Abstract
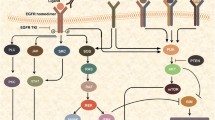
The understanding of the epidermal growth factor pathway in terms of intracellular signaling and its role in proliferation and cell survival has impacted the therapeutic management of many solid tumor malignancies in which this pathway has been dysregulated. Once the receptor is targeted at its cellular membrane level or tyrosine kinase domain, its blockage induces downregulation of oncogenic and tumorigenesis mechanisms which were in place, and thus inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of the malignant cell. Nowadays, we have several monoclonal antibodies as well as small molecules which target the receptor of epidermal growth factor. Although several receptors have been described within the human epidermal receptor family, our discussion will be focused on the impact of human epidermal receptor-1 as a therapeutic option for locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
http://www.cancer.net/patient/Cancer+Types/Head+and+Neck+Cancer. Accessed on 6 June 2009
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ (2007) Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin 57:43–66
Vermorken JB, Mesia R, Rivera F et al (2008) Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 359:1116–1127
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J et al (2006) Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 354:567–578
Vermorken JB, Remenar E, van Herpen C et al (2007) Cisplatin, fluorouracil, and docetaxel in unresectable head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 357:1695–1704
Posner MR, Hershock DM, Blajman CR et al (2007) Cisplatin and fluorouracil alone or with docetaxel in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 357:1705–1715
Calais G, Pointreau Y, Alfonsi M et al (2006) Randomized phase III trial comparing induction chemotherapy using cisplatin (P) fluorouracil (F) with or without docetaxel (T) for organ preservation in hypopharynx and larynx cancer. Preliminary results of GORTEC 2000-01. J Clin Oncol 24(18S):281s abstr 5506
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G et al (2003) Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial). J Clin Oncol 21:2237–2246
Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS et al (2003) Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA 290:2149–2158
Shepherd FA, Pereira J, Ciuleanu TE et al (2004) A randomized placebo-controlled trial of erlotinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cances (NSCLC) following failure on 1st line or 2nd line chemotherapy. A National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group (NCICCTG) trial. J Clin Oncol 22:622s abstr 7022
Cohen EE, Rosen F, Stadler WM et al (2003) Phase II trial of ZD1839 in recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol 21:1980–1987
Kirby AM, A’Hern RP, D’Ambrosio C et al (2006) Gefitinib (ZD1839, Iressa) as palliative treatment in recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer. Br J Cancer 94:631–636
Soulieres D, Senzer NN, Vokes EE, Hidalgo M, Agarwala SS, Siu LL (2004) Multicenter phase II study of erlotinib, an oral epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol 22:77–85
Belón J, Irigoyen A, Rodríguez I et al (2005) Preliminary results of a Phase II study to evaluate gefitinib combined with docetaxel and cisplatin in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol 23(16S):515s abstr 5563
Siu LL, Soulieres D, Chen EX et al (2007) Phase I/II trial of erlotinib and cisplatin in patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a Princess Margaret Hospital phase II consortium and National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study. J Clin Oncol 25:2178–2183
Burtness B, Goldwasser MA, Flood W, Mattar B, Forastiere AA (2005) Phase III randomized trial of cisplatin plus placebo compared with cisplatin plus cetuximab in metastatic/recurrent head and neck cancer: an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 23:8646–8654
Vermorken JB, Trigo J, Hitt R et al (2007) Open-label, uncontrolled, multicenter phase II study to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of cetuximab as a single agent in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck who failed to respond to platinum-based therapy. J Clin Oncol 25:2171–2177
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J (2003) Status of epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists in the biology and treatment of cancer. J Clin Oncol 21:2787–2799
Rogers SJ, Harrington KJ, Rhys-Evans P, O-Charoenrat P (2005) Biological significance of c-erbB family oncogenes in head and neck cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 24:47–69
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J (2006) Epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in cancer. Semin Oncol 33:369–385
Fry WH, Kotelawala L, Sweeney C, Carraway KL 3rd (2009) Mechanisms of ErbB receptor negative regulation and relevance in cancer. Exp Cell Res 315:697–706
Sok JC, Coppelli FM, Thomas SM, Lango MN, Xi S, Hunt JL, Freilino ML, Graner MW et al (2006) Mutant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFRvIII) contributes to head and neck cancer growth and resistance to EGFR targeting. Clin Cancer Res 12:5064–5073
Dassonville O, Formento JL, Francoual M et al (1993) Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor and survival in upper aerodigestive tract cancer. J Clin Oncol 11:1873–1878
Teman S, Kawaguchi H, El-Naggar AK et al (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor copy number alterations correlate with poor clinical outcome in patients with head and neck squamous cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:2164–2170
Magne N, Pivot X, Bensadoun RJ et al (2001) The relationship of epidermal growth factor receptor levels to the prognosis of unresectable pharyngeal cancer patients treated by chemo-radiotherapy. Eur J Cancer 37:2169–2177
Grandis JR, Melhem MF, Gooding WE et al (1998) Levels of TGF-alpha and EGFR protein in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and patient survival. J Natl Cancer Inst 90:824–832
Ciardiello F, Tortora G (2008) EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N Engl J Med 358:1160–1174
Le Tourneau C, Siu LL (2008) Molecular-targeted therapies in the treatment of squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Curr Opin Oncol 20:256–263
Hidalgo M, Siu LL, Nemunaitis J et al (2001) Phase I and pharmacologic study of OSI-774, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid malignancies. J Clin Oncol 19:3267–3279
Cohen EE, Kane MA, List MA et al (2005) Phase II trial of gefitinib 250 mg daily in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin Cancer Res 11:8418–8424
Bianchini D, Jayanth A, Chua YJ, Cunningham D (2008) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-related skin toxicity: mechanisms, treatment, and its potential role as a predictive marker. Clin Colorectal Cancer 7:33–43
Spano JP, Milano G, Vignot S, Khayat D (2008) Potential predictive markers of response to EGFR-targeted therapies in colorectal cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 66:21–30
Perez-Soler R, Van Cutsem E (2007) Clinical research of EGFR inhibitors and related dermatologic toxicities. Oncology 21:10–16
Thomas F, Rochaix P, Benlyazid A et al (2007) Pilot study of neoadjuvant treatment with erlotinib in nonmetastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13:7086–7092
Glisson BS, Saigal B, Xu Y, Johnson FM (2005) Sequence-dependent cytoxicity of docetaxel and erlotinib in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 25:abstr 6084
Agulnik M, Santos GC, Hedley D et al (2007) Predictive and pharmacodynamic biomarker studies in tumor and skin tissue samples of patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck treated with erlotinib. J Clin Oncol 25:2184–2190
Kim ES, Kies MS, Glisson BS et al (2007) Final results of a phase II study of erlotinib, docetaxel and cisplatin in patients with recurrent/metastatic head and neck cancer. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 25:abstr 6013
Chinnaiyan P, Huang S, Vallabhaneni G et al (2005) Mechanisms of enhanced radiation response following epidermal growth factor receptor signaling inhibition by erlotinib (Tarceva). Cancer Res 65:3328–3335
Savvides P, Agarwala SS, Greskovich J et al (2006) Phase I study of the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib in combination with docetaxel and radiation in locally advanced squamous cell cancer of the head and neck (SCCHN). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 24:abstr 5545
Herchenhorn D, Dias FL, Pineda RM et al (2007) Phase II study of erlotinib combined with cisplatin and radiotherapy for locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 25:abstr 6033
Huang S, Armstrong EA, Benavente S, Chinnaiyan P, Harari PM (2004) Dual-agent molecular targeting of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR): combining anti-EGFR antibody with tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res 64:5355–5362
Bozec A, Sudaka A, Fischel JL, Brunstein MC, Etienne-Grimaldi MC, Milano G (2008) Combined effects of bevacizumab with erlotinib and irradiation: a preclinical study on a head and neck cancer orthotopic model. Br J Cancer 99:93–99
Cohen EE, Davis DW, Karrison TG, Seiwert TY, Wong SJ, Nattam S, Kozloff MF, Clark JI et al (2009) Erlotinib and bevacizumab in patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a phase I/II study. Lancet Oncol 10:247–257
Blackledge G, Averbuch S (2004) Gefitinib (‘Iressa’, ZD1839) and new epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Br J Cancer 90:566–572
Wheeler RH, Jones D, Sharma P et al (2005) Clinical and molecular phase II study of gefitinib in patients with recurrent squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 23:abstr 5531
Choe MS, Chen Z, Cm Klass, Zhang X, Shin DM (2007) Enhancement of docetaxel-induced cytotoxicity by blocking epidermal growth factor receptor and cyclooxygenase-2 pathways in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin Cancer Res 13:3015–3023
Al-Hazzaa A, Bowen ID, Randerson P, Birchall MA (2005) The effect of ZD1839 (Iressa), an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in combination with cisplatin, on apoptosis in SCC-15 cells. Cell Prolif 38:77–86
Wirth LJ, Haddad RI, Wieczorek TJ et al (2004) Phase I study of gefitinib plus celecoxib in patients with metastatic and/or locally recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 22:abstr 5540
Stewart JS, Cohen EE, Licitra L et al (2009) Phase III study of gefitinib compared with intravenous methotrexate for recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol 27:1864–1871
Ochs JS (2004) Rationale and clinical basis for combining gefitinib (IRESSA, ZD1839) with radiation therapy for solid tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:941–949
Caponigro F, Romano C, Milano A et al (2008) A phase I/II trial of gefitinib and radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced inoperable squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Anticancer Drugs 9:739–744
Rueda A, Medina JA, Mesía R et al (2007) Gefitinib plus concomitant boost accelerated radiation (AFX-CB) and concurrent weekly cisplatin for locally advanced unresectable squamous cell head and neck carcinomas (SCCHN): a phase II study. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 25:abstr 6031
Doss HH, Greco FA, Meluch AA et al (2006) Induction chemotherapy + gefitinib followed by concurrent chemotherapy/radiation therapy/gefitinib for patients (pts) with locally advanced squamous carcinoma of the head and neck: a phase I/II trial of the Minnie Pearl Cancer Research Network. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 24:abstr 5543
Ahmed SM, Cohen EE, Haraf DJ et al (2007) Updated results of a phase II trial integrating gefitinib (G) into concurrent chemoradiation (CRT) followed by G adjuvant therapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer (HNC). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 25:abstr 6028
Chen C, Kane M, Song J et al (2007) Phase I trial of gefitinib in combination with radiation or chemoradiation for patients with locally advanced squamous cell head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:4880–4886
Matar P, Rojo F, Cassia R et al (2004) Combined epidermal growth factor receptor targeting with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib (ZD1839) and the monoclonal antibody cetuximab (IMC-C225): superiority over single-agent receptor targeting. Clin Cancer Res 10:6487–6501
Herbst RS, Heymach JV, Lippman SM (2008) Molecular origins of cancer: lung cancer. N Engl J Med 359:1367–1380
Chang SS, Califano J (2008) Current status of biomarkers in head and neck cancer. J Surg Oncol 97:640–643
Sheikh Ali MA, Gunduz M, Nagatsuka H et al (2008) Expression and mutation analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci 99:1589–1594
Lee JW, Soung YH, Kim SY et al (2005) Somatic mutations of EGFR gene in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin Cancer Res 11:2879–2882
Cohen EE, Lingen MW, Martin LE et al (2005) Response of some head and neck cancers to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors may be linked to mutation of ERBB2 rather than EGFR. Clin Cancer Res 11:8105–8108
Karamouzis MV, Grandis JR, Argiris A (2007) Therapies directed against epidermal growth factor receptor in aerodigestive carcinomas. JAMA 298:70–82
Erjala K, Sundvall M, Junttila TT et al (2006) Signaling via ErbB2 and ErbB3 associates with resistance and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) amplification with sensitivity to EGFR inhibitor gefitinib in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 12:4103–4111
Normanno N, Bianco C, De Luca A, Maiello MR, Salomon DS (2003) Target-based agents against ErbB receptors and their ligands: a novel approach to cancer treatment. Endocr Relat Cancer 10:1–21
Foon KA, Yang XD, Weiner LM et al (2004) Preclinical and clinical evaluations of ABX-EGF, a fully human anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:984–990
Fan Z, Lu Y, Wu X, Mendelsohn J (1994) Antibody-induced epidermal growth factor receptor dimerization mediates inhibition of autocrine proliferation of A431 squamous carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 269:27595–27602
Goldstein NI, Prewett M, Zuklys K, Rockwell P, Mendelsohn J (1995) Biological efficacy of a chimeric antibody to the epidermal growth factor in a human tumor xenograft model. Clin Cancer Res 1:1311–1318
Prewett M, Rockwell P, Rockwell RF et al (1996) The biologic effects of C225, a chimeric monoclonal antibody to the EGFR, on human prostate carcinoma. J Immunother Emphasis Tumor Immunol 19:419–427
Mendelsohn J, Fan Z (1997) Epidermal growth factor receptor family and chemosensitization. J Natl Cancer Inst 89:341–343
Saleh MN, Raisch KP, Stackhouse MA et al (1999) Combined modality therapy of A431 human epidermal cancer using anti-EGFr antibody C225 and radiation. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 14:451–463
Baselga J, Pfister D, Cooper MR et al (2000) Phase I studies of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor chimeric antibody C225 alone and in combination with cisplatin. J Clin Oncol 18:904–914
Robert F, Ezekiel MP, Spencer SA et al (2001) Phase I study of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody cetuximab in combination with radiation therapy in patients with advanced head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 19:3234–3243
Herbst RS, Arquette M, Shin DM et al (2005) Phase II multicenter study of the epidermal growth factor receptor antibody cetuximab and cisplatin for recurrent and refractory squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol 23:5578–5587
Baselga J, Trigo JM, Bourhis J et al (2005) Phase II multicenter study of the antiepidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with platinum-refractory metastatic and/or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol 23:5568–5577
Knoedler M, Gauler TC, Matzdorff A et al (2008) Phase II trial to evaluate efficacy and toxicity of cetuximab plus docetaxel in platinum pretreated patients with recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 26:332s, abstr 6066
Kuperman DI, Nussenbaum B, Thorstad W, Haughey B, Lewis J, Adkins D (2007) Retrospective analysis of the addition of cetuximab to induction chemotherapy (IC) with docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil (TPF-C) for locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (LA-HNSCC). J Clin Oncol 25:316s, abstr 6072
Tishler RB, Posner MR, Wirth LJ et al (2008) Cetuximab added to docetaxel, cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil Induction chemotherapy (C-TPF) in patients with newly diagnosed locally advanced head and neck cancer: a phase I study. J Clin Oncol 26(15S):316s abstr 6001
Bernier J, Domenge C, Ozsahin M et al (2004) Postoperative irradiation with or without concomitant chemotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 350:1945–1952
Cooper JS, Pajak TF, Forastiere AA et al (2004) Postoperative concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy for high-risk squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 350:1937–1944
Tsoutsou PG, Danielidis V, Koukourakis MI (2008) Cetuximab, cisplatin and amifostine during accelerated radiotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 26(15S):633s abstr 14582
Pfister DG, Su YB, Kraus DH et al (2006) Concurrent cetuximab, cisplatin, and concomitant boost radiotherapy for locoregionally advanced, squamous cell head and neck cancer: a pilot phase II study of a new combined-modality paradigm. J Clin Oncol 24:1072–1078
Yang XD, Jia XC, Corvalan JR, Wang P, Davis CG (2001) Development of ABX-EGF, a fully human anti-EGF receptor monoclonal antibody, for cancer therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 38:17–23
Yang XD, Jia XC, Corvalan JR et al (1999) Eradication of established tumors by a fully human monoclonal antibody to the epidermal growth factor receptor without concomitant chemotherapy. Cancer Res 59:1236–1243
Lynch DH, Yang XD (2002) Therapeutic potential of ABX-EGF: a fully human anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody for cancer treatment. Semin Oncol 29:47–50
Jia XC, Corvalan JRF, Zhang L et al (2000) Inhibition of vascular endothelial cell growth factor and interleukin-8 production in tumor and endothelial cell lines by a fully human monoclonal antibody to epidermal growth factor receptor. In: Proceedings of the 91st Annual Meeting of the American Association of Cancer Research, San Francisco, USA, p 290
Yang XD, Corvalan JRF, Wang P et al (2000) Inhibition of human cancer growth by ABX-EGF, a fully human anti-EGF receptor monoclonal antibody. In: Proceedings of the 91st Annual Meeting of the American Association of Cancer Research, San Francisco, USA, p 530
Van Cutsem E, Peeters M, Siena S et al (2007) Open-label phase III trial of panitumumab plus best supportive care compared with best supportive care alone in patients with chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:1658–1664
Wirth LJ, Posner MR, Tishler RB et al (2008) Phase I study of panitumumab + chemoradiotherapy (CRT) for head and neck cancer (HNC). J Clin Oncol 26:abstr 6007
Abidoye OO, Cohen EE, Wong SJ et al (2006) A phase II study of lapatinib (GW572016) in recurrent/metastatic (R/M) squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN). J Clin Oncol 24(18S):297s abstr 5568
Harrington KJ, El-Hariry IA, Holford CS et al (2009) Phase I study of lapatinib in combination with chemoradiation in patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol 27:1100–1107
http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00424255. Accessed on 6 June 2009
Bentzen SM, Atasoy BM, Daley FM et al (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in pretreatment biopsies from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma as a predictive factor for a benefit from accelerated radiation therapy in a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol 23:5560–5567
Rubin Grandis J, Melhem MF, Gooding WE et al (1998) Levels of TGF-alpha and EGFR protein in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and patient survival. J Natl Cancer Inst 90:824–832
Chung CH, Ely K, McGavran L et al (2006) Increased epidermal growth factor receptor gene copy number is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J Clin Oncol 24:4170–4176
Loeffler-Ragg J, Witsch-Baumgartner M, Tzankov A et al (2006) Low incidence of mutations in EGFR kinase domain in Caucasian patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 42:109–111
Willmore-Payne C, Holden JA, Layfield LJ (2006) Detection of EGFR and HER2-activating mutations in squamous cell carcinoma involving the head and neck. Mod Pathol 19:634–640
Van Cutsem E, Lang I, D’haens G et al (2008) KRAS status and efficacy in the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) treated with FOLFIRI with or without cetuximab: the CRYSTAL experience. J Clin Oncol 26:abstr 2
Bissada E, Abou-Chacra Z, Weng X et al (2008) Prevalence of K-RAS codon 12 mutations in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and influence with regards to response to chemoradiation therapy. J Clin Oncol 26:abstr 17005
Stoehlmacher J, Goekkurt E, Arnold D et al (2008) Associations between the EGFR status as well as KRAS mutations and clinical outcome in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients (pts) treated with erlotinib monotherapy in 2nd or 3rd line—a study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische O. J Clin Oncol 26:abstr 14574
http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=panitumumab+and+head+and+neck+cancer. Accessed on 6 June 2009
Conflict of interest statement
Luis E. Raez received research funding from Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Genentech, Imclone Systems Incorporated, and Sanofi-Aventis and serves as Speaker's Bureau for Genentech, Imclone System Incorporated, OSI Pharmaceuticals, and Sanofi-Aventis. Edgardo S. Santos has served as Speaker's Bureau for Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi-Aventis, and Amgen. Cesar A. Perez and Chancellor E. Donald have nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perez, C.A., Donald, C.E., Raez, L.E. et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor pathway as therapeutic development in head and neck cancers: present and future. Oncol Rev 3, 137–148 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12156-009-0022-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12156-009-0022-7