Abstract
Background
Serum carnitine is decreased in recurrent pulmonary infections. We aimed to evaluate serum carnitine levels in asthmatic children.
Methods
Study group consisted of children with stable asthma and those with acute asthma attacks, while control group included healthy children. Attack severity was determined by the pulmonary score system. Total and free carnitine levels were studied in one blood sample from the control group and stable asthmatics and in two samples from children with acute asthma exacerbation during and after the attack.
Results
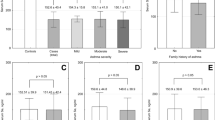
All the 40 patients in the study group had moderate asthma including 30 with acute attack (13 mild and 17 moderate) and 10 with stable asthma. Carnitine levels were significantly lower in acute attack asthmatics than in the stable asthmatics and controls, while there was no significant difference between the latter two groups. Carnitine levels were not different between asthmatics with mild and moderate attack, and were similar during and after an acute attack.
Conclusions
Serum carnitine levels decrease in children with moderate asthma during exacerbation of asthma and shortly thereafter. Further studies are needed to evaluate the effect of carnitine treatment on serum carnitine level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brass EP. Supplemental carnitine and exercise. Am J Clin Nutr 2000;72(2 Suppl):S618–623.
Borghi-Silva A, Baldissera V, Sampaio LM, Pires-DiLorenzo VA, Jamami M, Demonte A, et al. L-carnitine as an ergogenic aid for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease submitted to whole-body and respiratory muscle training programs. Braz J Med Biol Res 2006;39:465–474.
Ahmad S. L-carnitine in dialysis patients. Semin Dial 2001;14:209–217.
Kavukcu S, Turkmen M, Salman S, Onvural B, Oktay G, Karaman O, et al. The effects of L-carnitine on respiratory function tests in children undergoing chronic hemodialysis. Turk J Pediatr 1998;40:79–84.
From the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention, Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) 2007. http://www.ginasthma.org (accessed October 15, 2008)
Smith SR, Baty JD, Hodge D 3rd. Validation of the pulmonary score: an asthma severity score for the children. Acad Emerg Med 2002;9:99–104.
Andreeva AV, Kutuzov MA, Voyno-Yasenetskaya TA. Regulation of surfactant secretion in alveolar type II cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2007;293:L259–271.
Ozturk MA, Gunes T, Koklu E, Erciyes A. Free carnitine levels in respiratory distress syndrome during the first week of life. Am J Perinatol 2006;23:445–449.
Ackerman SJ, Kwatia MA, Doyle CB, Enhorning G. Hydrolysis of surfactant phospholipids catalyzed by phospholipase A2 and eosinophil lysophospholipases causes surfactant dysfunction: a mechanism for small airway closure in asthma. Chest 2003;123(3 Suppl):355S.
Torel Ergur A, Tanzer F, Cetinkaya O. Serum free carnitine levels in children with recurrent pulmonary infections. Acta Paediatr Jpn 1997;39:406–408.
Calvani M, Benatti P, Mancinelli A, D’Iddio S, Giordano V, Koverech A, et al. Carnitine replacement in endstage renal disease and hemodialysis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2004;1033:52–66.
Uzuner N, Kavukcu S, Yilmaz O, Ozkal S, Islekel H, Karaman O, et al. The role of L-carnitine in treatment of a murine model of asthma. Acta Med Okayama 2002;56:295–301.
Huang SL, Pan WH. Dietary fats and asthma in teenagers: analyses of the first Nutrion and Health Survey in Taiwan (NAHSIT). Clin Exp Allergy 2001;31:1875–1880.
Yeh YF, Huang SL. Dietary cholesterol enhances pulmonary eosinophilic inflammation in murine model of asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2001;125:329–334.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asilsoy, S., Bekem, Ö., Karaman, Ö. et al. Serum total and free carnitine levels in children with asthma. World J Pediatr 5, 60–62 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-009-0011-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-009-0011-8