Abstract
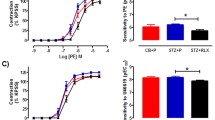
The aim of this study was to examine the effect of chronic administration of nimesulide, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, on endothelial dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Three groups of Sprague-Dawley rats (300–350 g, n = 6) were used. The first group served as normoglycemic control and the second and third groups were rendered diabetic by an intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (60 mg/kg). The third group received the selective COX-2 inhibitor, nimesulide (20 mg/kg/day), orally by gavage for 4 weeks while the second group received only drinking water and served as diabetic control. At the end of the treatment period, the rats were anesthetized with urethane (1.2 g/kg) and mean arterial pressure, heart rate and hindlimb blood flow were monitored. This was followed by the injection of acetylcholine (endothelium-dependent vasodilator, 0.1–0.8 μg/kg) and sodium nitroprusside (endothelium-independent vasodilator 1–4 μg/kg). Mean arterial pressure was significantly reduced and hindlimb vascular conductance was not significantly affected in the control diabetic group when compared to the normoglycemic control group. Nimesulide treatment did not cause any significant change in any of the measured hemodynamic parameters. Acetylcholine and sodium nitroprusside induced dose-dependent increases in hindlimb vascular conductance in control normoglycemic rats which were attenuated in diabetic control rats. Nimesulide reversed the attenuation of acetylcholine-induced increase in hindlimb vascular conductance. In conclusion, chronic administration of the selective COX-2 inhibitor, nimesulide improved endothelial dysfunction in the hindlimb vasculature of streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. This suggests that COX-2 products might be involved in the pathogenesis of endothelial dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angulo, J., Rodriguez-Manas, L., Peiro, C., Neira, M., Marin, J., and Sanchez-Ferrer, C. F, Impairment of nitric oxidemediated relaxations in anaesthetized autoperfused streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Naunyn Schmiedbergs’ Arch. Pharmacol., 358, 529–537 (1988).
Bardal, S., Misurski, D., Qiu, X., Desai, K., and McNeill, J. R., Chronic treatment with vascular endothelial growth factor preserves agonist-evoked vascular responses in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Diabetologia, 49, 811–818 (2006).
Bulut, D., Liaghat, S., Hanefeld, C., Koll, R., Miebach, T., and Mugge, A., Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition with parecoxib acutely impairs endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in patients with essential hypertension. J. Hypertens., 21, 1663–1667 (2003).
Calles-Escandon, J. and Cipolla, M., Diabetes and endothelial dysfunction: A clinical perspective. Endocr. Rev., 22, 36–52 (2001).
Calver, A., Collier, J., and Vallance, P., Inhibition and stimulation of nitric oxide synthesis in the human forearm arterial bed of patients with insulin-dependent diabetes. J. Clin. Invest., 90, 2548–2554 (1992).
Chenevard, R., Hurlimann, D., Bechir, M., Enseleit, F., Spieker, L., Hermann, M., Riesen, W., Gay, S., Gay, R. E., Neidhart, M., Michel, B., Luscher, T. F., Noll, G., and Ruschitzka, F., Selective COX-2 inhibition improves endothelial function in coronary artery disease. Circulation, 107, 405–409 (2003).
Cheng, Z. J., Tikkanen, I., Vapaatalo, H., and Mervaala, E. M., vascular effects of COX inhibition and AT1 receptor blockade in transgenic rats harboring mouse renin-2 gene. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 53, 597–613 (2002).
Consentino, F., Francia, P., and Volpe, M., Do COX-2 inhibitors really prevent hypertension and proteinuria? Another brick in the wall for the COX-2 inhibition and cardiovascular controversy. J. Hypertens., 21, 501–503 (2003).
Famaey, J. P., In vitro and in vivo pharmacological evidence of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition by nimesulide: an overview. Inflamm. Res., 46, 437–446 (1997).
FitzGerald, G. A. and Patrono, C., The coxibs, selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2. N. Engl. J. Med., 345, 433–442 (2001).
Harding, P., Carretero, O. A., and Beierwaltes, W. H., Chronic cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition blunts low sodium-stimulated renin without changing renal haemodynamics. J. Hypertens., 18, 1107–1113 (2000).
Hattori, Y., Kawasaki, H., Abe, K., and Kamo, M., Superoxide dismutase recovers altered endothelium-dependent relaxation in diabetic rat aorta. Am. J. Physiol., 261, H1086–H1094 (1991).
Hermann, M., Camici, G., Fratton, A., Hurlimann, D., Tanner, F. C., Hellermann, J. P., Fiedler, M., Thiery, J., Neidhart, M., Gay, R. E., Gay, S., Lusher, T. F., and Ruschitzka, F., Differential effects of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors on endothelial function in salt induced hypertension. Circulation, 108, 2308–2311 (2003).
Jain, S., Gupta, M., Malhorta, S., and Pandhi, P., Effect of rofecoxib on antihypertensive effects of candesartan in experimental models of hypertension. Method. Find. Exp. Clin., 27, 11–16 (2005).
Johnstone, M. T., Creager, S. J., Scales, K. M., Cusco, J. A., Lee, B. K., and Creager, M. A., Impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Circulation, 88, 2510–2516 (1993).
Kamata, K., Miyata, N., and Kasuya, Y., Impairment of endothelium-dependent relaxation and changes in levels of cyclic GMP in aorta from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Br. J. Pharmacol., 97, 614–618 (1989).
Kiff, R. J., Gardiner, S. M., Compton, A. M., and Bennett, T., Selective impairment of hindquarters vasodilator responses to bradykinin in conscious Wistar rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Br. J. Pharmacol., 103, 1357–1362 (1991).
Llinas, M. T., Rodriguez, F., Moreno, C., and Salazar, F. J., Role of cyclooxygenase-2 derived metabolites and nitric oxide in regulating renal function. Am. J. Physiol., 279,R1641–R1646 (2000).
Rebolledo, A., Ayala-Paredes, F., Milesi, V., Grassi, A. O., and Rinaldi, G. J. Short-term streptozotocin-induced diabetes induces blood pressure decrease associated with reduced aortic (45)Ca(2+) uptake and selective depression of the sustained noradrenergic contraction. Diabetes Metab., 27, 40–48 (2001).
Shi, Y. and Vanhoutte, P. M., Oxidative stress and COX cause hyper-responsiveness in vascular smooth muscle of the femoral artery from diabetic rats. Br. J. Pharmacol., 154, 639–651 (2008).
Tatchum-Talom, R., Gopalakrishnan, V., and McNeill J. R., Radiotelemetric monitoring of blood pressure and mesenteric arterial bed responsiveness in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Can. J. Physiol. Pharm., 78, 721–728 (2000).
Title, L. M., Giddens, K., McInerney, M. M., McQueen, M. J., and Nassar, B. A., Effect of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition with rofecoxib on endothelial dysfunction and inflammatory markers in patients with coronary artery disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 42, 1747–1753 (2003).
Widlansky, M. E., Price, D. T., Gokce, N., Eberhardt, R. T., Duffy, S. J., Holbrook, M., Maxwell, C., Palmisano, J., Keaney, J. F. Jr., Morrow, J. D., and Vita, J. A., Short and long-term COX-2 inhibition reverses endothelial dysfunction in patients with hypertension. Hypertension, 42, 310–315 (2003).
Wu, R., Laplante, M-A., and de Champlain, J., Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors attenuate angiotensin II-induced oxidative stress, hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy in rats. Hypertension, 45, 1139–1144 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelrahman, A.M., Al Suleimani, Y.M. Four-week administration of nimesulide, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, improves endothelial dysfunction in the hindlimb vasculature of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 31, 1584–1589 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-2155-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-2155-5