cognit. 11: 185–191.
Underwood, B. J. (1961). Ten years of massed practice on distributed practice.Psychol. Rev. 68: 229–247.
Underwood, B. J. (1970). A breakdown of the total-time law in free-recall learning.J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 9: 573–580.
Watts, G. H., and Anderson, R. C. (1971). Effects of three types of inserted questions learning from prose.J. Educat. Psychol. 62: 387–394.
Whitten, W. B., II, and Bjork, R. A. (1977). Learning from tests: Effects of spacing.J. Verb. Learn. Verb. Behav. 16: 456–478.
Woolfolk, A. E. (1987).Educational Psychology (3rd ed.). Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, Prentice-Hall.
Yeh, J. P. (1978).Test Use in Schools. Washington, D.C., National Institute of Education, U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare.
Zechmeister, E. B., and Shaughnessy, J. J. (1980). When you know that you know and when you think that you know but you don't.Bull. Psychonom. Soc. 15: 41–44.