Abstract
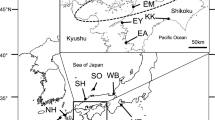
The spotted sea bass, Lateolabrax maculatus, is popular in recreational fishing and aquaculture in Korea. Its natural population has declined during the past two decades; thus, beginning in the early 2000s stock-enhancement programs were introduced throughout western and southern coastal areas. In this study, genetic similarities and differences between wild and hatchery populations were assessed using multiplex assays with 12 highly polymorphic microsatellite loci; 96 alleles were identified. Although many unique alleles were lost in the hatchery samples, no significant reductions were found in heterozygosity or allelic diversity in the hatchery compared to the wild population. High genetic diversity (He = 0.724–0.761 and Ho = 0.723–0.743), low inbreeding coefficient (F IS = 0.003–0.024) and Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium were observed in both wild and hatchery populations. However, the genetic heterogeneity between the populations was significant. Therefore, genetic drift likely promoted inter-population differentiation, and rapid loss of genetic diversity remains possible. Regarding conservation, genetic variation should be monitored and inbreeding controlled in a commercial breeding program.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allendorf FW (1986) Genetic drift and the loss of alleles versus heterozygosity. Zoo Biol 5:181–190
Allendorf FW, Pyman N (1987) Genetic management of hatchery stocks. In: Ryman N, Utter F (eds) Population genetics and fishery management. Washington Sea Grant, Seattle, pp 141–159
An HS, Byun SG, Kim YC, Lee JW, Myeong JI (2011a) Wild and hatchery populations of Korean starry flounder (Platichthys stellatus) compared using microsatellite DNA marker. Int J Mol Sci 12:9189–9202
An HS, Kim EM, Lee JH, Noh JK, An CM, Yoon SJ, Park KD, Myeong JI (2011b) Population genetic structure of wild and hatchery black rockfish Sebastes inermis in Korea, assessed using cross-species microsatellite markers. Genet Mol Res 10:2492–2504
An HS, Lee JW, Dong CM (2012) Population genetic structure of Korean pen shell (Atrina pectinata) in Korea inferred from microsatellite marker analysis. Genes Genom 34:681–688
An HS, Lee JW, Park JY, Jung HT (2013) Genetic structure of the Korean black scraper Thamnaconus modestus inferred from microsatellite marker analysis. Mol Biol Rep 40:3445–3456
Beaumont MA, Nichols RA (1996) Evaluating loci for use in the genetic analysis of population structure. Proc R Soc Lond B 263:1619–1626
Bell JD, Bartley DM, Lorenzen K, Loneragan NR (2006) Restocking and stock enhancement of coastal fisheries: potential, problems and progress. Fish Res 80:1–8
DeWoody JA, Avise JC (2000) Microsatellite variation in marine, freshwater and anadromous fishes compared with other animals. J Fish Biol 56:461–473
Excoffier L, Smouse PE, Quattro JM (1992) Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131:479–491
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) ARLEQUIN version 3.0. An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinform 1:47–50
Goudet J, Raymond M, De Meiis T, Rousset F (1996) Testing differentiation in diploid populations. Genetics 144:933–940
Guichoux E, Lagache L, Wagner S, Chaumeil P, Leger P, Lepais O, Lepoittevin C, Malausa T, Revardel E, Salin F, Petit RJ (2011) Current trends in microsatellite genotyping. Mol Ecol Resour 11:591–611
Han HS, Nam BH, Kang JH, Kim YK, Jee YJ, Hur YB, Yoon M (2012) Genetic variation in wild and cultured populations of the sea squirt Halocynthia roretzi inferred from microsatellite DNA analysis. Fish Aquat Sci 15:151–155
Henrik Sønstebø J, Borgstrøm R, Heun M (2007) Genetic structure of brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) from the Hardangervidda mountain plateau (Norway) analyzed by microsatellite DNA, a basis for conservation guidelines. Conserv Genet 8:33–44
Hong SE, Kim JG, Yu JN, Kim KY, Lee CI, Hong KE, Park KY, Yoon M (2012) Genetic variation in the Asian shore crab Hemigrapsus sanguineus in Korean coastal waters as inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Fish Aquat Sci 15:49–56
Hutchings JA, Fraser DJ (2008) The nature of fisheries- and farming-induced evolution. Mol Ecol 17:294–313
Jiang X, Liao MJ, Liu YJ, Gao TX, Yang GP (2007) Isolation and characterization of 22 polymorphic microsatellite DNA markers of Japanese sea bass (Laterolabrax japonicas). Mol Ecol Note 7:492–494
Kalinowski ST, Taper ML, Marshall TC (2007) Revising how the computer program CERVUS accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Mol Ecol 16:1099–1106
Kim C, Jun J (1997) Provisional classification of temperate sea bass, the genus Lateolabrax (Pisces: Moronidae) from Korea. Korean J Ichthyol 9:108–113
Lee HJ, Hur SB (2012) Comparison between phylogenetic relationships based on 18S rDNA sequences and growth by salinity of Chlorella-like species (Chlorophyta). Fish Aquat Sci 5:125–135
Lefèvre S, Wagner S, Petit RJ, De Lafontaine G (2012) Multiplexed microsatellite markers for genetic studies of beech. Mol Ecol Resour 12:484–491
Liu JX, Gao TX, Yokogawa K, Zhang YP (2006) Differential structuring and demographic history of two closely related fish species, Japanese sea bass (Lateolabrax japomicus) and spotted sea bass (Lateolabrax maculates) in Northwestern Pacific. Mol Phylogenet Evol 39:799–811
Liu F, Xia JH, Bai ZY, Fu JJ, Li JL, Yue GH (2009) High genetic diversity and substantial population differentiation in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) revealed by microsatellite analysis. Aquaculture 297:51–56
Madeira MJ, Gomez-Moliner BJ, Machordom-Barbe A (2005) Genetic introgression on freshwater fish populations caused by restocking programmes. Biol Invasion 7:117–125
Marchant S, Haye PA, Marin SA, Winkler FM (2009) Genetic variability revealed with microsatellite markers in an introduced population of the abalone Haliotis discus hannai Ino. Aquac Res 40:298–304
Oh SY, Shin CH, Jo JY, Noh CH, Myoung JG, Kim JM (2006) Effects of water temperature and salinity on the oxygen consumption rate of Juvenile Spotted Sea Bass, Lateolabrax maculates. Korean J Ichthyol 18:202–208
Pan G, Yang J (2010) Analysis of microsatellite DNA markers reveals no genetic differentiation between wild and hatchery populations of Pacific threadfin in Hawaii. Int J Biol Sci 6:827–833
Rice WR (1989) Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution 43:223–225
Rousset F (1996) Equilibrium values of measures of population subdivision for stepwise mutation processes. Genetics 142:1357–1362
Rousset F (2008) Genepop’007: a complete re-implementation of the genepop software for Windows and Linux. Mol Ecol Resour 8:103–106
Sadovy Y, Cornish AS (2000) Reef fishes of Hong Kong. Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong, p 321
Shao C, Chen S, Xu G, Liao X, Tian Y (2009) Eighteen novel microsatellite markers for the Chinese sea perch, Lateolabrax maculates. Conserv Genet 10:623–625
Sint D, Raso L, Traugott M (2012) Advances in multiplex PCR: balancing primer efficiencies and improving detection success. Method Ecol Evol 3:898–905
Slatkin M, Excoffier L (1996) Testing for linkage disequilibrium in genotypic data using the EM algorithm. Heredity 76:377–383
Stottrup JG, Sparrevohn CR (2007) Can stock enhancement enhance stocks? J Sea Res 57:104–113
van Oosterhout C, Hutchinson WF, Wills DPM, Shipley P (2004) MICRO-CHECKER, Software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol Ecol Notes 4:135
Weir BS, Cockerham CC (1984) Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution 38:1358–1370
Wilcoxon F (1945) Individual comparisons by ranking methods. Biometrics Bull 1:80–83
Yokogawa K, Seki S (1995) Morphological and genetic differences between Japanese and Chinese sea bass of the genus Lateolabrax. Jpn J Ichthyol 41:437–455
Yoon M, Jung J-Y, Nam YK, Kim DS (2011) Genetic diversity of thread-sail filefish Stephanolepis cirrhifer populations in Korean coastal waters inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequence analysis. Fish Aquat Sci 14:16–21
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by a grant from the National Fisheries Research and Development Institute (NFRDI; contribution number RP-2013-BT-071). The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of NFRDI.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest on this article contents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, H.S., Lee, J.W., Kim, H.Y. et al. Genetic differences between wild and hatchery populations of Korean spotted sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus) inferred from microsatellite markers. Genes Genom 35, 671–680 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-013-0135-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-013-0135-z