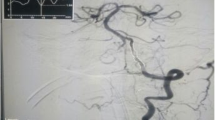
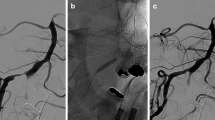
Abstract
Introduction
Intracranial arterial stenosis is an important factor in the development of cerebral infarction; however, no effective treatment has been established. A phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3) inhibitor, cilostazol, has been reported to suppress progression of symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis in combination with aspirin, but the study used magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) for evaluation, which is not considered optimal for assessment of stenotic lesions.
Methods
A preliminary study was conducted to investigate the efficacy of cilostazol using MRA and intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography (DSA). DSA was performed in 18 patients for whom intracranial arterial stenosis was suspected from MRA. Cilostazol (200 mg/day) was administered orally for 1 year to 13 patients with 16 lesions (nine symptomatic, seven asymptomatic) confirmed by DSA. MRA and DSA were repeated at 6 and 12 months.
Results
Through MRA at 6 and 12 months, regression was observed in nine (56.3%) and eight (50.0%) patients, six (37.5%) and seven (43.8%) patients remained stationary, and one (6.3%) and one (6.3%) patient progressed, respectively. From DSA, percent stenosis for all lesions significantly improved from 49.2 (±15.4%) to 42.6 (±12.7%) at 12 months (P=0.023). In nine symptomatic lesions, stenosis was 55.3 (±7.3%) at baseline, 46.3 (±12.5%) at 6 months (P=0.029), and 47.7 (±9.9%) at 12 months (P=0.049). In contrast, in seven asymptomatic lesions, no significant improvement was observed at 6 months (P=0.113) or 12 months (P=0.157). When evaluated by severity, there was a significant improvement in 11 lesions with ≥50% stenosis, but no significant improvement was observed in five lesions with <50% stenosis. No patient developed symptomatic stroke events.
Conclusion
Cilostazol may induce improvement of symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis or severe lesions. A combination of MRA and DSA might be another diagnostic option for more precise examination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borozan PG, Schuler JJ, LaRosa MP, Ware MS, Flanigan DP. The natural history of isolated carotid siphon stenosis. J Vasc Surg. 1984;1:744–749.
Craig DR, Meguro K, Watridge C, Robertson JT, Barnett HJ, Fox AJ. Intracranial internal carotid artery stenosis. Stroke. 1982;13:825–828.
Marzewski DJ, Furlan AJ, St Louis P, Little JR, Modic MT, Williams G. Intracranial internal carotid artery stenosis: longterm prognosis. Stroke. 1982;13:821–824.
Moufarrij NA, Little JR, Furlan AJ, Leatherman JR, Williams GW. Basilar and distal vertebral artery stenosis: long-term follow up. Stroke. 1986;17:938–942.
Sacco RL, Kargman DE, Gu Q, Zamanillo MC. Race-ethnicity and determinants of intracranial atherosclerotic cerebral infarction: the Northern Manhattan Stroke Study. Stroke. 1995;26:14–20.
Arenillas JF, Molina CA, Montaner J, Abilleira S, González-Sánchez MA, Alvarez-Sabín J. Progression and clinical recurrence of symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis. A long-term follow up transcranial doppler ultrasound study. Stroke. 2001;32:2898–2904.
Bogousslavsky J, Barnett HJ, Fox AJ, Hachinski VC, Taylor W, for the EC/IC Bypass Study Group. Atherosclerotic disease of middle cerebral artery. Stroke. 1986;17:1112–1120.
Chimowitz MI, Kokkinos J, Strong J, et al., for the Warfarin-Aspirin Symptomatic Intracranial Disease Study Group. The warfarin-aspirin symptomatic intracranial disease study. Neurology. 1995;45:1488–1493.
Corston RN, Kendall BE, Marshall J. Prognosis in middle cerebral artery stenosis. Stroke. 1984;15:237–241.
Hinton RC, Mohr JP, Ackerman RH, Adair LB, Fisher CM. Symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis. Ann Neurol. 1979;5:152–157.
Kasner SE, Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, et al., Warfarin Aspirin Symptomatic Intracranial Disease Trial Investigators. Predictors of ischemic stroke in territory of a symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. Circulation. 2006;113:553–563.
The WASID study group. Prognosis of patients with symptomatic vertebral or basilar artery stenosis. Stroke. 1998;29:1389–1392.
Thijs VN, Albers GW. Symptomatic intracranial atherosclerosis: outcome of patients who fail antithrombotic thrapy. Neurology. 2000;55:490–497.
Kern R, Steinke W, Daffertshofer M, Prager R, Hennerici M. Stroke recurrence in patients with symptomatic vs asymptomatic middle cerebral artery disease. Neurology. 2005;65:859–864.
Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Howlett-Smith H, et al., Warfarin-Aspirin Symptomatic Intracranial Disease Trial Investigators. Comparison of warfarin and aspirin for symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1305–1316.
Kwon SU, Cho YJ, Koo JS, et al. Cilostazol prevents the progression of the symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis: the multicenter double-blind placebo-controlled trial of cilostazol in symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. Stroke. 2005;36:782–786.
Samuels OB, Joseph GJ, Lynn MJ, Smith HA, Chimowitz MI. A standard method for measuring intracranial arterial stenosis. AJNR. 2000;21:643–646.
Komotar RJ, Wilson DA, Mocco J, et al. Natural history of intracranial atherosclerosis: a critical review. Neurosurgery. 2006;58:595–601.
Akins P, Pilgram T, Cross DT 3rd, Moran CJ. Natural history of stenosis from intracranial athrosclerosis by serial angiography. Stroke. 1998;29:433–438.
Wong KS, Li H, Lam WW, Chan YL, Kay R. Progression of middle cerebral artery occlusive disease and relationship with further vascular events after stroke. Stroke. 2002;33:532–536.
Famakin BM, Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Stern BJ, George MG, for the WASID Trial Investigators. Causes and severity of ischemic stroke in patients with symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. Stroke. 2009;40:1999–2003.
Mazighi M, Tanasescu R, Ducrocq X, et al. Prospective study of symptomatic atherothrombotic intracranial stenoses: the GESICA study. Neurology. 2006;66:1187–1191.
Ikeda Y, Kikuchi M, Murakami H, et al. Comparison of the inhibitory effects of cilostazol, acetylsalicylic acid and ticlopidine on palatelet function ex vivo. Randomized, double blind cross-over study. Arzneimittelforschung. 1987;37:563–566.
Takahashi S, Oida K, Fujiwara R, et al. Effect of cilostazol, a cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor, on the proliferation of smooth muscle cell culture. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1992;20:900–906.
Shin HK, Kim YK, Kim KY, Lee JH, Hong KW. Remnant lipoprotein particles induce apoptosis in endothelial cells by NAD(P)H oxidase-mediated production of superoxide and cytokines via lection-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 activation: prevention by cilostazol. Circulation. 2004;109:1022–1028.
Tanaka T, Ishikawa T, Hagiwara M, Onoda K, Itoh H, Hidaka H. Effect of cilostazol, a selective cAMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor, on the contraction of vascular smooth muscle. Pharmacology. 1988;36:313–320.
Van Laar PJ, van der Grond J, Mali WP, Hendrikse J. Magnetic resonance evaluation of the cerebral circulation in obstructive arterial disease. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2006;21:297–306.
Hendrikse J, Klijn CJ, van Huffelen AC, Kappelle LJ, van der Grond J. Diagnosing cerebral collateral flow patterns: accuracy of non-invasive testing. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008;25:430–437.
Uehara T, Mori E, Tabuchi M, Ohsumi Y, Yamadori A. Detection of occlusive lesions in intracranial arteries by three-dimensional time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography. Cerebrovasc Dis. 1994;4:365–370.
Heiserman JE, Drayer BP, Keller PJ, Fram EK. Intracranial vascular stenosis and occlusion: evaluation with three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography. Radiology. 1992;185:667–673.
Hirai T, Korogi Y, Ono K, et al. Prospective evaluation of suspected stenoocclusive disease of intracranial artery: combined MR angiography compared with digital subtraction angiography. AJNR. 2002;23:93–101.
Korogi Y, Takahashi M, Mabuchi N, et al. Intracranial vascular stenosis and occlusion: diagnostic accuracy of three-dimensional, Fourier transform, time-of-flight MR angiography. Radiology. 1994;193:187–193.
Wentz KU, Röther J, Schwartz A, Mattle HP, Suchalla R, Edelman RR. Intracranial vertebrobasilar system: MR angiography. Radiology. 1994;190:105–110.
Lee JH, Oh GT, Park SY, et al. Cilostazol reduces atherosclerosis by inhibition of superoxide and tumor necrosis factor-α formation in low-density lipoprotein receptor-null mice fed high cholesterol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;313:502–509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, K., Fujimoto, Y. Efficacy of cilostazol for intracranial arterial stenosis evaluated by digital subtraction angiography/magnetic resonance angiography. Adv Therapy 28, 866–878 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-011-0060-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-011-0060-y