Abstract
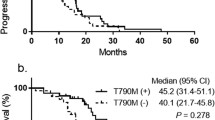
To investigate the clinicopathologic and molecular features of the T790M mutation and c-MET amplification in a cohort of Chinese non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients resistant to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). EGFR TKI-resistant NSCLC patients (n = 29) and corresponding tumor specimens, and 53 samples of postoperative TKI-naïve NSCLC patients were collected. EGFR exon 19, 20, and 21 mutations were analyzed. And c-MET gene copy number was determined. The EGFR T790M mutation in exon 20 was not detected in the population of 53 TKI-naïve patients, but found in 48.3% (14/29) of the enrolled TKI-resistant patients. c-MET was amplified in 3.8% (2/53) of the TKI-naïve NSCLC patients and highly amplified in 17.2% (5/29) of the cohort. Most of T790M mutations were frequently associated with non-smoker, adenocarcinoma and EGFR activating mutations. Three male patients with T790M mutation occurred with wild-type EGFR, and were resistant to the treatments following TKI resistance. Features of c-MET amplification in TKI-naïve patients were indistinguishable from TKI-resistant patients. In the group of wild-type EGFR, patients with T790M mutation had median progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) as 9.6 months and 12.6 months, respectively; whereas the median PFS and OS of c-MET amplified patients was 4.1 months and 8.0 months, respectively. These results suggest that EGFR T790M mutation and c-MET amplification can occur in TKI-resistant NSCLC with wild-type EGFR, and these genetic defects might be related to different survival outcome. c-MET amplification in TKI-naïve or -resistant patients might share similarities in clinicopathologic features.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- (ARMS):
-
amplification refractory mutation system
- (EGFR):
-
epidermal growth factor receptor
- (NSCLC):
-
non-small cell lung cancer
- (OS):
-
overall survival
- (PFS):
-
progression free survival
- (TKI):
-
tyrosine kinase inhibitor
References
Pao W, Miller VA, Politi KA et al (2005) Acquired resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib is associated with a second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain. PLoS Med 2:e73
Pao W, Balak MN, Riely GJ et al (2006) Molecular analysis of NSCLC patients with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib. J Clin Oncol 24(Suppl):383s abstract 7078
Kwak EL, Sordella R, Bell DW et al (2005) Irreversible inhibitors of the EGF receptor may circumvent acquired resistance to gefitinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:7665–7670
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T et al (2005) EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 352:786–792
Yun CH, Mengwasser KE, Toms AV et al (2008) The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2070–2075
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T et al (2007) MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ErbB3 signaling. Science 316:1039–1043
Ogino A, Kitao H, Hirano S et al (2007) Emergence of epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation during chronic exposure to gefitinib in a non small cell lung cancer cell line. Cancer Res 67:7807–7814
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T et al (2006) Allelic dilution obscures detection of a biologically significant resistance mutation in EGFR-amplified lung cancer. J Clin Invest 116:2695–2706
Wu YL, Zhong WZ, Li LY et al (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and their correlation with gefitinib therapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis based on updated individual patient data from six medical centers in mainland China. J Thorac Oncol 2(5):430–439
Beasley MB, Brambilla E, Travis WD (2005) The 2004 World Health Organization classification of lung tumors. Semin Roentgenol 40:90–97
Ling G, Persson A, Berne B et al (2001) Persistent p53 mutations in single cells from normal human skin. Am J Pathol 159:1247–1253
Dietmaier W, Hartmann A, Wallinger S et al (1999) Multiple mutation analyses in single tumor cells with improved whole genome amplification. Am J Pathol 154:83–95
Bae NC, Chae MH, Lee MH et al (2007) EGFR, ERBB2, and KRAS mutations in Korean non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 173:107–113
Pallis AG, Voutsina A, Kalikaki A et al (2007) ‘Classical’ but not ‘other’ mutations of EGFR kinase domain are associated with clinical outcome in gefitinib-treated patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 97:1560–1566
Kimura H, Fujiwara Y, Sone T et al (2006) High sensitivity detection of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in the pleural effusion of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Sci 97:642–648
Kimura H, Suminoe M, Kasahara K et al (2007) Evaluation of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status in serum DNA as a predictor of response to gefitinib (IRESSA). Br J Cancer 97:778–784
Beau-Faller M, Ruppert AM, Voegeli AC et al (2008) MET gene copy number in non-small cell lung cancer: molecular analysis in a targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor naïve cohort. J Thorac Oncol 3:331–339
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(3):205–216
Balak MN, Gong Y, Riely GJ et al (2006) Novel D761Y and common secondary T790M mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinomas with acquired resistance to kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 12:6494–6501
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H et al (2006) Analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutation in patients with non small cell lung cancer and acquired resistance to gefitinib. Clin Cancer Res 12:5764–5769
Newton CR, Graham A, Heptinstall LE et al (1989) Analysis of any point mutation in DNA. The amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS). Nucleic Acids Res 17:2503–2516
Whitcombe D, Theaker J, Guy SP et al (1999) Detection of PCR products using self-probing amplicons and fluorescence. Nat Biotechnol 17:804–807
Bean J, Brennan C, Shih JY et al (2007) MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:20932–20937
Inukai M, Toyooka S, Ito S et al (2006) Presence of epidermal growth factor receptor gene T790M mutation as a minor clone in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 66:7854–7858
Shih JY, Gow CH, Yang PC (2005) EGFR mutation conferring primary resistance to gefitinib in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 353(2):207–208
Toyooka S, Kiura K, Mitsudomi T (2005) EGFR mutation and response of lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 352(20):2136 author reply 2136
Bell DW, Gore I, Okimoto RA et al (2005) Inherited susceptibility to lung cancer may be associated with the T790M drug resistance mutation in EGFR. Nat Genet 37(12):1315–1316
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China 30772531, the Foundation of Guangdong Science and Technology Department, 2007A032000002, and the Chinese Lung Cancer Research Foundation.
We thank Pasi A. Jänne (Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA, USA) for DNA samples of NSCLC cell lines HCC827 parental and HCC827 GR6. We thank Qiu-Xiong Lin and Dong-Lan Luo (Department of Pathology, Guangdong General Hospital) for their assistance in microdissection. We also thank the AstraZeneca Innovation Center China (ICC) in Shanghai for the excellent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The data were presented in part at the 2008 ASCO annual meeting (Abstract-No. 8107).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, HJ., Mok, T.S., Chen, ZH. et al. Clinicopathologic and Molecular Features of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor T790M Mutation and c-MET Amplification in Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-resistant Chinese Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 15, 651–658 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9167-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9167-8