Abstract
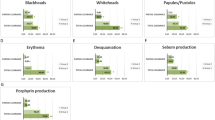
In a double-blind randomised study, 14 volunteers applied 4% erythromycin plus 1.2% zinc (Zineryt lotion) and 4% erythromycin lotions, each on half of the forehead twice daily for 3 months. The sebum output was evaluated at 3-week intervals using the photometric and the lipid-sensitive film methods. Evaluations of casual level (CL) and sebum excretion rate (SER) were made with a Sebumeter, and total area of lipid spots (TAS) was measured on Sebutapes. Compared to baseline values, the formulation of the erythromycin-zinc complex induced significant reductions in SER after 6 and 9 weeks, and in CL and TAS at 3, 6, 9 and 12 weeks. The mean reduction in TAS was over 20% for four successive 1-h samplings on completion of the study. Significant reductions in CL, SER and TAS were observed for the erythromycin-zinc formulation compared to the control lotion at 6 and 9 weeks, and also at 3 weeks for SER and TAS, and at 12 weeks for CL and TAS. This study indicates that sebum output is significantly reduced by the erythromycin-zinc complex. This reduction is theoretically beneficial for the acneic patient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cunliffe WJ, Shuster S (1969) The rate of sebum excretion in man. Br J Dermatol 81: 697–704
Layton AM, Hughes BR, MacDonald Hull S, Eady EA, Cunliffe WJ (1992) Seborrhoea — an indicator for poor clinical response in acne patients treated with antibiotics. Clin Exp Dermatol 17: 173–175
Schachner L, Eaglstein W, Kittles C, Mertz P (1990) Topical erythromycin and zinc therapy for acne. J Am Acad Dermatol 22: 253–260
Habbema L, Koopmans B, Menke HE, Doornweerd S, de Boulle K (1989) A 4% erythromycin and zinc combination (Zineryt) versus 2% erythromycin (Eryderm) in acne vulgaris: a randomized, double-blind comparative study. Br J Dermatol 121: 497–502
Sugarman B (1983) Zinc and infection. Rev Infect Dis 5: 137–147
Valee BL, Galdes A (1984) The metallobiochemistry of zinc enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat. Areas Mol Biol 46: 283–430
Norris D (1985) Zinc and cutaneous inflammation. Arch Dermatol 121: 985–989
Dreno B. Amblard P, Agache P, Sirot S, Litoux P (1989) Low doses of zinc gluconate for inflammatory acne. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh) 69: 541–543
Morgan AJ, Lewis G, Van den Hoven WE, Akkerboom PJ (1993) The effect of zinc in the form of erythromycin-zinc complex (Zineryt® lotion) and zinc acetate on metallothionein expression and distribution in hamster skin. Br J Dermatol 129: 563–570
Leake A, Chisholm GD, Habib FK (1984) The effect of zinc on the 5-alpha-reduction of testosterone by the hyperplastic human prostate gland. J Steroid Biochem 20: 651–655
Stamatiadis D, Bulteau-Portois MC, Mowszowics I (1988) Inhibition of 5-alpha-reductase activity in human skin by zinc and azelaic acid. Br J Dermatol 119:627–632
Dijkstra AC, Goos CM, Cunliffe WJ, Sultan C, Vermorken AJM (1987) Is increased 5-alpha-reductase activity a primary phenomenon in androgen-dependent skin disorders? J Invest Dermatol 89: 209–211
Piérard GE, Piérard-Franchimont C (1993) Effect of topical erythromycin-zinc formulation on sebum delivery. Evaluation by combined photometric multistep samplings with Sebutape®. Clin Exp Dermatol 18: 410–413
Saint-Léger D, Lévêque JL (1980) Les méthodes d'évaluation quantitative des lipides de surface chez l'homme. Présentation d'une nouvelle procédure. Int J Cosmet Sci 2: 283–294
Kligman AM, Miller D, McGinley KJ (1986) Sebutape: a device for visualizing and measuring human sebaceous excretion. J Soc Cosmet Chem 37: 369–374
Nordström RM, Schmus HG, McGinley KJ, Leyden JJ (1986) Measurement of sebum output using a lipid absorbent tape. J Invest Dermatol 87: 260–263
Piérard GE (1986) Follicle to follicle heterogeneity of sebum excretion. Dermatologica 173: 61–65
Piérard GE, Kligman A (1989) An update about the sebutape technique. In: Marks RM, Plewig G (eds) Acne and related disorders. Martin Dunitz, London, pp 111–112
Exner JH, Comite H, Dahod S (1983) Topical erythromycin/zinc effect on acne and sebum secretion. Curr Therap Res 134: 762–767
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piérard-Franchimont, C., Goffin, V., Piérard, G.E. et al. A double-blind controlled evaluation of the sebosuppressive activity of topical erythromycin-zinc complex. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 49, 57–60 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192359
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192359