Abstract
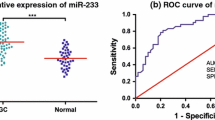
MicroRNA-421 (miR-421) plays crucial roles during carcinogenesis and is a potential tumor marker in the diagnosis of several types of cancers. However, whether miR-421 in gastric juice, which is specific for gastric tissue, can be used as a biomarker for gastric cancer screening is unclear. In the present study, real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was used to analyze miR-421 levels in gastric juice from patients with gastric cancer or benign gastric disease, or normal. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was constructed to evaluate the diagnostic values. The results showed that gastric juice levels of miR-421 in patients with gastric cancer were significantly different from those in benign gastric diseases (P < 0.001). The area under the ROC curve of miR-421 was up to 0.767 (95 % CI = 0.684–0.850). The levels of miR-421 in gastric juice from gastric patients were not significantly associated with the main clinicopathological factors such as tumor size, Lauren’s classification, and Borrmann’s classification. For the detection of early gastric cancer, the use of gastric juice miR-421showed a remarkable improvement compared with the use of serum carcinoembryonic antigen alone. These results indicated that gastric juice miRNAs such as miR-421 are useful biomarkers for screening gastric cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nardone G, Compare D. Epigenetic alterations due to diet and Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric carcinogenesis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;2:243–8.
Sapari NS, Loh M, Vaithilingam A, Soong R. Clinical potential of DNA methylation in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2012;7:e36275.
Halon A, Donizy P, Biecek P, Rudno-Rudzinska J, Kielan W, Matkowski R. HER-2 expression in immunohistochemistry has no prognostic significance in gastric cancer patients. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:941259.
Nair VS, Maeda LS, Ioannidis JP. Clinical outcome prediction by microRNAs in human cancer: a systematic review. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104:528–40.
Tsujiura M, et al. Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients with gastric cancers. Br J Cancer. 2010;102:1174–9.
Zhou H, et al. Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood from patients with gastric cancer using microRNA as a marker. J Mol Med. 2010;88:709–17.
Jiang Z, et al. Increased expression of miR-421 in human gastric carcinoma and its clinical association. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:17–23.
Etheridge A, Lee I, Hood L, Galas D, Wang K. Extracellular microRNA: a new source of biomarkers. Mutat Res. 2011;717:85–90.
Tzimagiorgis G, Michailidou EZ, Kritis A, Markopoulos AK, Kouidou S. Recovering circulating extracellular or cell-free RNA from bodily fluids. Cancer Epidemiol. 2011;35:580–9.
Weber JA, et al. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin Chem. 2010;56:1733–41.
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma—2nd English edition. Gastric Cancer. 1998;1:10–24.
Li C, et al. Macroscopic Borrmann type as a simple prognostic indicator in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Oncology. 2009;77:197–204.
Lauren P. The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: diffuse and so-called intestinal-type carcinoma. An attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:31–49.
Cui L, et al. Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood from patients with gastric cancer using piRNAs as markers. Clin Biochem. 2011;44:1050–7.
McDonald JS, Milosevic D, Reddi HV, Grebe SK, Algeciras-Schimnich A. Analysis of circulating microRNA: preanalytical and analytical challenges. Clin Chem. 2011;57:833–40.
Wu CW, et al. Detection of miR-92a and miR-21 in stool samples as potential screening biomarkers for colorectal cancer and polyps. Gut. 2012;61:739–45.
Hsu PI, et al. Diagnosis of gastric malignancy using gastric juice alpha1-antitrypsin. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19:405–11.
Zhou LY, et al. The intrinsic fluorescence spectrum of dilute gastric juice as a novel diagnostic tool for gastric cancer. J Dig Dis. 2011;12:279–85.
Xiao B, et al. Detection of miR-106a in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance. Clin Chim Acta. 2009;400:97–102.
Zhou H, et al. MiR-421 is a functional marker of circulating tumor cells in gastric cancer patients. Biomarkers. 2012;17:104–10.
Xie Y, et al. Altered miRNA expression in sputum for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2010;67:170–6.
O’Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT. c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature. 2005;435:839–43.
Cortez MA, Bueso-Ramos C, Ferdin J, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK, Calin GA. MicroRNAs in body fluids—the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8:467–77.
Hao J, Zhang S, Zhou Y, Liu C, Hu X, Shao C. MicroRNA 421 suppresses DPC4/Smad4 in pancreatic cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;406:552–7.
Guo J, et al. Differential expression of microRNA species in human gastric cancer versus non-tumorous tissues. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:652–7.
Zhang Y, et al. Downregulation of human farnesoid X receptor by miR-421 promotes proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2012;10:516–22.
Zhong XY, et al. MicroRNA-421 functions as an oncogenic miRNA in biliary tract cancer through down-regulating farnesoid X receptor expression. Gene. 2012;493:44–51.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ningbo Medical Research Project (no. 2010B06), the Zhejiang Provincial Research Project (nos. 2010C33112 and 2012C23127), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81171660), the Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo (no. 2010A610044 and 2012A610207), the Scientific Innovation Team Project of Ningbo (no. 2011B82014), the Project of Key Disciplines in Ningbo (no. XKL11D2128), the Excellent Dissertation Fund of Ningbo University (no. PY20110020), and the K. C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Cui, L., Ye, G. et al. Gastric juice microRNA-421 is a new biomarker for screening gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 33, 2349–2355 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0497-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0497-x