Abstract
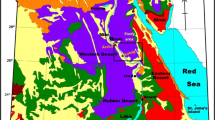
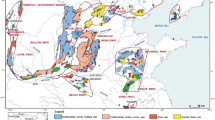
In Kunming area (6.8 mio population), two big interventions are in progress: construction of a new airport, the 23 km2 area of which will extend across karst terrain northeast of the city, and extensive uptake of water from karst aquifers for drinking and agricultural use. In the study, an interdisciplinary approach was utilized to demonstrate the need for holistic karstology studies prior to performing extensive interferences in the karst environment. This study included survey of surface karst features and microscopic analyses of rock samples in the area of the new airport location, accompanied by hydrogeological studies and microbiological analyses of two karst drinking water sources in its vicinity (Qinglongdong, Huanglongdong). Results showed the specific characteristics of the subsoil stone forest that indicated a high level of karstification. The direction and characteristics of groundwater flow from the sinking Qiaotou Stream at the margin of the new airport area toward the Huanglongdong Spring were defined with a single tracer test. Additional information about hydrogeological characteristics of the karst aquifer was obtained by individual measurements of physical and chemical parameters of the springs and sinking stream. Selected chemical and bacteriological parameters showed substantial pollution of both springs due to various types of human activities in the catchments. The results of the study pointed to the necessity of taking immediate measures for the springs’ protection and showed the importance of interdisciplinary research when planning anthropogenic activities in the karst.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen X, Gabrovšek F, Huang C et al (1998) South China Karst 1. ZRC Publishing, Ljubljana
Guo F, Jiang G (2010) Problems of Flood and Drought in a Typical Peak Cluster Depression Karst Area (SW China). Environ Earth Sci, Advances in Research in Karst Media, Part 1:107–113
Guo F, Yuan DX, Qin ZJ (2010) Groundwater contamination in karst areas of Southwestern China and recommended countermeasures. Acta Carsol 39/2:389–399
Jiang Y, Yuan D, Zhang C, Zhang G, He R (2008) Impact of land use change on groundwater quality in a typical karst watershed of southwest China. Hydrogeol J 16(4):727–735
Jiang Y, Wue Y, Groves C, Yuan D, Kambesis P (2009) Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the groundwater quality in the Nandong karst underground river system in Yunan, China. J Contam Hydrol 109:49–61
Knez M, Kogovšek J, Kranjc A, Liu H, Petrič M, Slabe T (2009) The Shuilian cave in the upper region of the Chang River (Karst of NW Yunnan, China). Acta Carsol 38/1:97–106
Knez M, Liu H, Slabe T (2010a) High Mountain Karren in Northwestern Yunnan, China. Acta Carsol 39/1:103–114
Knez M, Liu H, Slabe T (eds) (2010b) South China Karst 2. ZRC Publishing, Ljubljana
Kogovšek J (2010) Characteristics of Underground Water Flow at Different Water Levels in Tianshengan Karst Area, Yunnan, China. Acta Geol Sin 84/1:206–212
Kogovšek J, Liu H (1999) Water tracing test in Tianshengan region, China at low water level in November 1998. Acta Carsol 28/2:241–253
Lu Y (2006) Karst water resources and geo-ecology in typical regions of China. Environ Geol 51/5:695–699
Mulec J, Krištůfek V, Chroňáková A (2012) Comparative microbial sampling from eutrophic caves in Slovenia and Slovakia using RIDA®COUNT test kits. Int J Speleol 41/1:1–8
Shaw E (1994) Hydrology in practice. Chapman & Hall, London
Shi Z, Liu X, Liu Y, Huang Y, Peng H (2009) Catastrophic groundwater pollution in a karst environment: a study of phosphorus sludge waste liquid pollution at the Penshuidong Cave in Yunnan, China. Environ Earth Sci 59:757–763
Slabe T (1998) Rock relief of pillars in the Lunan Stone Forest. In: Chen X et al (eds) South China Karst I. ZRC Publishing, Ljubljana, pp 51–67
Slabe T (2005) Two experimental modelings of karst rock relief in plaster: subcutaneous “rock teeth” and “rock peaks” exposed to rain. Z Geomorphol 49:107–119
Slabe T, Liu H (2009) Significant subsoil rock forms. In: Ginés A, Knez M, Slabe T, Dreybrodt W (eds) Karst Rock Features–Karren Sculpturing. ZRC Publishing, Postojna-Ljubljana, pp 123–137
Greenberg AE, Clesceri LS, Eaton AD (eds) (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 18th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Toranzos GA, McFeters GA (1997) Detection of indicator microorganisms in environmental freshwaters and drinking waters. In: Hurst CJ, Knudsen GR, McInerney MJ, Stetzenbach LD, Walter MV (eds) Manual of environmental microbiology. ASM Press, Washington, pp 184–194
Zhang S, Hu H, Zhou Z, Xu K, Yan N, Li S (2005) Photosynthetic performances of transplanted Cypripedium flavum. Bot Bull Acad Sin 46:307–313
Acknowledgments
The research was supported under bilateral Project No. BI-CN/07-09-015 by the Slovenian Research Agency and the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (code: 2004DFA02200) in the framework of Slovenia–China Cooperation in Science and Technology, 2007–2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knez, M., Kogovšek, J., Liu, H. et al. Karstological study of the new Kunming airport building area (Yunnan, China). Environ Earth Sci 67, 273–283 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1506-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1506-x