Summary
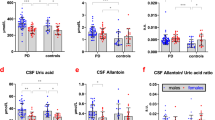
Death of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease (PD) may partially be caused by synthesis and accumulation of endogenous and exogenous toxins. Because of structural similarity to MPTP, β-carbolines, like norharman and harman, have been proposed as putative neurotoxins. In vivo they may easily be formed by cyclization of indoleamines with e.g. aldehydes. For further elucidation of the role of β-carbolines in neurodegenerative disorders harman and norharman levels in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) were measured in 14 patients with PD and compared to an age- and sex-matched control group (n=14). CSF levels of norharman and harman in PD were significantly higher compared to controls. These results may suggest a possible role of harman and norharman or its N-methylated carbolinium ions in the pathophysiological processes initiating PD. However the origin of increased levels of these β-carbolines remains unclear. On the one hand one may speculate, that unknown metabolic processes induce the increased synthesis of harman and norharman in PD. On the other hand a possible impact of exogenous sources may also be possible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albores R, Neafsey EJ, Drucker G, Fields JZ, Collins MA (1990) Mitochondrial respiratory inhibition by N-methylated β-carboline derivatives structurally resembling N-methyl-4-phenylpyridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci 87: 9368–9372
Collins MA, Neafaey EJ, Matsubara K, Cobuzzi RJ Jr, Rollema H (1992) Indole-N-methylated β-carbolinium ions as potential brain-bioactivated neurotoxins. Brain Res 570: 154–160
Fekkes D, Bode WT (1993) Occurrence and partition of the beta-carboline norharman in rat organs. Life Sci 52: 2045–2054
Fekkes D, Schouten MJ, Pepplinkhuizen L, Bruinvels J, Lauwers W, Brinkman UA (1992) Norharman, a normal body constituent [letter]. Lancet 339: 506
Fields JZ, Albores R, Neafsey EJ, Collins MA (1992) Similar inhibition of mitochondrial respiration by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-pyridinium (MMP+) and by a unique N-methylated beta-carboline analogue, 2,9-dimethyl-norharman (2,9Me2NH). Ann NY Acad Sci 648: 272–274
Green S, Buttrum S, Molloy H, Steventon G, Sturman S, Waring R, Pall H, Williams A (1991) N-methylation of pyridines in Parkinson's disease. Lancet 338: 120–121
Matsubara K, Neafsey EJ, Collins MA (1992) Novel S-adenosylmethionine-dependent indole-N-methylation of beta-carbolines in brain particulate fractions. J Neurochem 59: 511–518
Matsubara K, Collins MA, Akane A (1993) Potential bioactivated neurotoxicants, N-methylated beta-carbolinium ions, are present in human brain. Brain Res 610: 90–96
Neafsey EJ, Drucker G, Raikoff K, Collins MA (1989) Striatal dopaminergic toxicity following intranigral injection in rats of 2-methyl-norharman, a beta-carbolinium analog of N-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+). Neurosci Lett 105: 344–349
Pawlik M, Kaulen P, Baumgarten HG, Rommelspacher H (1990) Quantitative autoradiography of [3H]norharman ([3H]beta-carboline) binding sites in the rat brain. J Chem Neuroanat 3: 19–24
Rommelspacher H, May T, Susilo R (1991a) β-carbolines and tetrahydroisoquinolines: detection and function in mammals. Planta Med 57: 85–92
Rommelspacher H, Schmidt LG, May T (1991b) Plasma norharman (β-carboline) levels are elevated in chronic alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 15: 553–559
Rommelspacher H, May T, Salewski B (1994) Harman (1-methyl-β-carboline) is a natural inhibitor of monoamine oxidase type A in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 14: 51–59
Sayre LM, Wang F, Arora PK, Riachi NJ, Harik SI, Hoppel CL (1990) Depaminergic neurotoxicity in vivo and inhibition of mitochondrial respiration in vitro by possible endogenous Pyridinium-like substances. J Neurochem 57: 2106–2115
Schulz JB, Flint Beal M (1994) Mitochondrial dysfunction in movement disorders. Neurology 7: 333–339
Stohler R, Rommelspacher H, Ladewig D, Dammann G (1993) β-Carbolines (harman/norharman) are increased in heroin dependent patients. Ther Umsch 50: 178–181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuhn, W., Müller, T., Groβe, H. et al. Elevated levels of harman and norharman in cerebrospinal fluid of Parkinsonian patients. J. Neural Transmission 103, 1435–1440 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01271257
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01271257