Abstract
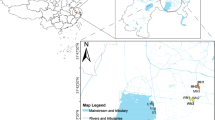
Alluvial aquifers are one of the mainwater resources in many countries. Iron reduction in alluvial aquifers is often a major anaerobic process involved in bioremediation or causing problems, including the release of As trapped in Fe(III) oxide. We investigated the distribution of potential iron-reducing bacteria (IRB) in riverine alluvial aquifers (B1, B3, and B6 sites) at the Mankyeong River, Republic of Korea. Inactive iron reduction zones, the diversity and abundance of IRB can be examined using a clone library and quantitative PCR analysis of 16S rRNA genes. Geobacter spp. are potential IRB in the iron-reducing zone at the B6 (9 m) site, where high Fe(II) and arsenic (As) concentrations were observed. At the B3 (16 m) site, where low iron reduction activity was predicted, a dominant clone (10.6%) was 99% identical in 16S rRNA gene sequence with Rhodoferax ferrireducens. Although a major clone belonging to Clostridium spp. was found, possible IRB candidates could not be unambiguously determined at the B1 (18 m) site. Acanonical correspondence analysis demonstrated that, among potential IRB, only the Geobacteraceae were well correlated with Fe(II) and As concentrations. Our results indicate high environmental heterogeneity, and thus high spatial variability, in thedistribution of potential IRB in the riverine alluvial aquifersnear the Mankyeong River.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abulencia, C.B., Wyborski, D.L., Garcia, J.A., Podar, M., Chen, W., Chang, S.H., Chang, H.W., Watson, D., Brodie, E.L., Hazen, T.C., and et al. 2006. Environmental whole-genome amplification to access microbial populations in contaminated sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.72, 3291–3301.
Acinas, S.G., Sarma-Rupavtarm, R., Klepac-Ceraj, V., and Polz, M.F. 2005. PCR-induced sequence artifacts and bias: insights from comparison of two 16S rRNA clone libraries constructed from the same sample. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.71, 8966–8969.
Ashelford, K.E., Chuzhanova, N.A., Fry, J.C., Jones, A.J., and Weightman, A.J. 2006. New screening software shows that most recent large 16S rRNA gene clone libraries contain chimeras. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.72, 5734–5741.
Baker, G.C., Smith, J.J., and Cowan, D.A. 2003. Review and re-analysis of domain-specific 16S primers. J. Microbiol. Methods55, 541–555.
Bond, D.R. and Lovley, D.R. 2002. Reduction of Fe(III) oxide by methanogens in the presence and absence of extracellular quinones. Environ. Microbiol.4, 115–124.
Bourg, A.C.M. and Bertin, C. 1993. Biogeochemical processes during the infiltration of river water into an alluvial aquifer. Environ. Sci. Technol.27, 661–666.
Brown, C.J., Walter, D.A., and Colabufo, S. 1999. Iron in the aquifer system of suffolk county, New York, p. 10. USGS, New York, N.Y., USA.
Chao, A. and Shen, T.J. 2005. Program SPADE (Species Prediction and Diversity Estimation). v2.1. Program and User’s Guide published at http://chao.stat.nthu.edu.tw.
Chapelle, F.H., Bradley, P.M., Thomas, M.A., and McMahon, P.B. 2009. Distinguishing iron-reducing from sulfate-reducing conditions. Ground Water47, 300–305.
Childers, S.E., Ciufo, S., and Lovley, D.R. 2002. Geobacter metallireducens accesses insoluble Fe(III) oxide by chemotaxis. Nature416, 767–769.
Choi, B.Y., Kim, H.J., Kim, K., Kim, S.H., Jeong, H.J., Park, E., and Yun, S.T. 2008. Evaluation of the processes affecting vertical water chemistry in an alluvial aquifer of Mankyeong Watershed, Korea, using multivariate statistical analyses. Environ. Geol.54, 335–345.
Choi, B.K., Koh, D.C., Ha, K., and Cheon, S.H. 2007. Effect of redox processes and solubility equilibria on the behavior of dissolved iron and manganese in groundwater from a riverine alluvial aquifer. Econ. Environ. Geol.40, 29–45.
Coates, J.D., Ellis, D.J., Gaw, C.V., and Lovley, D.R. 1999. Geothrix fermentans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel Fe(III)-reducing bacterium from a hydrocarbon-contaminated aquifer. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol.49, 1615–1622.
Coleman, M.L., Hedrick, D.B., Lovley, D.R., White, D.C., and Pye, K. 1993. Reduction of Fe(III) in sediments by sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nature361, 436–438.
Collins, M.D., Lawson, P.A., Willems, A., Cordoba, J.J., Fernandez-Garayzabal, J., Garcia, P., Cai, J., Hippe, H., and Farrow, J.A. 1994. The phylogeny of the genus Clostridium: proposal of five new genera and eleven new species combinations. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol.44, 812–826.
Cummings, D.E., Caccavo, F.Jr., Spring, S., and Rosenzweig, R.F. 1999. Ferribacterium limneticum, gen. nov., sp. nov., an Fe(III)-reducing microorganism isolated from mining-impacted freshwater lake sediments. Arch. Microbiol.171, 183–188.
Cummings, D.E., Snoeyenbos-West, O.L., Newby, D.T., Niggemyer, A.M., Lovley, D.R., Achenbach, L.A., and Rosenzweig, R.F. 2003. Diversity of Geobacteraceae species inhabiting metal-polluted freshwater lake sediments ascertained by 16S rDNA analyses. Microb. Ecol.46, 257–269.
Felsenstein, J. 1985. Confidence limit on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution39, 783–791.
Finneran, K.T., Johnsen, C.V., and Lovley, D.R. 2003. Rhodoferax ferrireducens sp. nov., a psychrotolerant, facultatively anaerobic bacterium that oxidizes acetate with the reduction of Fe(III). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.53, 669–673.
Good, I.J. 1953. The population frequencies of species and the estimation of population parameters. Biometrika40, 237–264.
Harvey, C.F., Swartz, C.H., Badruzzaman, A.B., Keon-Blute, N., Yu, W., Ali, M.A., Jay, J., Beckie, R., Niedan, V., Brabander, D., and et al. 2002. Arsenic mobility and groundwater extraction in Bangladesh. Science298, 1602–1606.
He, J., Zhang, L., Jin, S., Zhu, Y., and Liu, F. 2008. Bacterial communities inside and surrounding soil iron-manganese nodules. Geomicrobiol. J.25, 14–24.
Hiscock, K.M. and Grischek, T. 2002. Attenuation of groundwater pollution by bank filtration. J. Hydrol.266, 139–144.
Hori, T., Muller, A., Igarashi, Y., Conrad, R., and Friedrich, M.W. 2010. Identification of iron-reducing microorganisms in anoxic rice paddy soil by 13C-acetate probing. ISME J.4, 267–278.
Islam, F.S., Gault, A.G., Boothman, C., Polya, D.A., Charnock, J.M., Chatterjee, D., and Lloyd, J.R. 2004. Role of metal-reducing bacteria in arsenic release from Bengal delta sediments. Nature430, 68–71.
Jongman, R.H., Braak, C.J.F.t., and Van Tongeren, O.F.R. 1995. Data analysis in community and landscape ecology, p. xxi, 299, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Kelly, W.R. 1997. Heterogeneities in ground-water geochemistry in a sand aquifer beneath an irrigated field. J. Hydrol.198, 154–176.
Kim, K., Kim, H.J., Choi, B.Y., Kim, S.H., Park, K., Park, E., Koh, D.C., and Yun, S.T. 2008. Fe and Mn levels regulated by agricultural activities in alluvial groundwaters underneath a flooded paddy field. Appl. Geochem.23, 44–57.
Kim, K., Moon, J.T., Kim, S.H., and Ko, K.S. 2009. Importance of surface geologic condition in regulating as concentration of groundwater in the alluvial plain. Chemosphere77, 478–484.
Kimura, M. 1983. The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Kumar, S., Tamura, K., and Nei, M. 2004. MEGA3: Integrated software for Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform.5, 150–163.
Lin, B., Braster, M., Röling, W.F.M., and van Breukelen, B.M. 2007. Iron-reducing microorganisms in a landfill leachate-polluted aquifer: complementing culture-independent information with enrichments and isolations. Geomicrobiol. J.24, 283–294.
Lin, B., Braster, M., van Breukelen, B.M., van Verseveld, H.W., Westerhoff, H.V., and Roling, W.F. 2005. Geobacteraceae community composition is related to hydrochemistry and biodegradation in an iron-reducing aquifer polluted by a neighboring landfill. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.71, 5983–5991.
Lindsay, S.S. and Baedecker, M.J. 1988. Determination of aqueous sulfide in contaminated and natural water using the methylene blue method, pp. 349–356. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, USA.
Lovley, D.R. 1995. Bioremediation of organic and metal contaminants with dissimilatory metal reduction. J. Ind. Microbiol.14, 85–93.
Lovley, D.R., Holmes, D.E., and Nevin, K.P. 2004. Dissimilatory Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction. Adv. Microb. Physiol.49, 219–286.
Lovley, D.R., Roden, E.E., Philips, E.J.P., and Woodward, J.C. 1993. Enzymatic iron and uranium reduction by sulfate-reducing bacteria. Marine Geobiolgy113, 41–53.
Massmann, G., Pekdeger, A., and Merz, C. 2004. Redox processes in the Oderbruch polder groundwater flow system in Germany. Appl. Geochem.19, 863–886.
McArthur, J.M., Banerjee, D.M., Hudson-Edwards, K.A., Mishra, R., Purohit, R., Ravenscroft, P., Cronin, A., Howarth, R.J., Chatterjee, A., Talukder, T., and et al. 2004. Natural organic matter in sedimentary basins and its relation to arsenic in anoxic ground water: the example of West Bengal and its worldwide implications. Appl. Geochem.19, 1255–1293.
McMahon, P.B. and Chapelle, F.H. 2008. Redox processes and water quality of selected principal aquifer systems. Ground Water46, 259–271.
Min, J.H., Yun, S.T., Kim, K., Kim, H.S., and Kim, D.J. 2003. Geologic controls on the chemical behaviour of nitrate in riverside alluvial aquifer, Korea. Hydrolog. Proc.17, 1197–1211.
Muyzer, G., de Waal, E.C., and Uitterlinden, A.G. 1993. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.59, 695–700.
Nevin, K.P., Holmes, D.E., Woodard, T.L., Hinlein, E.S., Ostendorf, D.W., and Lovley, D.R. 2005. Geobacter bemidjiensis sp. nov. and Geobacter psychrophilus sp. nov., two novel Fe(III)-reducing subsurface isolates. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.55, 1667–1674.
Nevin, K.P. and Lovley, D.R. 2000. Lack of production of electron-shuttling compounds or solubilization of Fe(III) during reduction of insoluble Fe(III) oxide by Geobacter metallireducens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.66, 2248–2251.
Newman, D.K. and Kolter, R. 2000. A role for excreted quinones in extracellular electron transfer. Nature405, 94–97.
Ng, S.P., Davis, B., Palombo, E.A., and Bhave, M. 2009. A Tn5051-like mer-containing transposon identified in a heavy metal tolerant strain Achromobacter sp. AO22. BMC Res. Notes2, 38.
Nickson, R.T., McArthur, J.M., Ravenscroft, P., Burgess, W.G., and Ahmed, K.M. 2000. Mechanism of arsenic release to groundwater, Bangladesh and West Bengal. Appl. Geochem.15, 403–413.
Norris, R.D. and Matthews, J.E. 1994. Handbook of bioremediation, p. xiii, p. 257 Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, USA.
Papacostas, N.P., Bostick, B.C., Quicksall, A.N., Landis, J.D., and Sampson, M. 2008. Geomorphological controls on groundwater arsenic distribution in the Mekong River Delta, Cambodia. Geology36, 891–894.
Park, S.J., Park, B.J., and Rhee, S.K. 2008. Comparative analysis of archaeal 16S rRNA and amoA genes to estimate the abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in marine sediments. Extremophiles12, 605–615.
Petrie, L., North, N.N., Dollhopf, S.L., Balkwill, D.L., and Kostka, J.E. 2003. Enumeration and characterization of iron(III)-reducing microbial communities from acidic subsurface sediments contaminated with uranium (VI). Appl. Environ. Microbiol.69, 7467–7479.
Polya, D.A., Gault, A.G., Bourne, N.J., Lythgoe, P.R., and Cooke, D.A. 2003. Coupled HPLC-ICP-MS analysis indicates highly hazardous concentrations of dissolved arsenic species in Cambodian groundwaters. Plasma Source Mass Spectrometry: Applications and Emerging Technologies. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, UK.
Porsch, K., Meier, J., Kleinsteuber, S., and Wendt-Potthoff, K. 2009. Importance of different physiological groups of iron reducing microorganisms in an acidic mining lake remediation experiment. Microb. Ecol.57, 701–717.
Quicksall, A.N., Bostick, B.C., and Sampson, M. 2008. Linking organic matter deposition and iron mineral transformations to groundwater arsenic levels in the Mekong delta, Cambodia. Appl. Geochem.23, 3088–3098.
Röling, W.F.M., van Breukelen, B.M., Braster, M., Lin, B., and van Verseveld, H.W. 2001. Relationships between microbial community structure and hydrochemistry in a landfill leachate-polluted aquifer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.67, 4619–4629.
Scholten, J.C. and Stams, A.J. 2000. Isolation and characterization of acetate-utilizing anaerobes from a freshwater sediment. Microb. Ecol.40, 292–299.
Snoeyenbos-West, O.L., Nevin, K.P., Anderson, R.T., and Lovley, D.R. 2000. Enrichment of Geobacter species in response to stimulation of Fe(III) reduction in sandy aquifer sediments. Microb. Ecol.39, 153–167.
Stein, L.Y., La Duc, M.T., Grundl, T.J., and Nealson, K.H. 2001. Bacterial and archaeal populations associated with freshwater ferromanganous micronodules and sediments. Environ. Microbiol.3, 10–18.
Sung, Y., Ritalahti, K.M., Apkarian, R.P., and Loffler, F.E. 2006. Quantitative PCR confirms purity of strain GT, a novel trichloroethene-to-ethene-respiring Dehalococcoides isolate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.72, 1980–1987.
Ter Braak, C.J.F. 1987. The analysis of vegetation-environment relationships by canonical correspondence analysis. Vegetatio69, 69–77.
Thompson, J.D., Gibson, T.J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., and Higgins, D.G. 1997. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res.25, 4876–4882.
Tufenkji, N., Ryan, J.N., and Elimelech, M. 2002. The promise of bank filtration. Environ. Sci. Technol.36, 422A–428A.
Turick, C.E., Tisa, L.S., and Caccavo, F. 2002. Melanin production and use as a soluble electron shuttle for Fe(III) oxide reduction and as a terminal electron acceptor by Shewanella algae BrY. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.68, 2436–2444.
Watanabe, K., Teramoto, M., and Harayama, S. 1999. An outbreak of nonflocculating catabolic populations caused the breakdown of a phenol-digesting activated-sludge process. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.65, 2813–2819.
Weber, K.A., Achenbach, L.A., and Coates, J.D. 2006. Microorganisms pumping iron: anaerobic microbial iron oxidation and reduction. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.4, 752–764.
Weisburg, W.G., Barns, S.M., Pelletier, D.A., and Lane, D.J. 1991. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol173, 697–703.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SJ., Koh, DC., Park, SJ. et al. Molecular analysis of spatial variation of iron-reducing bacteria in riverine alluvial aquifers of the Mankyeong River. J Microbiol. 50, 207–217 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-012-1342-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-012-1342-z