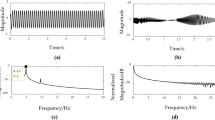
Abstract
Rotor electrical faults are common types of faults in squirrel cage induction motors (IMs) and have been investigated in detail under steady state conditions for direct mains-fed machines. Motor current signature analysis (MCSA) has been widely reported in the literature as a suitable fault diagnostic technique for directly-supplied IMs. However, when an induction motor is fed from a frequency converter composed of a rectifier, DC link filter and a PWM inverter, its characteristic signals (currents, voltages, electromagnetic torque, etc.) become very noisy. This paper presents an experimental analysis of a damaged squirrel cage induction motor supplied from an industrial frequency converter at different speed and load levels. The main purpose is to experimentally study the ability of the MCSA to diagnose the occurrence of broken rotor bars under these operating conditions.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akin B, Toliyat HA, Orguner U, Rayner M (2007) PWM inverter harmonics contributions to the inverter-Fed induction machine bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE, 22nd annual applied power electronics conference, Anaheim, CA, pp 1393–1399
Akin B, Orguner U, Toliyat HA, Rayner M (2008) Low order PWM inverter harmonics contributions to the inverter-fed induction machine fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(2):610–619
Bellini A, Fillippetti F, Franceschini G, Tassoni C, Kliman G (2001) Quantitative evaluation of induction motor broken bars by means of electrical signature analysis. Trans Ind Electron 37(5):1248–1255
Besnerais JL, Lanfranchi V, Hecquet M, Brochet P (2010) Characterization and reduction of audible magnetic noise due to PWM supply in induction machines. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(4):1288–1295
Bonett AH (1996) Analysis of the impact of pulse-width modulated inverter voltage waveforms on AC induction motors. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 32(2):386–392
Briz F, Degner MW, Guerrero JM, García P (2009) Stator windings fault diagnostics of induction machines operated from inverters and soft-starters using high-frequency negative-sequence currents. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 45(5):1637–1646
Cruz SMA, Cardoso AJM (1999) Rotor cage fault diagnosis in voltage source inverter fed induction motors, by the extended park’s vector approach. IEEE international symposium on diagnostics for electrical machines, power electronics and drives, Gijón, Spain, pp 105–110
Duque O, Pérez M, Morinigo D (2005) Detection of bearing faults in cage induction motors fed by frequency converter using spectral analysis of line current. IEEE International Conference on Electric Machines and Drives, San Antonio, pp 17–22
Jung JH, Lee JJ, Kwon BH (2006) Online diagnosis of induction motors using MCSA. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 53(6):1842–1852
Kliman GB, Stein J (1992) Methods of motor currents signature analysis. Electr Mach Power Syst 20(5):463–474
Lo WC, Chan CC, Zhu ZQ, Lie X, Howe D, Chau KT (2000) Acoustic noise radiated by PWM-controlled induction machine drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 47(4):880–889
Ruiz-González A, Meco-Gutiérrez MJ, Pérez-Hidalgo F, Vargas-Merino F, Heredia-Larrubia JR (2010) Reducing acoustic noise radiated by inverter-fed induction motors controlled by a new PWM strategy. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(1):228–236
Sotelo DM, Escudero LAG, Perez OD, Alonso MP (2010) Practical aspects of mixed-eccentricity detection in PWM voltage-source-inverter-fed induction motors. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(1):252–262
Technical guide (2008) Induction motors fed by PWM frequency inverters. http://www.weg.net/. Assessed 12 Jan 2012
Thomson WT, Fenger M (2001) Current signature analysis to detect induction motors faults. IEEE Ind Appl Mag 7(4):26–34
Uddin MN, Wang W, Huang ZR (2010) Modeling and minimization of speed ripple of a faulty induction motor with broken rotor bars. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 46(6):2243–2250
Villada F, Cadavid D, Munoz N, Valencia D, Parra D (2003) Fault diagnosis in induction motors fed by PWM inverters. IEEE international symposium on diagnostics for electric machines, power electronics and drives, Atlanta, CA, pp 24–26
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr. M. Sahraoui of the Electrical Engineering Laboratory of the University of Biskra for his role in the laboratory tests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yahia, K., Cardoso, A.J.M., Zouzou, S.E. et al. Broken rotor bars diagnosis in an induction motor fed from a frequency converter: experimental research. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 3, 40–46 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-012-0093-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-012-0093-x