Abstract
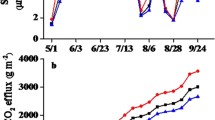
Changes in the composition of plant species induced by grassland degradation may alter soil respiration rates and decrease carbon sequestration; however, few studies in this area have been conducted. We used net primary productivity (NPP), microbial biomass carbon (MBC), and soil organic carbon (SOC) to examine the changes in soil respiration and carbon balance in two Chinese temperate grassland communities dominated by Leymus chinensis (undisturbed community; Community 1) and Puccinellia tenuiflora (degraded community; Community 2), respectively. Soil respiration varied from 2.5 to 11.9 g CO2 m−2 d−1 and from 1.5 to 9.3 g CO2 m−2 d−1, and the contribution of root respiration to total soil respiration from 38% to 76% and from 25% to 72% in Communities 1 and 2, respectively. During the growing season (May–September), soil respiration, shoot biomass, live root biomass, MBC and SOC in Community 2 decreased by 28%, 39%, 45%, 55% and 29%, respectively, compared to those in Community 1. The considerably lower net ecosystem productivity in Community 2 than in Community 1 (104.56 vs. 224.73 g C m−2 yr−1) suggests that the degradation has significantly decreased carbon sequestration of the ecosystems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANPP:
-
above-ground net primary productivity
- BNPP:
-
below-ground net primary productivity
- MBC:
-
microbial biomass carbon
- MR:
-
microbial respiration
- NEP:
-
net ecosystem production
- NPP:
-
net primary productivity
- SOC:
-
soil organic carbon
References
Behera N, Joshi S K and Pati D P 1990 Root contribution to total soil metabolism in a tropical forest soil from Orissa, India; Forest Ecol. Manag. 36 125–134
Bolstad P V, Raich P and Lee T 2003 Rapid temperature acclimation of leaf respiration rates in Quercus alba and Quercus rubra; Tree Physiol. 23 969–976
Boone R D, Nadelhoffer K J and Canary J D 1998 Roots exert a strong influence on the temperature sensitivity of soil respiration; Nature (London) 396 570–572
Buyanovsky G A, Kucera C L and Wagner G H 1987 Comparative analyses of carbon dynamics in native and cultivated ecosystems; Ecology 68 2023–2031
Cao G M, Tang Y H, Mo W H, Wang Y S, Li Y N and Zhao X Q 2004 Grazing intensity alters soil respiration in an alpine meadow on the Tibetan plateau; Soil Biol. Biochem. 36 237–243
Conant R T, Paustian K and Elliott E T 2001 Grassland management and conversion into grassland: effects on soil carbon. Ecol. Appl. 11 342–355
Cox P M, Betts R A, Jones C D, Spall S A and Totterdell I J 2000 Acceleration of global warming due to carbon-cycle feedbacks in a coupled climate model; Nature (London) 408 184–187
Dahlman R C and Kucera C L 1965 Root production and turnover in native prairie; Ecology 46 84–88
Dugas W A, Heuer M and Mayeux H S 1999 Carbon dioxide fluxes over bermuda grass, native prairie, and sorghum; Agric. For. Meteorol. 93 121–139
Fang C and Moncrieff J B 2001 The dependence of soil CO2 efflux on temperature; Soil Biol. Biochem. 33 155–165
Frank A B 2002 Carbon dioxide fluxes over a grazed prairie and seeded pasture in the Northern Great Plains. Environ. Pollut. 116 397–403
Fu S and Cheng W 2004. Defoliation affects rhizosphere respiration and rhizosphere priming effect on decomposition of soil organic matter under a sunflower species: Helianthus annuus; Plant Soil 263 345–352
Guo L B and Gifford R M 2002 Soil carbon stocks and land use change: a metaanalysis; Global Change Biol. 8 345–360
Gupta S R and Singh J S 1981 Soil respiration in a tropical grassland; Soil Biol. Biochem. 13 261–268
Hanson P J, Edwards N T, Garten C T and Andrew J A 2000 Separating root and soil microbial contribution to soil respiration: a review of methods and observations; Biogeochemistry 48 115–146
Hill P W, Marshall C M, Harmens H, Jones D L and Farrar J F 2004 Carbon sequestration: do N inputs and elevated atmospheric CO2 alter soil solution chemistry and respiratory C losses?; Water Air Soil Pollut.: Focus 4 177–186
Iwaki H 1973 Matter production of terrestrial plant communities II, grasslands (Kyoritu Press), pp 32–45 (in Japanese)
Jackson R B, Canadell J, Ehleringer J R, Mooney H A, Sala O E and Schulze E D 1996 A global analysis of root distributions for terrestrial biomes; Oecologia 108 389–411
Jia B, Zhou G, Wang F, Wang Y, Yuan W and Zhou L 2006 Partitioning root and microbial contributions to soil respiration in Leymus chinensis populations; Soil Biol. Biochem. (in press)
Joergensen R G 1996 The fumigation-extraction method to estimate soil microbial biomass: calibration of the KEC value; Soil Biol. Biochem. 28 25–31
Jones M B and Donnelly A 2004 Carbon sequestration in temperate grassland ecosystems and the influence of management, climate and elevated CO2; New Phytologist 164 423–439
Kelliher F M, Ross D J, Law B E, Baldocchi D D and Rodda N J 2004 Limitations to carbon mineralization in litter and mineral soil of young and old ponderosa pine forests; For. Ecol. Manag. 191 201–213
Kirschbaum M U F 1995 The temperature dependence of soil organic matter decomposition, and the effect of global warming on soil organic matter; Soil Biol. Biochem. 27 753–760
Kucera C L and Kirkham D R 1971 Soil respiration studies in tallgrass prairie in Missouri; Ecology 52 912–915
Kuzyakov Y 2006 Sources of CO2 efflux from soil and review of partitioning methods; Soil Biol. Biochem. 38 425–448
Li L H, Han X G, Wang Q B, Chen Q S, Zhang Y, Yang J, Bai W M, Song S H, Xing X R and Zhang S M 2002 [Separating root and soil microbial contributions to total soil respiration in a grazed grassland in the Xilin River Basin;] Acta Phytoecol. Sinica 26 29–32 (in Chinese)
Li L H, Li X, Bai W M, Wang Q B, Yan Z D, Yuan Z Y, Dong Y Z. 2004. [Soil carbon budget of a grazed Leymus chinensis steppe community in the Xilin River Basin of Inner Mongolia;] Acta Phytoecol. Sinica 28 312–317 (in Chinese)
Li L H, Wag Q B, Bai Y F, Zhou G S and Xing X R 2000 [Soil respiration of a Leymus chinensis grassland stand in the Xilin River Basin as affected by over-grazing and climate;] Acta Phytoecol. Sinica 24 680–686 (in Chinese)
Melillo J M P, Steudler A, Aber J D, Newkirk K, Lux H, Bowles F P, Catricala C, Magill A, Ahrens T and Morrisseau S 2002 Soil warming and carbon-cycle feedbacks to the climate system; Science 298 13
Mizue O, Koichiro G and Akira S 2000 Contribution of root respiration to total soil respiration in a Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don) artificial forest; Ecol. Res. 15 323–333
Nelson D W and Sommers L E 1982 Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter; in Methods of soil analysis. Part 2 (eds) A L Page et al (Madison, W I: ASA Publication No. 9) 2nd edition pp 539–577
Nina B 2000 Biotic and abiotic factors controlling soil respiration rates in Picea abies stands; Soil Biol. Biochem. 32 1625–1635
Norman J M Garica R and Verma S B 1992 Soil surface CO2 fluxes and the carbon budget of a grassland; J. Geophys. Res. 97 18845–18853
Oleksyn J, Zytkowiak R, Karolewski P, Reich P B and Tjoelker M G 2000 Genetic and environmental control of seasonal carbohydrate dynamics in trees of diverse Pinus sylvestris populations; Tree Physiol. 20 837–847
Raich J W and Potter C S 1995 Global patterns of carbon dioxide emissions from soils; Global Biogeochem. Cycles 9 23–26
Raich J W and Schlesinger W H 1992 The global carbon dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate; Tellus 44B 81–99
Raich J W and Tufekcioglu A 2000 Vegetation and soil respiration: correlations and controls; Biogeochemistry 48 71–90
Reichstein M, Rey A, Freibauer A, Tenhunen J, Valentini R, Banza J, Casals P, Cheng Y F, et al 2003 Modeling temporal and large-scale spatial variability of soil respiration from soil water availability, temperature and vegetation productivity indices; Global Biogeochem. Cycles 17 1029–1104
Rey A, Pegoraro E, Tedeschi V, De Parri, De Parri I, Jarvis P G and Valentini R 2002 Annual variation in soil respiration and its components in a coppice oak forest in Central Italy; Global Change Biol. 8 851–866
Rochette P and Flanagan L B 1997 Quantifying rhizosphere respiration in a corn crop under field conditions; Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 61 466–474
Rochette P, Gregorich E G and Desjardins R L 1992 Comparison of static and dynamic closed chambers for measurement of soil respiration under field conditions; Can. J. Soil Sci. 72 605–609
Rustad L E, Huntington T G. and Boone R D 2000 Controls on soil respiration: implications for climate change; Biogeochemistry 49 1–6
Ryan M G and Law B E 2005 Interpreting, measuring, and modeling soil respiration; Biogeochemistry 73 3–27
Ryan M G, Binkley D, Fownes J H, Giardina C P and Senock R S 2004 An experimental test of the causes of forest growth decline with stand age; Ecol. Monogr. 74 393–414
Ryan M G, Hubbard R M, Pongracic S, Raison R J and McMurtrie R E 1996 Foliage, fine-root, woody-tissue and stand respiration in Pinus radiate in relation to nutrient status; Tree Physiol. 16 333–343
Schlesinger W H and Andrews J A 2000 Soil respiration and the global carbon cycle; Biogeochemistry 48 7–20
Schulze E D, Valentini R and Sanz M J 2002 The long way from Kyoto to Marrakesh: Implications of the Kyoto Protocol negotiations for global ecology; Global Changes Biol. 8 505–518
Schuman G E, Janzen H H and Herrick J E 2002 Soil carbon dynamics and potential carbon sequestration by rangelands. Environ. Pollut. 116 391–396
Vance E D, Brookes P C and Jenkinson D S 1987 An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C; Soil Biol. Biochem. 19 703–707
Wang R Z and Earle A R 1997 Effects of grazing on a Leymus chinensis grassland on the Songnen plain of northeastern China; J. Arid Environ. 36 307–318
Wang W, Ose K J, Liu J J, Mo W H and Oikawa T 2005 Contribution of root respiration to soil respiration in a C3/C4 mixed grassland; J. Biosci. 30 507–514
Xiao X M, Wang Y F, Jiang S, Ojima D S and Bonham C D 1995 Interannual variation in the climate and shoot biomass of Leymus chinensis steppe and Stipa grandis steppe in the Xilin river basin, Inner Mongolia, China; J. Arid Environ. 31 283–299
Zan C S, Fyles J W, Girouard P and Samson R A 2001 Carbon sequestration in perennial bioenergy, annual corn and uncultivated systems in southern Quebec. Agric. Ecosystem Environ. 86 135–144
Zhang Y, Li L H, Wang Y F, Tang F, Cheng Q S, Yang J, Yuan Z Y and Dong Y S 2003 Comparison of soil respiration in two grass-dominated communities in the Xilin River Basin: correlations and controls; Acta Bot. Sin. 45 1024–1029
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Guo, J. & Oikawa, T. Contribution of root to soil respiration and carbon balance in disturbed and undisturbed grassland communities, northeast China. J Biosci 32, 375–384 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-007-0036-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-007-0036-x