Abstract
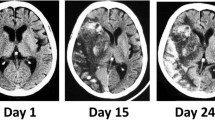
A 29-year-old woman suffered a cardiac arrest, due to profound hyperkalaemia, caused by the use of a potassium-containing salt substitute. She was resuscitated, but post-hypoxic brain damage occurred. Some of the sparse literature is reviewed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaplan M (1969) Suicide by oral ingestion of a potassium preparation. Ann Intern Med 71:363
Illingworth RN, Proudfoot AT (1980) Rapid poisoning with slow-release potassium. Br Med J 281:485
Wetli ChV, Davis JH (1978) Fatal hyperkalaemia from accidental overdose of potassium chloride. JAMA 240:1339
Kallen RJ, Rieger ChHL, Cohen HS, Sutter MA, Ong RT (1976) Near-fatal hyperkalaemia due to ingestion of salt substitute by an infant. JAMA 235:2125
Hoyt RE (1986) Hyperkalaemia due to salt substitutes JAMA 256:1726
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schim van der Loeff, H.J., Strack van Schijndel, R.J.M. & Thijs, L.G. Cardiac arrest due to oral potassium intake. Intensive Care Med 15, 58–59 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00255641
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00255641