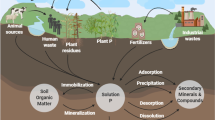
Abstract
Sequential P extraction was combined with electron microscop and X-ray spectroscopy to characterise various P species and to study their transformation in settling seston and in recent sediment. During early diagenesis most of the particulate P formed in the water was redissolved. No net transformation into species that would resist dissolution was observed.
It was shown that
-
• the phosphorus (P) content and the P flux of settling particles varied seasonally over one order of magnitude
-
• particles became enriched with reductant soluble P (BD-P) while settling through the hypolimnion
-
• changes in BD-P were highly significantly correlated with changes in reductant soluble iron (BD-Fe)
-
• bacteria oxidising Fe and Mn seemed to be mainly responsible for this increase in P concentration
-
• other fractions including organic P did not change during sedimentation
-
• most of the organic P and of the Fe bound P and 70% of TP was released from the sediment during early diagenesis
-
• the sediment surface did not act as a trap for P migrating upwards from deeper sediment layers
-
• CaCO3 sedimentation contributed little to P sedimentation but significantly to the permanent burial of P.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boström, B., I. Ahlgren, R. Bell, 1985. Internal loading in a eutrophic lake, reflected in seasonal variations of some sediment parameters. Verh. Int. Verein. Limnol. 22:3335–3339.
Caraco, N. F., J. J. Cole and G. E. Likens, 1993. Sulfate control of phosphorus availability in lakes. Hydrobiologia 253:275–280.
Carignan, R. and R. J. Flett, 1981. Postdepositional mobility of phosphorus in lake sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 26, 2:361–366.
Diem, D., 1983. Die Oxydation von Mangan (II) im See. PhD thesis Nr. 7359, Eidgen. Techn. Hochschule, Zürich.
Forsgren, G. and M. Jansson, 1993. Sedimentation of phosphorus in limnetic and estuarine environments in the River Öre system, northern Sweden. Hydrobiologia 253:233–248.
Gächter, R., 1987. Lake restoration. Why oxygenation and artificial mixing cannot substitute for a decrease in external phosphorus load. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 49:170–185.
Gächter, R. and T. Mares, 1985. Does settling seston release soluble reactive phosphorus in the hypolimnion of lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 30, 2:364–371.
Gächter, R. and J. S. Meyer, 1990. Mechanism controlling fluxes of nutrients across the sediment/water interface in a eutrophic lake. In: Baudo, R., J. Giesy, H. Muntau (eds.): Sediments: Chemistry and Toxicity of In-Place Pollutants, Lewis Publishers, pp. 131–162.
Gächter, R., J. S. Meyer and A. Mares, 1988. Contribution of bacteria to release and fixation of phosphorusin lake sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 33, 6:1542–1558.
Gächter, R., A. Mares, E. Grieder, A. Zwyssig and P. Höhener, 1989. Auswirkungen der Belüftung und Sauerstoffbegasung auf den P-Haushalt des Sempachersees. Wasser, Energie, Luft 81, 11/12:335–341.
Gächter, R., A. Tessier, E. Szabo and R. Carignan, 1992. Measurement of total dissolved phosphorus in small volumes of iron rich interstitial water. Aquatic Sciences 54:1–9.
Giovanoli, R., R. Brütsch, D. Diem, G. Osman-Sigg and L. Sigg, 1980. The composition of settling particles in Lake Zürich. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 42, 2:89–100.
Golterman, H. L., 1982. Differential extraction of sediment phosphates with NTA solutions. Hydrobiologia 92:683–687.
Gregory, E., R. S. Perry and J. T. Staley, 1980. Characterisation, distribution, and significance ofMetallogenium in lake Washington. Microb. Ecol. 6, 2:125–140.
Hieltjes, A. H. M. and L. Lijklema, 1980. Fractionation of inorganic phosphates in calcareous sediments. J. Environ. Qual. 9, 3:405–407.
Hupfer, M., R. Gächter and H. Rüegger, 1995. Polyphosphate in lake sediments:31P NMR spectroscopy as a tool for its identification. Limnol. Oceanogr. 40, 3:610–617.
Jensen, H. S. and B. Thamdrup, 1993. Iron-bound phosphorus in marine sediments as measured by bicarbonate-dithionite extraction. Hydrobiologia 253:47–59.
Jorgensen, S. E., L. Kamp-Nielsen and O. S. Jackobsen, 1975. A submodel for anaerobic mudwater exchange of phosphate. Ecol. Model. 1:133–146.
Kamp-Nielsen, L., 1974. Mud-water exchange of phosphate and other ions in undisturbed sediment cores and factors affecting the exchange rates. Arch. Hydrobiol. 73:218–237.
Kemp, A. L., T. W. Anderson, R. L. Thomas and A. Mudrochova, 1974. Sedimentation rates and recent sediment history of lakes Ontario, Erie and Huron. J. Sediment. Petrol. 44:207–218.
Koschel, R., J. Benndorf, G. Proft and F. Recknagel, 1983. Calcite precipitation as a natural control mechanism of eutrophication. Arch. Hycrobiol. 98:380–408.
Liebezeit, G., 1991. Analytical phosphorus fractionation of sediment trap material. Marine Chem. 33:61–69.
Miyajima, T., 1992. Biological manganese oxidation in a lake. 1: Occurrence and distribution ofMetallogenium sp. and its kinetic properties. Arch. Hydrobiol. 124, 3:317–335.
Pettersson, K. and V. Istvanovics, 1988. Sediment phosphorus in Lake Balaton — forms and mobility. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. 30:25–41.
Psenner, R., R. Pucsko and M. Sager, 1984. Die Fraktionierung organischer und anorganischer Phosphorverbindungen von Sedimenten — Versuch einer Definition ökologisch wichtiger Fraktionen. Arch. Hydrobiol./Suppl. 70, 1:111–155.
Psenner, R., B. Boström, M, Dinka, K. Pettersson, R. Pucsko and M. Sager, 1988. Fractionation of phosphorus in suspended matter and sediment. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. 30:98–110.
Redfield, A. C., B. H. Ketchum and F. A. Richards, 1963. The influence of organisms on the composition of sea water. In: M. H. Hill (ed.), The sea, vol 2. Wiley-Intescience, New York, pp. 26–77.
Ruttenberg, K. C., 1992. Development of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 37:1460–1482.
Stadelmann, P., 1988. Zustand des Sempachersees vor und nach Inbetriebnahme der seeinternen Maßnahmen: Künstlicher Sauerstoffeintrag und Zwangszirkulation 1980–1987. Wasser, Energie, Luft 80:81–96.
Tessenow, U., 1975. Solution, diffusion and sorption in the upper layer of lake sediments. V. The differentiation of the profundal sediments of an oligotrophic mountain lake (Feldsee, Hochschwarzwald) by sediment-water interaction. Arch. Hydrobiol./Suppl. 47, 3:325–412.
Ulén, B., 1978. Seston and sediment in Lake Norvikken III: Nutrient release from sediment. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 40:104–305.
Uhlmann, D., I. Röske, M. Hupfer and G. Ohms, 1990. A simple method to distinguish between polyphosphate and other fractions of activated sludge. Wat. Res. 24:1355–1360.
Vogler, P., 1965. Beiträge zur Phosphoranalytik in der Limnologie. 2. Die Bestimmung des gelösten Orthophosphates. Fortschr. Wasserchem. Grenzgeb. 2:109–119.
Waara, T., M. Jansson, K. Pettersson, 1993. Phosphorus composition and release in sediment bacteria of the genusPseudomonas during aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Hydrobiologia 253:131–140.
Williams, J.D., J.K. Syers, D.E. Armstrong and F. Harris, 1971. Fractionation of inorganic phosphate in calcareous lake sediments. Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc. 35:250–255.
Williams, J. D. and T. Mayer, 1972. Effects of sediment diagenesis and regeneration of phosphorus with special reference to Lakes Erie and Ontario. In: H.E. Allen, J.R. Kramer (eds.), Nutrients in natural waters. Wiley-Interscience, pp. 281–315.
Zinder, B., 1985. Phosphorrücklösung aus Sedimenten als Folge der Reduktion von Eisenoxiden. PhD thesis Nr. 7738, Eidgen. Techn. Hochschule Zürich.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hupfer, M., Gächter, R. & Giovanoli, R. Transformation of phosphorus species in settling seston and during early sediment diagenesis. Aquatic Science 57, 305–324 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00878395
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00878395