Abstract
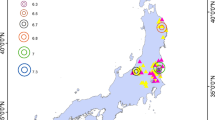
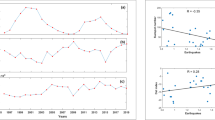
Detection of precursory phenomena in observation data is essential to earthquake prediction studies. Continuous monitoring of radon concentration in groundwater in Japan in one case showed a short-term anomaly related to a nearby earthquake. With the exception of the 1978 Izu-Oshimakinkai earthquake (M7.0), however, no abnormal change has been noted. This may be due partially to difficulty in detecting insignificant precursory signals from observation data, which ordinarily contains a noise-induced fluctuations, and partially to lack of understanding of the mechanism controlling the appearance of precursory phenomena. In order to increase our knowledge of the variation pattern of precursory changes in radon concentration of groundwater, hydrologic precursors with significant features are examined in this paper. Complexity of appearance of precursory phenomena and problems in assignment of the specific earthquake are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barsukov, V. L., Varshal, G. M. andZamolina, N. S. (1985),Recent results of hydrogeochemical studies for earthquake prediction in the USSR, PAGEOPH122, 143–156.
Hiraga, S. (1981),Anomalous records of hot springs and groundwaters as precursory phenomena of earthquakes—The 1923 Great Kanto earthquake. Bull. Hot Springs Res. Inst.12, 144–146.
King, C.-Y. (1985),Radon monitoring for earthquake prediction in China. Earthq. Predict. Res.3, 47–68.
Matsuda, T. andSibano, M. (1965),The Shizuoka-Shimizu earthquake of April 20, 1965, and ‘the Seismological Blocks’ revealed by the earthquake, Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst.43, 625–639.
Mogi, K. (1981),Active tectonic zone along the Japan Sea coast of northeastern Honshu, the Fossa Magna and the Tokai-Izu region, and the recent seismic activity in the Izu region. Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst.56, 691–711.
Mogi, K. (1987),Comparison of precursory phenomena before the 1975 Haicheng (China) earthquake and the 1978 Izu-Oshima-kinkai (Japan) earthquake—The possible effect of stress history on precursory phenomena. InEarthquake Prediction, (eds. K. Mogi and K. N. Khattri) Special Issue of Tectonophysics (in press).
Nakamura, S. (1925),Reports on the Great Kanto earthquake. Inthe Sinsai Yobo Tyosakwai Hokoku (Reports of the Imperial Earthquake Investigation Committee), No. 100 A (Iwanami Shoten, Tokyo) pp. 67–140.
Raleigh, B., Bennet, G., Craig, H., Hanks, T., Molnar, P., Nur, A., Savage, J., Scholz, C., Turner, R., andWu, F. (1977),Prediction of the Haicheng earthquake, EOS Trans., Amer. Geophys. Union58, 236–272.
Teng, T. A. (1980),Some recent studies on groundwater radon content as earthquake precursor. J. Geophys. Res.85, 3089–3099.
Wakita, H. (1978a),Earthquake prediction and geochemical studies in China. Chinese Geophysics,1, 443–457
Wakita, H., Nakamura, Y., Notsu, K., Noguchi, M. andAsada, T. (1980),Radon anomaly: A possible precursory of the 1978 Izu-Oshima-kinkai earthquake. Science207, 882–883.
Wakita, H. (1981),Precursory changes in groundwater prior to the 1978 Izu-Oshima-kinkai earthquake. InEarthquake Prediction—An International Review, Maurice Ewing Series (eds. D. W. Simpson and P. G. Richard) (Amer. Geophys. Union, Washington, D.C.), pp. 527–532.
Wakita, H. (1982),Changes in groundwater level and chemical composition. InEarthquake Prediction Technique (ed. T. Asada), (Univ. Tokyo Press, Tokyo), pp. 175–216.
Wakita, H. (1984),Groundwater observations for earthquake prediction in Japan. InA Collection of Papers of International Symposium on Continental Seismicity and Earthquake Prediction (ISCSEP) (Seismological Press, Beijing), pp. 494–500.
Zhang, G. andFu, Z. (1980),Some features of medium-and short-term anomalies before great earthquakes. InEarthquake Prediction—An International Review, Maurice Ewing Series (eds. D. W. Simpson and P. G. Richard) (Amer. Geophys. Union, Washington, D.C.), pp. 497–509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wakita, H., Nakamura, Y. & Sano, Y. Short-term and intermediate-term geochemical precursors. PAGEOPH 126, 267–278 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00878999
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00878999