Abstract
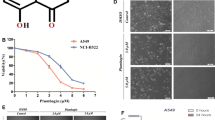
To explore the anticancer effects of the flavonoid quercetin on human breast cancer MDA-MB-453 cells via cell cycle regulation and the induction of apoptosis, the antiproliferative effect of quercetin was first examined by MTT assay. When MDA-MB-453 cells were treated with quercetin for various periods of time (3–24 hrs) and at various doses (1–100 μM), cell growth decreased significantly in a time-and dose-dependent manner. To elucidate the mechanism underlying the antiproliferative effect of quercetin, cell cycle progression and the induction of apoptosis in MDA-MB-453 cells exposed to 100 μM quercetin for 24 hrs were investigated. Quercetin caused a remarkable increase in the number of sub-G1 phase cells, and an Annexin-V assay revealed that exposure to quercetin affected apoptosis. Moreover, treatment with quercetin increased Bax expression but decreased Bcl-2 expression. Cleaved caspase-3 and PARP expression was also increased by quercetin. Thus, quercetin has probable anticancer activity. Our results suggest the existence of multiple pathways for the induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by quercetin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Qare, A. W. and Abou-Donia, M. B., Biomarkers of apoptosis: Release of cytochrome c, activation of caspase-3, induction of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine, increased 3-nitrotyrosine, and alteration of p53 gene. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev., 4, 313–332 (2001).
Agarwal, M. L., Agarwal, A., Taylor, W. R., and Stark, G. R., p53 controls both the G2/M and the G1 cell cycle checkpoints and mediates reversible growth arrest in human fibroblasts. Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA., 92, 8493–8497 (1995).
Alcocer, F., Whitley, D., Salazar-Gonzalez, J. F., Jordan, W. D., Sellers, M. T., Eckhoff, D. E., Suzuki, K., Macrae, C., and Bland, K. I., Quercetin inhibits human vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Surgery, 131, 198–204 (2002).
Chang, Y. F., Chi, C. W., and Wang, J. J., Reactive oxygen species production is involved in quercetin-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma cells. Nutr. Cancer, 55, 201–209 (2006).
Choi, E. J., Chee, K. M., and Lee, B. H., Anti-and prooxidant effects of chronic quercetin administration in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 482, 281–285 (2003).
Collins, A. R., Antioxidant intervention as a route to cancer prevention. Eur. J., 41, 1923–1930 (2005).
Cotelle, N., Role of flavonoids in oxidative stress. Curr. Top. Med. Chem., 1, 569–590 (2001).
Frankel, E. N., Kanner, J., German, J. B., Parks, E., and Kinsella, J. E., Inhibition of oxidation of human lowdensity lipoprotein by phenolic substances in red wine. Lancet, 341, 454–457 (1993).
Hertog, M. G., Bueno-de-Mesquita, H. B., Fehily, A. M., Sweetnam, P. M., Elwood P. C., and Kromhout, D., Fruit and vegetable consumption and cancer mortality in the Caerphilly Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev., 5, 673–677 (1996).
Hertog, M. G., Epidemiological evidence on potential health properties of flavonoids. Proc. Nutr. Soc., 55, 385–397 (1996).
Hertog, M. G., Hollman, P. C., Katan, M. B., and Kromhout, D., Intake of potentially anticarcinogenic flavonoids and their determinants in adults in the Netherlands. Nutr. Cancer, 20, 21–29 (1993).
Huang, S. L., Hsu, C. L., and Yen, G. C., Growth inhibitory effect of quercetin on SW 872 human liposarcoma cells. Life Sci., 79, 203–209 (2006).
Kandaswami, C. and Middleton, E. Jr., Free radical scavenging and antioxidant activity of plant flavonoids. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 366, 351–376 (1994).
Kandaswami, C., Lee, L. T., Lee, P. P., Hwang, J. J., Ke, F. C., Huang, Y. T., and Lee, M. T., The antitumor activities of flavonoids. In Vivo, 19, 895–909 (2005).
Kim, W. K., Bang, M. H., Kim, E. S., Kang, N. E., Jung, K. C., Cho, H. J., and Park, J. H., Quercetin decreases the expression of ErbB2 and ErbB3 proteins in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. J. Nutr. Biochem., 16, 155–162 (2005).
Kook, D., Wolf, A. H., Yu, A. L., Neubauer, A. S., Priglinger, S. G., Kampik, A., and Welge-Lüssen, U. C., The protective effect of quercetin against oxidative stress in the human RPE in Vitro. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 49, 1712–1720 (2008).
Kris-Etherton, P. M. and Keen, C. L., Evidence that the antioxidant flavonoids in tea and cocoa are beneficial for cardiovascular health. Curr. Opin. Lipidol., 13, 41–49 (2002).
Lamson, D. W. and Brignall, M. S., Antioxidants and cancer, part 3: quercetin. Altern. Med. Rev., 5, 196–208 (2000).
Lepik, D., Jaks, V., Kadaja, L., Varv, S., and Maimets, T., Electroporation and carrier DNA cause p53 activation, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis. Anal. Biochem., 318(1), 52–59 (2003).
Lim, J. H., Park, J. W., Min, D. S., Chang, J. S., Lee, Y. H., Park, Y. B., Choi, K. S., and Kwon, T. K., NAG-1 up-regulation mediated by EGR-1 and p53 is critical for quercetin-induced apoptosis in HCT116 colon carcinoma cells. Apoptosis, 12, 411–421 (2007).
Liu, H., Zhang, C., and Zeng, W., Estrogenic and antioxidant effects of a phytoestrogen daidzein on ovarian germ cells in embryonic chickens. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol., 31, 258–268 (2006).
Lopez-Lazaro, M., Flavonoids as anticancer agents: structureactivity relationship study. Curr. Med. Chem. Anticancer Agents., 2, 691–714 (2002).
Metodiewa, D., Jaiswal, A. K., Cenas, N., Dickancaité, E., and Segura-Aguilar, J., Quercetin may act as a cytotoxic prooxidant after its metabolic activation to semiquinone and quinoidal product. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 26, 107–116 (1999).
Notoya, M., Tsukamoto, Y., Nishimura, H., Woo, J. T., Nagai, K., Lee, I. S., and Hagiwara, H., Quercetin, a flavonoid, inhibits the proliferation, differentiation, and mineralization of osteoblasts in vitro. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 48, 89–96 (2004).
Oakea, S. A., Lin, S. S., and Bassik, M. C., The control of endoplasmic reticulum-initiated apoptosis by the BCL-2 family of proteins. Curr. Mol. Med., 6, 99–109 (2006).
Park, M., Chae, H. D., Yun, J., Jung, M., Kim, Y. S., Kim, S. H., Han, M. H., and Shin, D. Y., Constitutive activation of cyclin B1-associated cdc2 kinase overrides p53-mediated G2-M arrest. Cancer Res., 60, 542–545 (2000).
Parker, M. A., Anderson, J. K., Corliss, D. A., Abraria, V. E., Sidman, R. L., Park, K. I., Teng, Y. D., Cotanche, D. A., and Snyder, E. Y., Expression profile of an operationallydefined neural stem cell clone. Exp. Neurol., 194, 320–332 (2005).
Pathak, S. K., Sharma, R. A., and Mellon, J. K., Chemoprevention of prostate cancer by diet-derived antioxidant agents and hormonal manipulation (Review). Int. J. Oncol., 22, 5–13 (2003).
Porter, A. G. and Janicke, R. U., Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ., 6, 99–104 (1999).
Ramos, A. A., Lima, C. F., Pereira, M. L., Fernandes-Ferreira, M., and Pereira-Wilson, C., Antigenotoxic effects of quercetin, rutin and ursolic acid on HepG2 cells: evaluation by the comet assay. Toxicol. Lett., 177, 66–73 (2008).
Rao, A. V. and Agarwal, S., Role of antioxidant lycopene in cancer and heart disease. J. Am. Coll. Nutr., 19, 563–569 (2000).
Ren, W., Qiao, Z., Wang, H., Zhu, L., and Zhang, L., Flavonoids: Promising anticancer agents. Med. Res. Rev., 23, 519–534 (2003).
Russo, G. L., Ins and outs of dietary phytochemicals in cancer chemoprevention. Biochem. Pharmacol., 74, 533–544 (2007).
Sahu, S. C. and Gray, G. C., Pro-oxidant activity of flavonoids: Effects on glutathione and glutathione S-transferase in isolated rat liver nuclei. Cancer Lett., 104, 193–196 (1996).
Shen, S. C., Chen, Y. C., Hsu, F. L., and Lee, W. R., Differential apoptosis-inducing effect of quercetin and its glycosides in human promyeloleukemic HL-60 cells by alternative activation of the caspase 3 cascade. J. Cell Biochem., 89, 1044–1055 (2003).
Singh, R. P. and Agarwal, R., Natural flavonoids targeting deregulated cell cycle progression in cancer cells. Curr. Drug Targets., 7, 345–354 (2006).
van Delft, M. F. and Huang, D. C., How the Bcl-2 family of proteins interact to regulate apoptosis. Cell Res., 16, 203–213 (2006).
Zhang, J., Stanley, R. A., Adaim, A., Melton, L. D., and Skinner, M. A., Free radical scavenging and cytoprotective activities of phenolic antioxidants. Mol. Nutr. Food Res., 50, 996–1005 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, E.J., Bae, S.M. & Ahn, W.S. Antiproliferative effects of quercetin through cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human breast cancer MDA-MB-453 cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 31, 1281–1285 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-2107-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-2107-0