Summary
-
1.
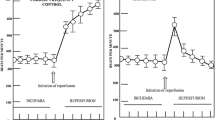
Na-free media, with or without atropine, induced tonic contractures and enhanced spontaneous contractions of the rat ileum.
-
2.
Quinine and lanthanum did not significantly inhibit these Na-free contractures, and neither agent, nor Na-free saline itself, caused any significant net gain of tissue calcium.
-
3.
Na-free media enormously stimulated calcium efflux from the ileum whether atropine was present or not, suggesting a high tissue calcium turnover due to stimulation of surface transport sites. Quinine and lanthanum had no significant effect on this calcium efflux.
-
4.
Mg-free media increased tension in the ileum and enhanced spontaneous contractions while high-Mg media inhibited contractility.
-
5.
Mg-free media were without significant effect on calcium efflux from the ileum but they did induce a very small rise in tissue calcium.
-
6.
These results are not consistent with the concept of a simple Na/Ca membrane counter exchange system in the ileum to regulate tissue calcium. On present evidence, a linked counter exchange system of Ca with Mg and Na would seem more likely.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altura, B.M., Altura, B.T.: Magnesium and contraction of arterial smooth muscle. Microvasc. Res.7, 145–155 (1974)
Altura, B.M., Altura, B.T.: Magnesium withdrawal and contraction of arterial smooth muscle: Effects of EDTA, EGTA and divalent cations. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (NY)151, 752–755 (1976)
Baker, P.F.: Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Progr. Biophys. Mol. Biol.24, 177–223 (1972)
Brading, A.F., Widdicombe, J.H.: Interaction between sodium and calcium movements in smooth muscle. I.N.S.E.R.M.50, 235–246 (1976)
Casteels, R., Droogmans, G., Hendrickx, H.: Effect of sodium and sodium-substitutes on the active ion transport and on the membrane potential of smooth muscle cells. J. Physiol. (Lond.)228, 733–748 (1973)
Casteels, R., Van Breemen, C.: Active and passive Ca2+ fluxes across cell membranes of the guinea pig taenia coli. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.359, 197–207 (1975)
Casteels, R., Kitamura, K., Kuriyama, H., Suzuki, H.: The membrane properties of the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit main pulmonary artery. J. Physiol. (Lond.)271, 41–61 (1977a)
Casteels, R., Kitamura, K., Kuriyama, H., Suzuki, H.: Excitation-contraction coupling in the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit main pulmonary artery. J. Physiol. (Lond.)271, 63–79 (1977b)
Cheng, J.T.: “Calcium-induced release of calcium” in rectal smooth muscle of mice. Jap. J. Pharmacol.26, 73–78 (1976)
Huddart, H., Hunt, S.: Visceral muscle—Its structure and function. Glasgow: Blackie and Son 1976
Huddart, H., Price, N.R.: Calcium movements during excitation-contraction coupling in muscle cells. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.54A, 375–386 (1976)
Huddart, H., Saad, K.H.M.: Quinine and lanthanum effects on contractility and calcium movements of rat ileal smooth muscle. Gen. Pharmac.8, 341–347 (1977)
Huddart, H., Syson, A.J.: The effect of caffeine on calcium efflux and calcium translocation in skeletal and visceral muscle. J. exp. Biol.63, 131–142 (1975)
Jundt, H., Porzig, H., Reuter, H., Stucki, I.W.: The effect of substances releasing intracellular calcium ions on sodium-dependent calcium efflux from guinea pig auricles. J. Physiol. (Lond.)246, 229–253 (1975)
Ma, T.A., Bose, D.: Sodium in smooth muscle relaxation. Amer. J. Physiol.232, C59-C66 (1977)
Nanninga, L.B.: Calculation of free magnesium, calcium and potassium in muscle. Biochim. biophys. Acta54, 338–344 (1961)
Reuter, H.: Exchange of calcium ions in the mammalian myocardium. Circulat. Res.34, 599–605 (1974)
Van Breemen, C., Farinas, B.R., Casteels, C., Gerba, P., Wuytack, F., Deth, R.: Factors controlling cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration. Phil. Trans. B265, 57–71 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huddart, H., Saad, K.H.M. The effect of sodium and magnesium and their interaction with quinine and lanthanum on spontaneous activity and related calcium movements of rat ileal smooth muscle. J Comp Physiol B 126, 233–240 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688932
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688932