Abstract
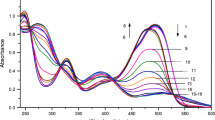
A simple, rapid and accurate colorimetric method is proposed for the determination of tannins, based on the reduction of tetrazolium blue in alkaline medium by tannins at 90 ± 2 °C for 15 min, leading to the formation of a highly coloured formazan derivative. Absorbance measurements were made at 527 nm and the calibration graph was linear for 0.2-9.0 μg/ml of tannic acid. For more accurate analysis, the Ringbom optimum concentration range was found to be 0.5–8.2 μg/ml. The relative standard deviation for the determination in a tea sample containing 7.55% tannins was 1.65%. Most of the ingredients commonly found in tea samples do not interfere with the determination. Several tea samples were analysed using the proposed method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Windholz (ed.),Merck Index, 10th Ed., Merck, Rahway, New Jersey, 1973, p. 1301.
L. H. Meyer (ed.),Food Chemistry, Litton Educational, New York, 1970, p. 250.
S. H. Schanderl, in:Methods in Food Analysis, 2nd Ed. (M. A. Joslyn, ed.), Academic Press, London, 1970, p. 70.
C. A. Mitchell,Analyst 1963,61, 295.
W. Horwitz (ed.),Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 13th Ed., Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, Virginia, 1980, Section 30, 019.
W. Horwitz (ed.),Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 13th Ed., Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, Virginia, 1980, Section 9, 100.
M. Kapel, R. Karunanithy,Analyst 1974,99, 661.
K. L. Bajaj, A. K. Devsharma,Mikrochim. Acta 1977,II, 249.
M. Celeste, C. Tomas, A. Cladera, J. M. Estela, V. Cerda,Anal. Chim. Acta 1992,269, 21.
V. L. Dressler, E. L. Machado, A. F. Martins,Analyst 1995,120, 1185.
O. W. Lau, S. F. Luk, H. L. Huang,Analyst 1989,114, 631.
R. B. Burton, A. Zafferoni, E. H. Keutmann,J. Biol. Chem. 1951,188, 763.
C. Chem, J. Wheeler, H. E. Tewell,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1953,42, 749.
W. J. Mader, R. R. Buck,Anal. Chem. 1952,24, 666.
A. S. Meyers, M. C. Lindberg,Anal. Chem. 1955,27, 813.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amin, A.S. Utilization of tetrazolium blue for the colorimetric assay of tannins in tea. Mikrochim Acta 126, 105–108 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01242670
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01242670