Abstract
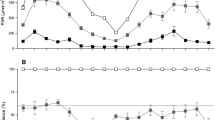
Quantum irradiance was measured at several depths in forests of the giant kelp Macrocystis pyrifera (L.) C. Agardh in southern California, USA, during the summer of 1983. The greatest reduction in irradiance occurred in the uppermost 1 m of the water column, where the floating portions of kelp fronds formed surface canopies with high blade densities. Average irradiances low enough to limit macroalgal photosynthesis (<200 μE m-2 s-1) were recorded at 1 m depth below dense kelp canopies under sunny surface conditions. Light penetration was exponentially related to canopy density, but was higher than predicted from transmission through individual kelp blades dae to the heterogeneous distribution of canopy tissue. Light penetration was considerably lower immediately adjacent to an individual kelp plant than in the interplant spaces, indicating significant self-shading. Spatial and temporal variability in both irradiance and light penetration were highest just below the canopy and decreased with increasing depth. Sunflecks (>200 μE m-2 s-1), ranging from <1 to 60s or more in duration, composed a considerable proportion of total irradiance at 1 m depth, even during recordings with low average irradiances. These fluctuations probably affect photosynthetic efficiency of kelp tissues within and just below the canopy. Predictions of kelp productivity based on irradiances averaged over hours or days and on photosynthetic parameters determined under laboratory conditions may be inaccurate, due to the spatial and temporal variability characteristic of the kelp forest light-environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Acock, B., J. H. M. Thornly and J. W. Wilson: Spatial variation of light in the canopy. In: Prediction and measurement of photosynthetic productivity, pp 91–102. Ed. by C. T. de Wit. Wageningen: Centre for Agricultural Publishing and Documentation 1970
Barrales, H. L. and C. S. Lobban: The comparative ecology of Macrocystis pyrifera, with emphasis on the forests of Chubut, Argentina. J. Ecol. 63, 657–677 (1975)
Dayton, P. K., V. Currie, T. Gerrodette, B. Keller, R. Rosenthal and D. V. Tresca: Patch dynamics and stability of southern California kelp communities. Ecol. Monogr. 54, 253–289 (1984)
Dayton, P. K. and M. J. Tegner: Catastrophic storms, El Niño, and patch stability in a southern California kelp community. Science, N.Y. 224, 283–285 (1984)
Duncan, M. J. and P. J. Harrison: Comparison of solvents for extracting chlorophylls from marine macrophytes. Botanica mar. 25, 445–447 (1982)
Federer, C. A. and C. B. Tanner: Spectral distribution of light in the forest. Ecology 47, 555–560 (1966)
Foster, M. S.: Regulation of algal community development in a Macrocystis pyrifera forest. Mar. Biol. 32, 331–342 (1975)
Gaudillere, J. P.: Effect of periodic oscillations of artificial light emission on photosynthetic activity. Physiologia Pl. 41, 95–98 (1977)
Gay, L. W., K. R. Knoerr and M. O. Braaten: Solar radiation variability on the floor of a pine plantation. Agric. Meteorology (Amsterdam) 8, 39–50 (1971)
Gerard, V. A.: Some aspects of material dynamics and energy flow in a kelp forest in Monterey Bay, California, 173 pp. Ph.D. thesis, University of California, Santa Cruz 1976
Gerard, V. A.: Physiological effects of El Niño on giant kelp in southern California. Mar. Biol. Lett. (In press) (1984)
Gross, L. J.: Photosynthetic dynamics in varying light environments: a model and its application to whole leaf carbon gain. Ecology 63, 84–93 (1982)
Gross, L. J. and B. F. Chabot: Time course of photosynthetic response to changes in incident light energy. Pl. Physiol., Baltimore, Md 63, 1033–1038 (1979)
Hatfield, J. L. and R. E. Carlson: Spectral and photosynthetically active radiation transmission patterns within soybean canopies. Iowa St. J. Res. 55, 47–60 (1980)
Heine, J. N.: Seasonal productivity of two red algae in a central California kelp forest. J. Phycol. 19, 146–152 (1983)
Horn, H. S.: The adaptive geometry of trees, 144 pp. Princeton: Princeton University Press 1971
Hutchison, B. A. and D. R. Matt: The distribution of solar radiation within a deciduous forest. Ecol. Monogr. 47, 185–207 (1977)
Jackson, G. A. and C. D. Winant: Effect of a kelp forest on coastal currents. Contin. Shelf Res. 2, 75–80 (1983)
Kriedemann, P. E., E. Torokfalvy and R. E. Smart: Natural occurrence and utilisation of sunflecks by grapevine leaves. Photosynthetica (Praha, Czechoslovakia) 7, 18–27 (1973)
Loomis, W. E.: Absorption of radiant energy by leaves. Ecology 46, 14–17 (1965)
Lüning, K.: Light. In: The biology of seaweeds, pp 326–355. Ed. by C. S. Lobban and M. J. Wynn. Berkeley: University of California Press 1981
Marra, J.: Effect of short-term variations in light intensity on photosynthesis of a marine phytoplankter: a laboratory simulation study. Mar. Biol. 46, 191–202 (1978)
McFarland, W. N. and E. R. Loew: Wave produced changes in underwater light and their relations to vision. Envir. Biol. Fish. 8, 173–184 (1983)
McFarland, W. N. and J. Prescott: Standing crop, chlorophyll content and in situ metabolism of a giant kelp community in southern California. Publs Inst. mar. Sci. Univ. Tex. 6, 109–132 (1959)
Monsi, M., Z. Uchijima and T. Oikawa: Structure of foliage canopies and photosynthesis. A. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 4, 301–327 (1973)
Monteith, J. L.: Light distribution and photosynthesis in field crops. Ann. Bot. 29, 17–37 (1965)
Neushul, M.: Submarine illumination in Macrocystis beds. Beih. Nova Hedwigia 32, 241–254 (1971)
Newton, J. E. and G. E. Blackman: The penetration of solar radiation through leaf canopies of different structure. Ann. Bot. 34, 329–349 (1970)
Pearse, J. S. and A. H. Hines: Expansion of a central California kelp forest following the mass mortality of sea urchins. Mar. Biol. 51, 83–91 (1979)
Pollard, D. F. W.: The effect of rapidly changing light on the rate of photosynthesis in largetooth aspen (Populus grandidentata). Can. J. Bot. 48, 823–829 (1970)
Ramus, J.: A physiological test of the theory of complementary chromatic adaptation. II. Brown, green and red seaweeds. J. Phycol. 19, 173–178 (1983)
Reed, D. C. and M. S. Foster: The effects of canopy shading on algal recruitment and growth in a giant kelp forest. Ecology 65, 937–948 (1984)
Reifsnyder, W. E., G. M. Furnival and J. L. Horowitz: Spatial and temporal distribution of solar radiation beneath forest canopies. Agric. Meteorology (Amsterdam) 9, 21–37 (1971)
Rosenthal, R. J., W. D. Clarke and P. K. Dayton: Ecology and natural history of a stand of giant kelp, Macrocystis pyrifera, off Del Mar. California. Fish. Bull. U.S. 72, 670–684 (1974)
Santelices, B. and F. P. Ojeda: Effects of canopy removal on the understory algal community structure of coastal forests of Macrocystis pyrifera from southern South America. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 14, 165–173 (1984a)
Santelices, B. and F. P. Ojeda: Population dynamics of coastal forests of Macrocystis pyrifera in Puerto Toro, Isla Navarino, southern Chile. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 14, 175–183 (1984b)
Schenck, H. Jr.: On the focusing of sunlight by ocean waves. J. opt. Soc. Am. 47, 653–657 (1957)
Sinclair, T. R. and E. R. Lemon: The distribution of 660 and 730 nm radiation in corn canopies. Sol. Energy 15, 89–97 (1973)
Towle, D. W. and J. S. Pearse: Production of the giant kelp Macrocystis, estimated by in situ incorporation of 14C in polyethylene bags. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18, 155–159 (1973)
Walsh, P. and L. Legendre: Photosynthesis of natural phytoplankton under high frequency light fluctuations simulating those induced by sea surface waves. Limnol. Oceanogr. 28, 688–697 (1983)
Wheeler, W. N.: Pigment content and photosynthetic rate of the fronds of Macrocystis pyrifera. Mar. Biol. 56, 97–102 (1980)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by N. D. Holland, La Jolla
Please address all requests for reprints to the author at her second address in Stony Brook, New York
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerard, V.A. The light environment in a giant kelp forest: influence of Macrocystis pyrifera on spatial and temporal variability. Mar. Biol. 84, 189–195 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393004
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393004