Abstract
Background
Liver stiffness measurement (LSM) can assess liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). We evaluated whether LSM can be used to assess changes in liver fibrosis during antiviral treatment using nucleos(t)ide analogs in patients with CHB.
Methods
We recruited 41 patients with CHB who had significant liver fibrosis, normal or slightly elevated serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels (≤2 × upper limit of normal), and detectable serum hepatitis B virus DNA before antiviral treatment. Patients in Group 1 (n = 23) and Group 2 (n = 18) underwent follow-up LSM after antiviral treatment for 1 and 2 years, respectively.
Results
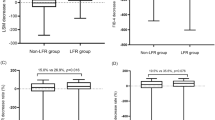
The mean age, ALT and LSM value of all patients (34 men and 7 women) before antiviral treatment were 46.6 ± 9.5 years, 40.6 ± 17.2 IU/L and 12.9 ± 8.6 kPa, respectively. Hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) was detected in 31 patients (75.6%). Fibrosis stage was F2 in 12 (29.3%), F3 in 6 (14.6%) and F4 in 23 (56.1%) patients. After antiviral treatment, LSM values and DNA positivity decreased significantly as compared to baseline (P = 0.018 and P < 0.001 in Group 1; P = 0.017 and P < 0.001 in Group 2, respectively), whereas ALT levels were unchanged (P = 0.063 in Group 1; P = 0.082 in Group 2).
Conclusions
Our preliminary data suggest that LSM can be used to assess liver fibrosis regression after antiviral treatment using nucleos(t)ide analogs in patients with CHB.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LB:
-
Liver biopsy
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B virus
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- CHB:
-
Chronic hepatitis B
- CHC:
-
Chronic hepatitis C
- CLD:
-
Chronic liver disease
- LSM:
-
Liver stiffness measurement
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- ULN:
-
Upper limit of normal
- HBsAg:
-
Hepatitis B surface antigen
- HBeAg:
-
Hepatitis B e antigen
- kPa:
-
Kilopascals
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- API:
-
Age–platelet count index
- APRI:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index
- ASPRI:
-
Age–spleen–platelet ratio index
- SVR:
-
Sustained viral response
References
Benyon RC, Iredale JP. Is liver fibrosis reversible? Gut 2000;46:443–446
Bonis PA, Friedman SL, Kaplan MM. Is liver fibrosis reversible? N Engl J Med 2000;344:452–454
Wanless IR, Nakashima E, Sherman M. Regression of human cirrhosis. Morphologic features and the genesis of incomplete septal cirrhosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:1599–1607
Kaplan MM, DeLellis RA, Wolfe HJ. Sustained biochemical and histologic remission of primary biliary cirrhosis in response to medical treatment. Ann Intern Med 1997;126:981–985
Hammel P, Couvelard A, O’Toole D, Ratouis A, Sauvanet A, Flejou JF, et al. Regression of liver fibrosis after biliary drainage in patients with chronic pancreatitis and stenosis of the common bile duct. N Engl J Med 2000;344:418–423
Shiratori Y, Lmazeki F, Moriyama M, Yano M, Arakawa Y, Yokosuka O, et al. Histologic improvement of fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C who have sustained response to interferon treatment. Ann Intern Med 2000;132:517–524
Poynard T, McHutchison J, Manns M, Trepo C, Lindsay K, Goodman Z, et al. Impact of pegylated interferon alfa-2b and ribavirin on liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2002;122:1303–1313
Lai CL, Chien RN, Leung NWY, Chang TT, Guan R, Tai DI, et al. A one-year trial of lamivudine for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 1998;339:61–68
Dienstag JL, Schiff ER, Wright TL, Perrillo RP, Hann HWL, Goodman Z, et al. Lamivudine as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis B in the United States. N Engl J Med 1999;341:1256–1263
Schalm SW, Heathcote J, Cianciara J, Farrell G, Sherman M, Willems B, et al. Lamivudine and alpha-interferon combination treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis B infection: a randomised trial. Gut 2000;46:562–568
Dienstag JL, Goldin RD, Heathcote EJ, Hann HW, Woessner M, Stephenson SL, et al. Histological outcome during long-term lamivudine treatment. Gastroenterology 2003;124:105–117
Wright TL. Introduction to chronic hepatitis B infection. Am J Gastroenterol 2006;101(Suppl 1):S1–S6
Fraquelli M, Rigamonti C, Casazza G, Conte D, Donato MF, Ronchi G, et al. Reproducibility of transient elastography in the evaluation of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease. Gut 2007;56:968–973
Ganne-Carrié N, Ziol M, de Ledinghen V, Douvin C, Marcellin P, Castera L, et al. Accuracy of liver stiffness measurement for the diagnosis of cirrhosis in patients with chronic liver diseases. Hepatology 2006;44:1511–1517
Sandrin L, Fourquet B, Hasquenoph JM, Yon S, Fournier C, Mal F, et al. Transient elastography: a new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Ultrasound Med Biol 2003;29:1705–1713
de Ledinghen V, Foucher J, Castera L, Bernard PH, Salzmann M, Moisset G, et al. Evaluation of fibrosis regression using non-invasive methods in very long-term follow-up of HCV responder patients. Hepatology 2006;44(Suppl 1):317A
Hezoda C, Castera L, Rosa I, Roulot D, Leroy V, Bouvier-Alias M, et al. Dynamics of liver stiffness during peginterferon alpha-ribavirin treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2007;46(Suppl 1):366–367
Colleta C, Smirne C, Fabris C, Foscolo AM, Toniutto P, Rapetti R, et al. Regression of fibrosis among long-term responders to antiviral treatment for chronic viral hepatitis. Hepatology 2007;46(Suppl 1):300–301
Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2007;45:507–539
Kim DY, Kim SU, Ahn SH, Park JY, Lee JM, Park YN, et al. Usefulness of FibroScan for detection of early compensated liver cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis B. Dig Dis Sci 2009;54:1758–1763
Kim SU, Ahn SH, Park JY, Kang W, Kim DY, Park YN, et al. Liver stiffness measurement in combination with non-invasive markers for the improved diagnosis of B-viral liver cirrhosis. J Clin Gastroenterol 2009;43:267–271
Poynard T, Bedossa P. Age and platelet count: a simple index for predicting the presence of histological lesions in patients with antibodies to hepatitis C virus. METAVIR and CLINIVIR Cooperative Study Groups. J Viral Hepat 1997;4:199–208
Wai CT, Greenson JK, Fontana RJ, Kalbfleisch JD, Marrero JA, Conjeevaram HS, et al. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003;38:518–526
Kim BK, Kim SA, Park YN, Cheong JY, Kim HS, Park JY, et al. Noninvasive models to predict liver cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int 2007;27:969–976
Poynard T, Bedossa P, Opolon P. Natural history of liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. The OBSVIRC, METAVIR, CLINIVIR, and DOSVIRC groups. Lancet 1997;349:825–832
Bravo AA, Sheth SG, Chopra S. Liver biopsy. N Engl J Med 2001;344:495–500
Schiff E, Simsek H, Lee WM, Chao YC, Sette H Jr, Janssen HL, et al. Efficacy and safety of entecavir in patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 2008;103:2776–2783
Kweon YO, Goodman ZD, Dienstag JL, Schiff ER, Brown NA, Burchardt E, et al. Decreasing fibrogenesis: an immunohistochemical study of paired liver biopsies following lamivudine treatment for chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2001;35:749–755
Myers RP, Tainturier MH, Ratziu V, Piton A, Thibault V, Imbert-Bismut F, et al. Prediction of liver histological lesions with biochemical markers in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2003;39:222–230
Arena U, Vizzutti F, Corti G, Ambu S, Stasi C, Bresci S, et al. Acute viral hepatitis increases liver stiffness values measured by transient elastography. Hepatology 2007;47:380–384
Coco B, Oliveri F, Maina AM, Ciccorossi P, Sacco R, Colombatto P, et al. Transient elastography: a new surrogate marker of liver fibrosis influenced by major changes of transaminases. J Viral Hepat 2007;14:360–369
Sagir A, Erhardt A, Schmitt M, Häussinger D. Transient elastography is unreliable for detection of cirrhosis in patients with acute liver damage. Hepatology 2008;47:592–595
Kim SU, Kim DY, Park JY, Lee JH, Ahn SH, Kim JK, et al. How can we enhance the performance of liver stiffness measurement using FibroScan® in diagnosing liver cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Clin Gastroenterol 2009 (Epub ahead of print)
Chan HL, Wong GL, Choi PC, Chan AW, Chim AM, Yiu KK, et al. Alanine aminotransferase-based algorithms of liver stiffness measurement by transient elastography (Fibroscan) for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat 2009;16:36–44
Park JY, Park YN, Kim DY, Paik YH, Lee KS, Moon BS, et al. High prevalence of significant histology in asymptomatic chronic hepatitis B patients with genotype C and high serum HBV DNA levels. J Viral Hepat 2008;15:615–621
Vergniol J, Foucher J, Castéra L, Bernard PH, Tournan R, Terrebonne E, et al. Changes of non-invasive markers and FibroScan values during HCV treatment. J Viral Hepat 2009;16:132–140
Han Kim SU, KH Park JY, Ahn SH, Chung MJ, Chon CY, et al. Liver stiffness measurement using FibroScan is influenced by serum total bilirubin in acute hepatitis. Liver Int 2009;29:810–815
Wong GL, Wong VW, Choi PC, Chan AW, Chim AM, Yiu KK, et al. Increased liver stiffness measurement by transient elastography in severe acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;24:1002–1007
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Grant of the Good Health R&D Project from the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A050021), and in part by Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science. The authors wish to thank Joon Seong Kim, Ji Won Kim and Jeong Min Cho for their critical comments and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.U., Park, J.Y., Kim, D.Y. et al. Non-invasive assessment of changes in liver fibrosis via liver stiffness measurement in patients with chronic hepatitis B: impact of antiviral treatment on fibrosis regression. Hepatol Int 4, 673–680 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-010-9201-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-010-9201-7