Abstract
Introduction
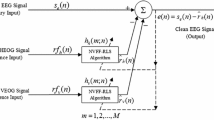
An improved method for adaptive noise canceller (ANC) is proposed for electroencephalography (EEG)/event related potential (ERP) filtering in case of EEG self interference. ANC is implemented through five versions of Particles Swarm Optimization (PSO) technique.
Methods
A comparative study of the performance of PSO and its different versions such as constant weighted inertia PSO (CWI PSO), linear decay inertia PSO (LDI-PSO), constriction factors inertia PSO (CFI-PSO), nonlinear inertia PSO (NLI-PSO), and dynamic inertia PSO (DI-PSO) has been done. Fidelity parameters like signal to noise ratio (SNR) in dB, correlation between resultant and template ERP, and mean square error (MSE) are observed with varying range of particles and inertia weights.
Results
In this the results of two data sets, simulated ERP and real visual evoked potential (VEP) are compared. Fidelity parameters as well as quality (shape) of extracted ERP are determined with Kurtosis and skewness measures.
Conclusions
From the simulation results and comparative studies, it is found that that NLI and LDI version of PSO are most suitable for ANC for ERP filtering.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanei S, Chambers JA. EEG signal processing, John Wiley & Sons Ltd. 2007.
Zhang JH, Janschek K, Bohme JF, Zeng YJ. Multi-resolution dyadic wavelet denoising approach for extraction of visual evoked potentials in the brain. IEE P-Vis Image Sign. 2004; 151(3):180–186.
Aydin S. Comparison of Basic linear filters in extracting auditory evoked potentials. Turk J Elect Eng. 2008; 16(2):111–123.
Odom JV, Bach M, Barber C, Brigell M, Marmor MF, Tormene AP, Holder GE. Visual evoked potentials standard. Doc Ophthalmol. 2004; 108:115–123.
Sano A, Bakardjian H. Movement-related cortical evoked potentials using four-limb imagery. Int J Neurosci. 2009; 119(5):639–663.
Rao R, Scherer R. Brain-computer interfacing [in the spotlight]. IEEE Signal Proc Mag. 2010; 27(4):147–150.
Machado S, Araújo F, Paes F, Velasques B, Cunha M, Budde H, Basile LF, Anghinah R, Arias-Carrión O, Cagy M, Piedade R, Graaf TA, Sack AT, Ribeiro P. EEG-based brain-computer interfaces: an overview of basic concepts and clinical applications in neurorehabilitation. Rev Neurosci. 2010; 21(6):451–468.
Croft RJ, Barry RJ. Removal of ocular artifacts: a review. Clin Neurophysiol Elsevier. 2000; 30(1):5–19.
Rajapakse JC, Cichocki A, Sanchez VD. Independent component analysis and beyond in brain imaging: EEG, MEG, fMRI, and PET. Neural Inform Process. 2002; 1:404–412.
Pfurtscheller G, Silva FHL. Event-related EEG/MEG synchronization and desynchronization: basic principles. Clin Neurophysiol. 1999; 110(11):1842–1857.
Yeung N, Bogacz R, Holroyd CB, Cohen JD. Detection of synchronized oscillations in the electroencephalogram: an evaluation of methods. Psychophysiol. 2004; 41:822–832.
James CJ, Hagan MT, Jones RD, Bones PJ, Carroll GJ. Multireference adaptive noise canceling applied to the EEG. IEEE T Bio-med Eng. 1997; 44(8):775–779.
Jung TP, Makeig S, Westerfield M, Townsend J, Courchesne E, Sejnowski TJ. Removal of eye activity artifacts from visual event-related potentials in normal and clinical subjects. Clin Neurophysiol. 2000; 111(10):1745–1758.
Makeig S, Bell AJ, Jung TP, Sejnowski TJ. Independent component analysis of electroencephalographic data. Adv Neural Inf Process Sys. 1996; 8:145–151.
Lee PL, Hsieh JC, Wu CH, Shyu KK, Chen SS, Yeh TC, Wu YT. The brain computer interface using flash visual evoked potential and independent component analysis. Ann Biomed Eng. 2006; 34(10):1641–1654.
Verobyov S, Cichocki A. Blind noise reduction for multisensory signals using ICA and subspace filtering with application to EEG analysis. Biol Cybern. 2002; 86(4):293–303.
Wang Z, Maier A, Leopold DA, Logothetis NK, Liang H. Single-trial evoked potential estimation using wavelets. Comput Biol Med. 2007; 37(4):463–473.
Quiroga RQ, Garcia H. Single-trial event-related potentials with wavelet denoising. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003; 114(2):376–390.
Zhang JH, Janschek K, Bohme JF, Zeng YJ. Multi-resolution dyadic wavelet denoising approach for extraction of visual evoked potentials in the brain. IEE P-Vis Image Sign. 2004; 151(3):180–186.
Widrow B, et al. Adaptive noise cancellation: principles and applications. Proc IEEE. 1975; 63:1692–1716.
He P, Wilson G, Russell C. Removal of ocular artifacts from electroencephalogram by adaptive filtering. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2004; 42(3):407–412.
Selvan S, Srinivasan R. Removal of ocular artefacts from EEG using an efficient neural network based adaptive filtering technique. IEEE Signal Proc Let. 1990; 6(12):330–332.
Svensson O. tracking of changes in latency and amplitude of the evoked potential by using adaptive LMS filters and exponential averages. IEEE T Bio-med Eng. 1993; 40(10):1074–1079.
Krusienski DJ, Jenkins WK. Design and performance of adaptive systems based on structured stochastic optimization strategies. Circuits Syst Mag IEEE. 2005; 5(1):8–20.
Krusienski DJ, Jenkins WK. Adaptive filtering via particle swarm optimization. Conf Signal Syst Comput. 2003; 1:571–575.
Mahbub U, Shahnaz C, Fattah SA. An adaptive noise cancellation scheme using particle swarm optimization algorithm. IEEE Int Conf Commun Cont Comput Tech (ICCCCT). 2010; 683–6.
Al-Awami AT, Zerguine A, Cheded L, Zidouri A, Saif W. A new modified particle swarm optimization algorithm for adaptive equalization. Digit Signal Process. 2011; 21(2):195–207.
Diniz PSR. Adaptive filtering: algorithms and practical implementation. Springer. 2008; 54–68.
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC. Particle swarm optimization. Proc IEEE Int Conf N.N. 1995; 4:1942–1948.
Poli R, Kennedy J, Blackwell T. Particle swarm optimization: an overview. Swarm Intell. 2007; 1:33–57.
Parsopoulos KE, Vrahatis MN. Particle swarm optimization and intelligence: advances and applications. Inform Sci Ref. 2010; 25–40.
Shi Y, Eberhart R. A modified particle swarm optimizer. IEEE Comput Intell. 1998; 69–73.
Chatterjee A, Siarry P. Nonlinear inertia weight variation for dynamic adaptation in particle swarm optimization. Comput Oper Res. 2006; 33:859–871.
Eberhart RC, Shi Y. Tracking and optimizing dynamic systems with particle swarms. Proc Evol Comput. 2001; 1:94–100.
Fang H, Chen L, Wang W. Comparison of PSO algorithm and its variants to optimal parameters of PID controller. Contr Decis Conf. 2008; 3100–3104.
Parsa V, Parker PA, Scott RN. Adaptive stimulus artifact reduction in noncortical somatosensory evoked potential studies. IEEE T Bio-med Eng. 1998; 45(2):165–179.
Generation of simulated EEG data [http://www.cs.bris.ac.uk/~rafal/phasereset/]
http://www.vis.caltech.edu/~rodri/data.htm [Rodrigo Quian Quiroga — EEG, ERP and single cell recordings database]
Wu X, Ye Z. The study of classification of motor imaginaries based on kurtosis of EEG. Lecture Notes Comput Sci. 2006; 3:74–81.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahirwal, M.K., Kumar, A. & Singh, G.K. Analysis and testing of PSO variants through application in EEG/ERP adaptive filtering approach. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2, 186–197 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-012-0071-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-012-0071-x