Abstract
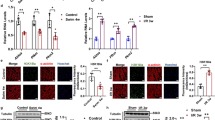
This study sought to evaluate the effects of a single session of exercise on the expression of Hsp70, of c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and insulin receptor substrate 1 serine 612 (IRSser612) phosphorylation in the skeletal muscle of obese and obese insulin-resistant patients. Twenty-seven volunteers were divided into three experimental groups (eutrophic insulin-sensitive, obese insulin-sensitive, and obese insulin-resistant) according to their body mass index and the presence of insulin resistance. The volunteers performed 60 min of aerobic exercise on a cycle ergometer at 60 % of peak oxygen consumption. M. vastus lateralis samples were obtained before and after exercise. The protein expressions were evaluated by Western blot. Our findings show that compared with paired eutrophic controls, obese subjects have higher basal levels of p-JNK (100 ± 23 % vs. 227 ± 67 %, p = 0.03) and p-IRS-1ser612 (100 ± 23 % vs. 340 ± 67 %, p < 0.001) and reduced HSP70 (100 ± 16 % vs. 63 ± 12 %, p < 0.001). The presence of insulin resistance results in a further increase in p-JNK (460 ± 107 %, p < 0.001) and a decrease in Hsp70 (46 ± 5 %, p = 0.006), but p-IRS-1ser612 levels did not differ from obese subjects (312 ± 73 %, p > 0.05). Exercise reduced p-JNK in obese insulin-resistant subjects (328 ± 33 %, p = 0.001), but not in controls or obese subjects. Furthermore, exercise reduced p-IRS-1ser612 for both obese (122 ± 44 %) and obese insulin-resistant (185 ± 36 %) subjects. A main effect of exercise was observed in HSP70 (p = 0.007). We demonstrated that a single session of exercise promotes changes that characterize a reduction in cellular stress that may contribute to exercise-induced increase in insulin sensitivity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre V, Uchida T, Yenush L, Davis R, White MF (2000) The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307). J Biol Chem 275:9047–9054
Bandyopadhyay GK, Yu JG, Ofrecio J, Olefsky JM (2005) Increased p85/55/50 expression and decreased phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in insulin-resistant human skeletal muscle. Diabetes 54:2351–2359
Bergström J, Hultman E (1966) Muscle glycogen synthesis after exercise: an enhancing factor localized to the muscle cells in man. Nature London 210:309–310
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brazilian Ministry of Health. Vigitel Brazil 2010: surveillance of risk and protective factors for chronic diseases through telephone survey. Brasilia: Office of Strategic and Participative Management, Bureau of Health Surveillance, Ministry of Health, 2011. p. 37
Christ-Roberts CY, Pratipanawatr T, Pratipanawatr W, Berria R, Belfort R, Mandarino LJ (2003) Increased insulin receptor signaling and glycogen synthase activity contribute to the synergistic effect of exercise on insulin action. J Appl Physiol 95:2519–2529
Chung J, Nguyen AK, Henstridge DC, Holmes AG, Chan MH, Mesa JL, Lancaster GI, Southgate RJ, Bruce CR, Duffy SJ, Horvath I, Mestril R, Watt MJ, Hooper PL, Kingwell BA, Vigh L, Hevener A, Febbraio MA (2008) HSP72 protects against obesity-induced insulin resistance. PNAS 105:1739–1744
Colditz GA, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Manson JE, Hennekens CH, Arky RA, Speizer FE (1990) Weight as a risk factor for clinical diabetes in women. Am J Epidemiol 132:501–513
Daviau A, Proulx R, Robitaille K, Di Fruscio M, Tanguay RM, Landry J, Patterson C, Durocher Y, Blouin R (2006) Down-regulation of the mixed-lineage dual leucine zipper-bearing kinase by heat shock protein 70 and its co-chaperone CHIP. J Biol Chem 281:31467–31477
Davis RJ (2000) Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103:239–252
De Fea K, Roth RA (1997) Protein kinase C modulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 tyrosine phosphorylation requires serine 612. Biochemistry 36:12939–12947
Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, Singh GM, Gutierrez HR, Lu Y, Bahalim AN, Farzadfar F, Riley LM, Ezzati M (2011) National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet 377:557–567
Garetto LP, Richter EA, Goodman MN, Ruderman NB (1984) Enhanced muscle glucose metabolism after exercise in the rat: the two phases. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 246:E471–E475
Geiger PC, Gupte AA (2011) Heat shock proteins are important mediators of skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 39:34–42
Geloneze B, Repetto EM, Geloneze SR, Tambascia MA, Ermetice MN (2006) The threshold value for insulin resistance (HOMAIR) in an admixtured population IR in the Brazilian Metabolic Syndrome Study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 72:219–220
Gupte AA, Bomhoff GL, Swerdlow RH, Geiger PC (2009) Heat treatment improves glucose tolerance and prevents skeletal muscle insulin resistance in rats fed a high-fat diet. Diabetes 58:567–578
Hirosumi J, Tuncman G, Chang L, Görgün CZ, Uysal KT, Maeda K, Karin M, Hotamisligil GS (2002) A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 420:333–336
Hotamisligil GS (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 140:900–917
Kline MP, Morimoto RI (1997) Repression of the heat shock factor 1 transcriptional activation domain is modulated by constitutive phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 17:2107–2115
Kurucz I, Morva A, Vaag A, Eriksson K, Huang X, Groop L, Koranyi L (2002) Decreased expression of heat shock protein 72 in skeletal muscle of patients with type 2 diabetes correlates with insulin resistance. Diabetes 51:1102–1109
Lee YH, Giraud J, Davis RJ, White MF (2003) c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) mediates feedback inhibition of the insulin signaling cascade. J Biol Chem 278:2896–2902
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Meriin AB, Yaglom JA, Gabai VL, Zon L, Ganiatsas S, Mosser DD, Zon L, Sherman MY (1999) Protein-damaging stresses activate c-Jun N-terminal kinase via inhibition of its dephosphorylation: a novel pathway controlled by HSP72. Mol Cell Biol 19:2547–2555
Myers J, Bellin D (2000) Ramp exercise protocols for clinical and cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Sports Med 30:23–29
O'Leary VB, Marchetti CM, Krishman RK, Stetzer BP, Gonzalez F, Kirwan JP (2006) Exercise-induced reversal of insulin resistance in obese elderly is associated with reduced visceral fat. J Appl Physiol 100:1584–1589
Park HS, Lee JS, Huh SH, Seo JS, Choi EJ (2001) Hsp72 functions as a natural inhibitory protein of c-Jun N-terminal kinase. EMBO J 20:446–456
Poole DC, Wilkerson DP, Jones AM (2008) Validity of criteria for establishing maximal O2 uptake during ramp exercise tests. Eur J Appl Physiol 102:403–410
Richter EA, Mikines KJ, Galbo H, Kiens B (1989) Effect of exercise on insulin action in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 66:876–888
Ropelle ER, Pauli JR, Prada PO, de Souza CT, Picardi PK, Faria MC, Cintra DE, Fernandes MF, Flores MB, Velloso LA, Saad MJ, Carvalheira JB (2006) Reversal of diet-induced insulin resistance with a single bout of exercise in the rat: the role of PTP1B and IRS-1 serine phosphorylation. J Physiol 577:997–1007
Sasai H, Sairenchi T, Iso H, Irie F, Otaka E, Tanaka K, Ota H, Muto T (2010) Relationship between obesity and incident diabetes in middle-aged and older Japanese adults: the Ibaraki Prefectural Health Study. Mayo Clin Proc 85:36–40
Schenk S, Horowitz JF (2007) Acute exercise increases triglyceride synthesis in skeletal muscle and prevents fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 117:1690–1698
Shafrir E (1996) Development and consequences of insulin resistance: lessons from animals with hyperinsulinaemia. Diabetes Metab 22:122–131
Simar D, Jacques A, Caillaud C (2012) Heat shock proteins induction reduces stress kinases activation, potentially improving insulin signalling in monocytes from obese subjects. Cell Stress Chaperones 17:615–621
Sinha R, Fisch G, Teague BRN, Tamborlane WV, Banyas RNB, Allen KRN, Savoye MRD, Rieger VMD, Taksali SMPH, Barbetta GRD, Sherwin RSE, Caprio S (2002) Prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance among children and adolescents with marked obesity. N Engl J Med 346:802–810
Uysal KT, Wiesbrock SM, Marino MW, Hotamisligil GS (1997) Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-alpha function. Nature 389:610–614
World Health Organization (2013) Global Health Observatory. Obesity. http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/risk_factors/obesity_text/en/index.html. Accessed 13 May 2013
Yi Z, Langlais P, De Filippis EA, Luo M, Flynn CR, Schroeder S, Weintraub ST, Mapes R, Mandarino LJ (2007) Global assessment of regulation of phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 by insulin in vivo in human muscle. Diabetes 56:1508–1516
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by CAPES (PNPD-2455/2011), FAPEMIG (CDS APQ01621-10), and CNPq (477154/2011-5) grants. The authors wish to acknowledge Dr. Valmor Alberto Augusto Tricoli of the University of São Paulo for teaching us the muscle biopsy technique, and Dr. David Lee Nelson for reviewing the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matos, M.A., Ottone, V.O., Duarte, T.C. et al. Exercise reduces cellular stress related to skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Cell Stress and Chaperones 19, 263–270 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-013-0453-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-013-0453-8