Abstract
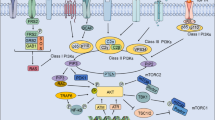
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway, including major downstream effectors Akt and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), plays a critical role in malignant transformation and subsequent processes of growth, proliferation, and metastases. Not surprisingly, the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway has emerged as an attractive drug target and numerous agents directed against various elements of the pathway are currently in clinical development. While early clinical trials with the first generations of these agents have shown limited single-agent efficacy, efforts are now focused on the development of more specific inhibitors, patient selection strategies, and combinational approaches. In this review, we discuss the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in cancer, the rationale for its emergence as a therapeutic target, and progress thus far in the clinical development of inhibitors targeting its various elements.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engelman JA, Luo J, Canley LC. The evolution of phosphosatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:606–19.
Qui Y, Kung HJ. Signaling network of Btk family kinases. Oncogene. 2000;19:5651–61.
Tessier M, Woodgett JR. Serum and glucocorticoid-regulated protein kinases: variations on a theme. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98(6):1391–407.
Nicholson KM, Anderson NG. The protein kinase B/Akt signaling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal. 2002;14:381–95.
Laplante M, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell. 2012;149:274–93.
Engelman JA, Janne PA, Mermel C, Pearlberg J, Mukohara T, Fleet C, Cichowski K, Johnson BE, Cantley LC. ErbB3 mediates phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity in gefitinib-sensitive non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:3788–93.
Yakes FM, Chinratanalab W, Ritter CA, King W, Seelig S, Arteaga CL. Herceptin-induced inhibition of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and Akt is required for antibody mediated effects on p27, cyclin D1, and antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 2002;62:4132–41.
Hollander MC, Blumenthal GM, Dennis PA. PTEN loss in the continuum of common cancers, rare syndromes and mouse models. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:289–301.
Carracedo A, Alimonti A, Pandolfi PP. PTEN level in tumor suppression: how much is too little? Cancer Res. 2011;71(3):629–33.
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, Yan H, Gazdar A, Powell SM, Riggins GJ, Willson JK, Markowitz S, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancer. Science. 2004;304:554.
Vasudevan KM, Barbie DA, Davies MA, Rabinovsky R, McNear CJ, Kim JJ, Hennessy BT, Tseng H, Pochanard P, Kim SY, Dunn IF, Schinzel AC, Sandy P, Hoersch S, Sheng Q, Gupta PB, Boehm JS, Reiling JH, Silver S, Lu Y, Stemke-Hale K, Dutta B, Joy C, Sahin AA, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Lluch A, Rameh LE, Jacks T, Root DE, Lander ES, Mills GB, Hahn WC, Sellers WR, Garraway LA. AKT-independent signaling downstream of oncogenic PIK3CA mutations in human cancer. Cancer Cell. 2009;16:21–32.
Philp AJ, Campbell IG, Leet C, Vincan E, Rockman SP, Whitehead RH, Thomas RJ, Phillips WA. The phosphatidylinostiol 3’kinase p85alpha gene is an oncogene in human ovarian and colon tumors. Cancer Res. 2001;61:7426–9.
Shaw RJ, Cantley LC. Ras, PI(3)K and mTOR signaling controls tumor cell growth. Nature. 2006;441:424–30.
Katso R, Okkenhaug K, Ahmadi K, White S, Timms J, Waterfield MD. Cellular function of phosphoinositide 3-kinases: implications for development, homeostasis, and cancer. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2001;17:615–75.
Ihle NT, Lemos R Jr, Wipf P, Yacoub A, Mitchell C, Siwak D, Mills GB, Dent P, Kirkpatrick DL, Powis G. Mutations in the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway predict for antitumor activity of the inhibitor PX-866 whereas oncogenic Ras is a dominant predictor for resistance. Cancer Res. 2009;69:143–50.
Carpten JD, Faber AL, Horn C, Donoho GP, Briggs SL, Robbins CM, Hostetter G, Boguslawski S, Moses TY, Savage S, Uhlik M, Lin A, Du J, Qian YW, Zeckner DJ, Tucker-Kellogg G, Touchman J, Patel K, Mousses S, Bittner M, Schevitz R, Lai MH, Blanchard KL, Thomas JE. A transforming mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1 in cancer. Nature. 2007;448:439–44.
Parsons DW, Wang TL, Samuels Y, Bardelli A, Cummins JM, DeLong L, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, Willson JK, Markowitz S, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Lengauer C, Velculescu VE. Colorectal cancer: mutations in a signaling pathway. Nature. 2005;436:792.
Davies MA, Stemke-Hale K, Tellez C, Calderone TL, Deng W, Prieto VG, Lazar AJ, Gershenwald JE, Mills GB. A novel AKT3 mutation in melanoma tumours and cell lines. Br J Cancer. 2008;99:1265–8.
Bleeker FE, Felicioni L, Buttitta F, Lamba S, Cardone L, Rodolfo M, Scarpa A, Leenstra S, Frattini M, Barbareschi M, Grammastro MD, Sciarrotta MG, Zanon C, Marchetti A, Bardelli A. AKT1 E17K in human solid tumors. Oncogene. 2008;27:5648–50.
Bellacosa A, de Feo D, Godwin AK, Bell DW, Cheng JQ, Altomare DA, Wan M, Dubeau L, Scambia G, Masciullo V, Ferrandina G, Benedetti Panici P, Mancuso S, Neri G, Testa JR. Molecular alterations of the AKT2 oncogene in ovarian and breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1995;64:280–5.
Ruggeri BA, Huang L, Wood M, Cheng JQ, Testa JR. Amplification and overexpression of the AKT2 oncogene in a subset of human pancreatic carcinomas. J Cell Biochem. 2002;87:470–6.
Zhao L, Vogt PK. Helical domain and kinase domain mutations in p110alpha of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase induce gain of function by different mechanisms. Proc Natl Sci USA. 2008;105:2652–7.
Liu J, Weiss HL, Rychahou P, Jackson LN, Evers BM, Gao T. Loss of PHLPP expression in colon cancer: role in proliferation and tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2009;28(7):994–1004.
Ouillette P, Erba H, Kujawski L, Kaminski M, Shedden K, Malek SN. Integrated genomic profiling of chronic lymphocytic leukemia identifies subtypes of deletion 13q14. Cancer Res. 2008;68:1012–21.
Sanchez-Cespedes M, Parrella P, Esteller M, Nomoto S, Trink B, Engles JM, Westra WH, Herman JG, Sidransky D. Inactivation of LKB1/STK11 is a common event in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Cancer Res. 2002;62:3659–62.
Matsumoto S, Iwakawa R, Takahashi K, Kohno T, Nakanishi Y, Matsuno Y, Suzuki K, Nakamoto M, Shimizu E, Minna JD, Yokota J. Prevalence and specificity of LKB1 genetic alterations in lung cancers. Oncogene. 2007;26:5911–8.
Shaw RJ, Bardeesy N, Manning BD, Lopez L, Kosmatka M, DePinho RA, Cantley LC. The LKB1 tumor suppressor negatively regulates mTOR signaling. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:91–9.
Knowles MA, Hornigold N, Pitt E. Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) gene involvement in sporadic tumors. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:591–602.
Iyer G, Hanrahan AJ, Milowsky MI, Al-Ahmadie H, Scott SN, Janakiraman M, Pirun M, Sander C, Socci ND, Ostrovnaya I, Viale A, Heguy A, Peng L, Chan TA, Bochner B, Bajorin DF, Berger MF, Taylor BS, Solit DB. Genome sequencing identifies a basis for everolimus sensitivity. Science. 2012;338:221.
Mao JH, Kim IJ, Wu D, Climent J, Kang HC, DelRosario R, Balmain A. FBXW7 targets mTOR for degradation and cooperates with PTEN in tumor suppression. Science. 2008;321:1499–502.
Ohne Y, Takahara T, Hatakeyama R, Matsuzaki T, Noda M, Mizushima N, Maeda T. Isolation of hyperactive mutants of mammalian target of rapamycin. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:31861–70.
Sato T, Nakashima A, Guo L, Coffman K, Tamanoi F. Single amino-acid changes that confer constitutive activation of mTOR are discovered in human cancer. Oncogene. 2010;29:2746–52.
Bar-Peled L, Chantranupong L, Cherniack AD, Chen WW, Ottina KA, Grabiner BC, Spear ED, Carter SL, Meyerson M, Sabatini DM. A Tumor suppressor complex with GAP activity for the Rag GTPases that signal amino acid sufficiency to mTORC1. Science. 2013;340(6136):1100–6.
Gupta S, Ramjaun AR, Haiko P, Wang Y, Warne PH, Nicke B, Nye E, Stamp G, Alitalo K, Downward J. Binding of ras to phosphoinositide 3-kinase p110alpha is required for ras-driven tumorigenesis in mice. Cell. 2007;129:957–68.
Yuan TL, Cantley LC. PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: variations on a theme. Oncogene. 2008;27:5497–510.
Wan X, Harkavy B, Shen N, Grohar P, Helman LJ. Rapamycin induces feedback activation of Akt signaling through an IGF-1R-dependent mechanism. Oncogene. 2007;26:1932–40.
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM. Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 2005;307:1098–101.
Brana I, Siu LL. Clinical development of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors for cancer treatment. BMC Med. 2012;10:161.
Sabatini DM. mTOR and cancer; insights into a complex relationship. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:729–34.
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Sengupta S, Sheen JH, Hsu PP, Bagley AF, Markhard AL, Sabatini DM. Prolonged rapamycin treatment inhibits mTORC2 assembly and Akt/PKB. Mol Cell. 2006;22:159–68.
Toschi A, Lee E, Xu L, Garcia A, Gadir N, Foster DA. Regulation of mTORC1 and mTORC2 complex assembly by phosphatidic acid: competition with rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29(6):1411–20.
Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, Dutcher J, Figlin R, Kapoor A, Staroslawska E, Sosman J, McDermott D, Bodrogi I, Kovacevic Z, Lesovoy V, Schmidt-Wolf IG, Barbarash O, Gokmen E, O’Toole T, Lustgarten S, Moore L, Motzer RJ. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Eng J Med. 2007;356:2271–5.
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, Grünwald V, Thompson JA, Figlin RA, Hollaender N, Urbanowitz G, Berg WJ, Kay A, Lebwohl D, Ravaud A. Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet. 2008;372:449–56.
Yao JC, Shah MH, Ito T, Bohas CL, Wolin EM, Van Cutsem E, Hobday TJ, Okusaka T, Capdevila J, de Vries EG, Tomassetti P, Pavel ME, Hoosen S, Haas T, Lincy J, Lebwohl D, Öberg K. Everolimus for advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:514–23.
Baselga J, Campone M, Piccart M, Burris HA 3rd, Rugo HS, Sahmoud T, Noguchi S, Gnant M, Pritchard KI, Lebrun F, Beck JT, Ito Y, Yardley D, Deleu I, Perez A, Bachelot T, Vittori L, Xu Z, Mukhopadhyay P, Lebwohl D, Hortobagyi GN. Everolimus in post-menopausal hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:520–9.
Hess G, Herbrecht R, Romaguera J, Verhoef G, Crump M, Gisselbrecht C, Laurell A, Offner F, Strahs A, Berkenblit A, Hanushevsky O, Clancy J, Hewes B, Moore L, Coiffier B. Phase III study to evaluate temsirolimus compared with investigator’s choice therapy for the treatment of relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3822–9.
O’Reilly KE, Rojo F, She QB, Solit D, Mills GB, Smith D, Lane H, Hofmann F, Hicklin DJ, Ludwig DL, Baselga J, Rosen N. mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates Akt. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1500–8.
Carracedo A, Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Rojo F, Salmena L, Alimonti A, Egia A, Sasaki AT, Thomas G, Kozma SC, Papa A, Nardella C, Cantley LC, Baselga J, Pandolfi PP. Inhibition of mTORC1 leads to MAPK pathway activation through a PI3K-dependent feedback loop in human cancer. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:3065–74.
Bendell JC, Rodon J, Burris HA, de Jonge M, Verweij J, Birle D, Demanse D, De Buck SS, Ru QC, Peters M, Goldbrunner M, Baselga J. Phase I, dose-escalation study of BKM120, an oral pan-Class I PI3K inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:282–90.
Moreno Garcia V, Baird RD, Shah KJ, Basu B, Tunariu N, Blanco M, Cassier PA, Pedersen JV, Puglisi M, Sarker D, Papadatos-Pastos D, Omlin AG, Biondo A, Ware JA, Koeppen H, Levy GG, Mazina KE, De Bono JS. A phase I study evaluating GDC-0941, an oral phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors or multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:a3021.
Shapiro GI, Rodon J, Bedell C, Kwak EL, Baselga J, Braña I, Pandya SS, Scheffold C, Laird AD, Nguyen LT, Xu Y, Egile C, Edelman G. Phase I safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of SAR245408 (XL147), an Oral Pan-Class I PI3K inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:233–45.
Naing A, Aghanjanian C, Raymond E, Kurzrock R, Blanco M, Oelmann E, Grinsted L, Burke W, Kaye S, Banerji U. First results from a phase I trial of AZD8055, a dual mTORC1 and mTORC2 inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10:A168.
Taberno J, Cervantes A, Gordon MS, Chiorean EG, Burris HA, Macarulla T, Perez-Fidalgo A, Martin M, Jessen K, Liu Y, Le T, Rommel C, Berk G, Bui L, Infante JR. A phase I, open label, dose escalation study of oral mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor INK128 administered by intermittent dosing regimens in patients with advanced malignancies. Cancer Res. 2012;72:CT-02.
Wagner A, Bendell JC, Dolly S, Morgan JA, Ware JA, Fredrickson J, Mazina KE, Lauchle JO, Burris HA, De Bono JS. A first-in-human phase I study to evaluate GDC-0980, an oral PI3 K/mTOR inhibitor, administered QD in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:a3020.
Burris H, Rodon J, Sharma S, Herbst RS, Tabernero J, Infante JR, Silva A, Demanse D, Hackl W, Baselga J. First-in-human phase I study of the oral PI3 K inhibitor BEZ235 in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:a3005.
Flaherty KT, Puzanov I, Kim KB, Ribas A, McArthur GA, Sosman JA, O’Dwyer PJ, Lee RJ, Grippo JF, Nolop K, Chapman PB. Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2012;363:809–19.
Torbett NE, Luna-Moran A, Knight ZA, Houk A, Moasser M, Weiss W, Shokat KM, Stokoe D. A chemical screen in diverse breast cancer cell lines reveals genetic enhancers and suppressors of sensitivity to PI3K isoform-selective inhibition. Biochem J. 2008;415:97–110.
Jia S, Liu Z, Zhang S, Liu P, Zhang L, Lee SH, Zhang J, Signoretti S, Loda M, Roberts TM, Zhao JJ. Essential roles of PI(3)K-p110beta in cell growth, metabolism and tumorigenesis. Nature. 2008;454:776–9.
Brown JR, Furman RR, Flinn I, Coutre SE, Wagner-Johnston ND, Kahl BS, Spurgeon SEF, Benson DM, Peterman S, Johnson DM, Li D, Dansey RD, Jahn TM, Byrd JC. Final results of a phase I study of idelalisib (GS-1101) a selective inhibitor of PI3 Kδ, in patients with relapsed or refractory CLL. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:a7003.
Taberno J, Saura D, Perez R, Dienstmann R, Rosello S, Prudkin L, Perez-Fidalgo JA, Graña B, Jones C, Musib L, Yan Y, Patel PH, Baselga J, Cervantes A. First-in-human phase I study evaluating the safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), and intratumor pharmacodynamics (PD) of the novel, oral, ATP-competitive Akt inhibitor GDC-0068. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:a3022.
Rodon J, Dienstmann R, Serra V, Tabernero J. Development of PI3K inhibitors: lessons learned from early clinical trials. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013;10:143–53.
Oliveira M, Navarro A, De Mattos-Arruda L, Sánchez-Ollé G, Bellet M, Balmaña J, Gómez-Pardo P, Perez-Garcia JM, Muñoz-Couselo E, Vidal M, Ortega V, Dienstmann R, Aura C, Prudkin L, Vivancos A, Ahnert JR, Baselga J, Tabernero J, Cortes J, Saura C. PI3K pathway (PI3Kp) dysregulation and response to pan-PI3K/AKT/mTOR/dual PI3K-mTOR inhibitors (PI3Kpi) in metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients (pts). J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:a509.
Acknowledgments and Disclosures
No funding sources supported this work. The authors have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, D.C. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway in Malignancy: Rationale and Clinical Outlook. BioDrugs 28, 373–381 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40259-014-0090-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40259-014-0090-5