Abstract
Introduction
The role of infliximab in the treatment of acute severe ulcerative colitis is established. However, all the data available in the literature are from western countries. This is the first report on the use of infliximab in patients with severe steroid-refractory ulcerative colitis from India.
Methods
Retrospective analysis of 28 patients who had received infliximab therapy for induction of remission, with three doses of 5 mg/kg at 0, 2, and 6 weeks, was performed.
Results
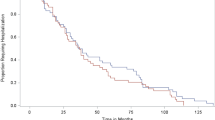
Twenty-four (85.6 %) patients had shown a clinical response by week 8 and, hence, avoided urgent colectomy. In 2 years of follow up, 9/16 (56 %) patients had not required colectomy.
Conclusion
Infliximab averted colectomy in a proportion of patients with severe steroid-refractory ulcerative colitis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Porro GB, Cassinotti A, Ferrara E, Maconi G, Ardizzone S. Review article: the management of steroid dependency in ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;26:779–94.
Kozuch PL, Hanauer SB. Treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: a review of medical therapy. World J Gasteroenterol. 2008;14:354–77.
Knight DM, Trin H, Le J, et al. Construction and initial characterization of a mouse–human chimeric anti-TNF antibody. Mol Immunol. 1993;30:1443–53.
Rutgeerts P, Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, et al. Infliximab for induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2462–76.
Reinisch W, Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, et al. Long-term infliximab maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis: the ACT1 and ACT2 extension studies. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012;18:201–11.
Lichtiger S, Present D, Kornbluth A, et al. Cyclosporine in severe ulcerative colitis refractory to steroid therapy. N Eng J Med. 1994;330:1841–5.
Willert RP, Lawrance IC. Use of infliximab in the prevention and delay of colectomy in severe steroid dependent and refractory ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:2544–9.
Aratari A, Papi C, Clemente V, et al. Colectomy rate in acute severe ulcerative colitis in the infliximab era. Dig Liver Dis. 2008;40:821–6.
Jarnerot G, Hertervig E, Friis-Liby I, et al. Infliximab as rescue therapy in severe to moderately severe ulcerative colitis: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:1805–11.
Probert CS, Hearing SD, Schreiber S, et al. Infliximab in moderately severe glucocorticoid resistant ulcerative colitis: a randomised controlled trial. Gut. 2003;52:998–1002.
Sands BE, Tremaine WJ, Sandborn WJ, et al. Infliximab in the treatment of severe, steroid-refractory ulcerative colitis: a pilot study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2001;7:83–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sood, A., Midha, V., Sharma, S. et al. Infliximab in patients with severe steroid-refractory ulcerative colitis: Indian experience. Indian J Gastroenterol 33, 31–34 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12664-013-0372-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12664-013-0372-8