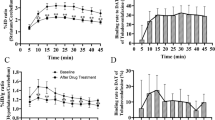
Abstract
For evaluating a newly developed radioligand for positron emission tomography (PET), successive measurements of regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) and the kinetics of the radioligand in the same subject are preferable in the first clinical trial. In this study, we demonstrate an example for the study of 11C-labeled 1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenethyl)-4-(3-phenylprophyl) piperazine (11C-SA4503) for mapping sigma1 receptors in the human brain. Five healthy male subjects underwent two successive PET scans with 15O-H2O to measure the rCBF and with 11C-SA4503 (dynamic 60-min scan). The brain kinetics of 11C-SA4503 was evaluated using the time-activity curve (TAC) of tissue in each of the 11 regions of the brain and the metabolite-corrected TAC of plasma on the basis of a two-tissue compartment fourparameter model. The estimated parameters were four rate constants: K 1, influx from plasma to brain tissue; k 2, efflux from tissue to plasma; k 3, association between tracer and receptors; and k 4, dissociation of tracer-receptor complex, and the binding potential (BP), k 3/k 4. 11CSA4503 was distributed all over the brain, and the TACs exhibited an accumulation pattern in all the 11 regions. K 1 of 11C-SA4503 correlated with rCBF, but the other three rate constant parameters and BP did not. The regional difference in the BP of 11C-SA4503 is compatible with those of sigma1 receptors. In conclusion, successive PET measurements of rCBF and the brain kinetics of radioligand-neuroreceptor binding are useful for the first clinical trial of a newly developed radioligand for mapping neuroreceptors, and the protocol is applicable to pathophysiological studies of brain disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carson RE. Interpretation of model rate constants. In: Valk PE, Bailey DL, Townsend DW, Maisey MN, editors. Positron emission tomography: basic science and clinical practice. London: Springer; 2003. p. 153–155.
Su TP. Delineating biochemical and functional properties of sigma receptors: emerging concepts. Crit Rev Neurobiol 1993;7:187–203.
Su TP, Hayashi T. Understanding the molecular mechanism of sigma-1 receptors: towards a hypothesis that sigma-1 receptors are intracellular amplifiers for signal transduction. Curr Med Chem 2003;10:2073–2080.
Junien JL, Leonard BE. Drugs acting on sigma and phencyclidine receptors: a review of their nature, function, and possible therapeutic importance. Clin Neuropharmacol 1989;12:353–374.
Mach RH, Smith CR, al-Nabulsi I, Whirrett BR, Childers SR, Wheeler KT. Sigma 2 receptors as potential biomarkers of proliferation in breast cancer. Cancer Res 1997;57:156–161.
Wheeler KT, Wang LM, Wallen CA, Childers SR, Cline JM, Keng PC, et al. Sigma-2 receptors as a biomarker of proliferation in solid tumours. Br J Cancer 2000;82:1223–1232.
Hashimoto K, Ishiwata K. Sigma receptor ligands: possible application as therapeutic drugs and as radiopharmaceuticals. Curr Pharm Des 2006;12:3857–3876.
Kawamura K, Ishiwata K, Tajima H, Ishii S, Matsuno K, Homma Y, et al. In vivo evaluation of [11C]SA4503 as a PET ligand for mapping CNS sigma1 receptors. Nucl Med Biol 2000;27:255–2561.
Kawamura K, Ishiwata K, Shimada Y, Kimura Y, Kobayashi T, Matsuno K, et al. Preclinical evaluation of [11C]SA4503: radiation dosimetry, in vivo selectivity and PET imaging of sigma1 receptors in the cat brain. Ann Nucl Med 2000;14:285–292.
Kawamura K, Kimura Y, Tsukada H, Kobayashi T, Nishiyama S, Kakiuchi T, et al. An increase of sigma1 receptors in the aged monkey brain. Neurobiol Aging 2003;24;745–752.
Sakata M, Kimura Y, Naganawa M, Oda K, Ishii K, Chihara K, et al. Mapping of human cerebral sigma1 receptors using positron emission tomography and [11C]SA4503. Neuroimage 2007;35:1–8.
Ishiwata K, Oda K, Sakata M, Kimura Y, Kawamura K, Oda K, et al. A feasible study of [11C]SA4503-PET for evaluating sigma1 receptor occupancy by neuroleptics: the binding of haloperidol to sigma1 and dopamine D2-like receptors. Ann Nucl Med 2006;20:569–573.
Ishikawa M, Ishiwata K, Ishii K, Kimura Y, Sakata M, Naganawa M, et al. High occupancy of sigma-1 receptors in the human brain after single oral administration of fluvoxamine: a PET study using [11C]SA4503. Biol Psychiatry 2007;62:878–883.
Mishina M, Ishiwata K, Ishii K, Kitamura S, Kimura Y, Kawamura K, et al. Function of sigma1 receptors in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand 2005;112:103–107.
Mishina M, Ohyama M, Ishii K, Kitamura S, Kimura Y, Oda K, et al. Low density of sigma1 receptors in early Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Nucl Med 2008;22:151–156.
Sakata M, Kimura Y, Naganawa M, Ishikawa M, Oda K, Ishii K, et al. Shortened protocol in practical [11C]SA4503-PET studies for the sigma1 receptor quantification. Ann Nucl Med 2008;22:143–146.
Iida H, Miura S, Kanno I, Murakami M, Takahashi K, Uemura K. Design and evaluation of HEADTOME-IV: a whole-body positron emission tomograph. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 1989;36:1006–1010.
Herscovitch P, Markham J, Raichle ME. Brain blood flow measured with intravenous H2 15O: I. Theory and error analysis. J Nucl Med 1983;24:782–789.
Mishina M, Senda M, Kimura Y, Toyama H, Ishiwata K, Ohyama M, et al. Intrasubject correlation between static scan and distribution volume images for [11C]flumazenil PET. Ann Nucl Med 2000;14:193–198.
Ardekani BA, Braun M, Hutton BF, Kanno I, Iida H. A fully automatic multimodality image registration algorithm. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1995;19:615–623.
Fukumitsu N, Ishii K, Kimura Y, Oda K, Sasaki T, Mori Y, et al. Imaging of adenosine A1 receptors in the human brain by positron emission tomography with [11C]MPDX. Ann Nucl Med 2003;17:511–515.
Shibuya H, Mori H, Toru M. Sigma receptors in schizophrenic cerebral cortices. Neurochem Res 1992;17:983–990.
Mash DC, Zabetian CP. Sigma receptors are associated with cortical limbic areas in the primate brain. Synapse 1992;12:195–205.
Okuyama S, Chaki S, Yae T, Nakazato A, Muramatsu M. Autoradiographic characterization of binding sites for [3H]NE-100 in guinea pig brain. Life Sci 1995;57:PL333–7.
Bouchard P, Quirion R. [3H]1,3-di(2-tolyl)guanidine and [3H](+)pentazocine binding sites in the rat brain: autoradiographic visualization of the putative sigma1 and sigma2 receptor subtypes. Neuroscience 1997;76:467–477.
Kitaichi K, Chabot JG, Moebius FF, Flandorfer A, Glossmann H, Quirion R. Expression of the purported sigma1 receptor in the mammalian brain and its possible relevance in deficits induced by antagonism of the NMDA receptor complex as revealed using an antisense strategy. J Chem Neuroanat 2000;20:375–387.
Kimura Y, Naganawa M, Sakata M, Ishikawa M, Mishina M, Oda K, et al. Distribution volume as an alternative to the binding potential for sigma1 receptor imaging. Ann Nucl Med 2007;21:533–535.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A part of this study was presented at the Seventh Annual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping at Brighton, UK June 10–14, 2001 [NeuroImage 2001;13(Number 6, Part 2 of 2 Parts) S984].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishiwata, K., Ishii, K., Kimura, Y. et al. Successive positron emission tomography measurement of cerebral blood flow and neuroreceptors in the human brain: an 11C-SA4503 study. Ann Nucl Med 22, 411–416 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-008-0133-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-008-0133-4