Summary
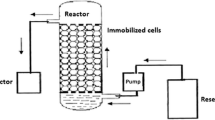
A Pseudomonas sp. which was isolated from phenol-containing soil was immobilized in alginate and polyacrylamide-hydrazide (PAAH) and cultivated in a special airlift fermenter.
The immobilized Pseudomonas sp. was able to degrade phenol at initial concentrations up to 2 g/l in less than 2 days, although the free cells did not grow at this concentration.
The immobilization materials act as a protective cover against phenol, PAAH being more effective than alginate. The degradation activity as well as the outgrowth of bacteria can be manipulated by the concentration of the immobilization material, the temperature and the nitrogen content in the medium.
The cells grew predominantly in microcolonies in the outer area of the beads when nitrogen was available as 1.0g NH4NO3/l and 0.5g (NH4)2SO4/l.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buswell JA (1975) Metabolism of phenol and cresols by Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol 124:1077–1083
Dagley S (1971) Catabolism of aromatic compounds by microorganisms. Adv Microbial Physiol 6:1–46
Ehrhardt HM, Rehm HJ (1984) Degradation of phenol by microorganisms adsorbed on activated carbon. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 20 (in press)
Freeman A, Aharonowitz Y (1981) Immobilization of microbial cells in crosslinked, prepolymerized, linear polyacrylamide gels: Antibiotic production by immobilized Streptomyces clavuligerus. Biotechnol Bioeng 23:2747–2759
Hackel U, Klein J, Megnet R, Wagner F (1975) Immobilization of microbial cells in polymeric matrices. Eur J Appl Microbiol 1:291–293
Hill GA, Robinson CW (1975) Substrate inhibition kinetics: Phenol degradation by Pseudomonas putida. Biotechnol Bioeng 17:1599–1615
Holladay DW, Hancher CW, Scott CD, Shilcote DD (1978) Biodegradation of phenolic waste liquors in stirred-tank, packed-bed and fluidized-bed bioreactors. J Water Pollut Control Fed 50:2573–2589
Klein JA, Lee DD (1978) Biological treatment of aqueous wastes from coal conversion processes. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp 8:379–390
Klein J, Schara P (1981) Entrapment of living microbial cells in covalent polymeric networks. II. A quantitative study on the kinetics of oxidative phenol degradation by entrapped Candida tropicalis cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 6:91–117
Klein J, Hackel U, Wagner F (1979) Phenol degradation by Candida tropicalis whole cells entrapped in polymeric ionic networks. ACS Symp Ser 106:101–118
Lee DD, Scott CD, Hancher CW (1979) Fluidized-bed bioreactor for coal conversion effluents. J Water Pollut Control Fed 51:974–984
Martin RW (1949) Rapid colorimetric estimation of phenol. Anal Chem 21:1419
Rübelt C, Dietz F, Kickuth R, Koppe P, Kunte H, Peschel G, Sonneborn M (1982) DFG Forschungsbericht “Schadstoffe im Wasser, Bd II Phenole”. Harald Boldt Verlag, Boppard
Takahashi S, Itoh M, Kaneko Y (1981) Treatment of phenolic wastes by Aureobasidium pullulans adhered to the fibrous supports. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 13:175–178
Tanaka J, Matsumura M, Veliky IA (1984) Diffusion characteristics of substrates in Ca-alginate gel beads. Biotechnol Bioeng 26:53–58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Prof. Dr. A. Fiechter dedicated to his 60th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bettmann, H., Rehm, H.J. Degradation of phenol by polymer entrapped microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 20, 285–290 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270587
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270587