Abstract
Introduction
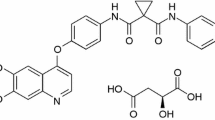
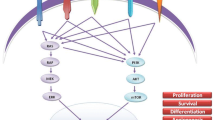
Patients with advanced medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) have poor prognoses and limited treatment options. Improved knowledge about molecular aberrations associated with MTC and the availability of novel targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have led to new potential treatment modalities. Cabozantinib is an oral multitargeted TKI with activity against multiple receptors including RET, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor type 2 (VEGFR2), and MET that has been evaluated in MTC in the preclinical and clinical arenas.
Methods
This article reviews unmet clinical needs in advanced MTC. The authors consider novel agents that have been studied in MTC, with a focus on the investigational agent cabozantinib. Up-to-date clinical data of cabozantinib in MTC are discussed.
Results
Recent clinical evaluation suggests that cabozantinib is the first agent to prolong progression-free survival in patients with progressive MTC. These findings indicate that cabozantinib may be an effective therapy in advanced MTC. No improvement in overall survival has been demonstrated but data are not mature.
Conclusion
Cabozantinib may be an effective treatment option for patients with advanced MTC and is worthy of further evaluation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schlumberger M, Carlomagno F, Baudin E, Bidart JM, Santoro M. New therapeutic approaches to treat medullary thyroid carcinoma. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2008;4:22–32.
Fugazzola L, Muzza M, Mian C, et al. RET genotypes in sporadic medullary thyroid cancer: studies in a large Italian series. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2008;69:418–425.
Mian C, Pennelli G, Barollo S, et al. Combined RET and Ki-67 assessment in sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma: a useful tool for patient risk stratification. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011;164:971–976.
Elisei R, Cosci B, Romei C, et al. Prognostic significance of somatic RET oncogene mutations in sporadic medullary thyroid cancer: A 10-year follow-up study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:682–687.
Moura MM, Cavaco BM, Pinto AE, Leite V. High prevalence of RAS mutations in RET-negative sporadic medullary thyroid carcinomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:E863–E868.
Kurzrock R, Sherman SI, Ball DW, et al. Activity of XL184 (cabozantinib), an oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with medullary thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2660–2666.
Roman S, Lin R, Sosa JA. Prognosis of medullary thyroid carcinoma: demographic, clinical, and pathologic predictors of survival in 1252 cases. Cancer. 2006;107:2134–2142.
Brierley J, Sherman E. The role of external beam radiation and targeted therapy in thyroid cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2012;22:254–262.
Brierley J, Tsang R, Simpson WJ, Gospodarowicz M, Sutcliffe S, Panzarella T. Medullary thyroid cancer: analyses of survival and prognostic factors and the role of radiation therapy in local control. Thyroid. 1996;6:305–310.
Fife KM, Bower M, Harmer CL. Medullary thyroid cancer: The role of radiotherapy in local control. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1996;22:588–591.
Martinez SR, Beal SH, Chen A, Chen SL, Schneider PD. Adjuvant external beam radiation for medullary thyroid carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2010;102:175–178.
Lessin LS. Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid; chemotherapy. In: Wartofsky L, Van Nostrand D, eds. Thyroid Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide to Clinical Management. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2006:609–611.
Mahler C, Verhelst J, de Longueville M, Harris A. Long-term treatment of metastatic medullary thyroid carcinoma with the somatostatin analogue octreotide. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1990;33:261–269.
Vitale G, Tagliaferri P, Caraglia M, et al. Slow release lanreotide in combination with interferon-alpha2b in the treatment of symptomatic advanced medullary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:983–988.
Frank-Raue K, Fabel M, Delorme S, Haberkorn U, Raue F. Efficacy of imatinib mesylate in advanced medullary thyroid carcinoma. Eur J Endocrinol. 2007;157:215–220.
de Groot JW, Zonnenberg BA, van Ufford-Mannesse PQ, et al. A phase II trial of imatinib therapy for metastatic medullary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:3466–3469.
Schlumberger MJ, Elisei R, Bastholt L, et al. Phase II study of safety and efficacy of motesanib in patients with progressive or symptomatic, advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3794–3801.
Lam ET, Ringel MD, Kloos RT, et al. Phase II clinical trial of sorafenib in metastatic medullary thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2323–2330.
De Souza JA, Busaidy N, Zimrin A, et al. Phase II trial of sunitinib in medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) [abstract]. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(Suppl.). Abstract 5504.
Cohen EE, Rosen LS, Vokes EE, et al. Axitinib is an active treatment for all histologic subtypes of advanced thyroid cancer: results from a phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4708–4713.
Wells SA, Gosnell JE, Gagel RF, et al. Vandetanib for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic hereditary medullary thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:767–772.
Wells SA, Robinson BG, Gagel RF, et al. Vandetanib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer: a randomized, doubleblind phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:134–141.
Robinson BG, Paz-Ares L, Krebs A, Vasselli J, Haddad R. Vandetanib (100 mg) in patients with locally advanced or metastatic hereditary medullary thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:2664–2671.
Schoffski P, Elisei R, Müller S, et al.; EXAM Study Group. An international, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase III trial (EXAM) of cabozantinib (XL184) in medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) patients (pts) with documented RECIST progression at baseline [abstract]. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:(Suppl.). Abstract 5508.
de Groot JW, Zonnenberg BA, Plukker JT, van Der Graaf WT, Links TP. Imatinib induces hypothyroidism in patients receiving levothyroxine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;78:433–438.
Wells SA, Gosnell JE, Gagel RF, et al. Vandetanib in metastatic hereditary medullary thyroid cancer: Follow-up results of an open-label phase II trial [abstract]. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:(Suppl.). Abstract 6018.
Vandetanib REMS Program. AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, 2001.
Yakes FM, Chen J, Tan J, et al. Cabozantinib (XL184), a novel MET and VEGFR2 inhibitor, simultaneously suppresses metastasis, angiogenesis, and tumor growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10:2298–2308.
Runeberg-Roos P, Saarma M. Neurotrophic factor receptor RET: structure, cell biology, and inherited diseases. Ann Med. 2007;39:572–580.
Capp C, Wajner SM, Siqueira DR, Brasil BA, Meurer L, Maia AL. Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2, in medullary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid. 2010;20:863–871.
Bunone G, Vigneri P, Mariani L, et al. Expression of angiogenesis stimulators and inhibitors in human thyroid tumors and correlation with clinical pathological features. Am J Pathol. 1999;155:1967–1976.
de la Torre NG, Buley I, Wass JA, Turner HE. Angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in thyroid proliferative lesions: relationship to type and tumour behaviour. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006;13:931–944.
Joao Bugalho M, Madureira D, Espadinha C, Paula Font A, Sobrinho LG. Serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels in patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008;159:167–169.
Feng Y, Thiagarajan PS, Ma PC. MET signaling: novel targeted inhibition and its clinical development in lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2012;7:459–467.
Papotti M, Olivero M, Volante M, et al. Expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its receptor (MET) in medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. Endocr Pathol. 2000;11:19–30.
Joly AH. Simultaneous blockade of VEGF and HGF receptors results in potent anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor effects. Eur J Cancer Supplements. 2006;4:35.
Sennino B, Ishiguro-Oonuma T, Wei Y, et al. Suppression of tumor invasion and metastasis by concurrent inhibition of c-Met and VEGF signaling in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:270–287.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagilla, M., Brown, R.L. & Cohen, E.E.W. Cabozantinib for the Treatment of Advanced Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Adv Therapy 29, 925–934 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-012-0060-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-012-0060-6