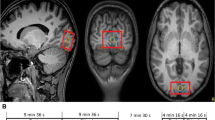
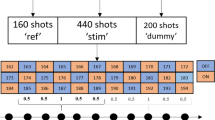
Abstract
N-acetyl-l-aspartic acid (NAA), an amino acid synthesized and stored primarily in neurons in the brain, has been proposed to be a molecular water pump (MWP) whose function is to rapidly remove water from neurons against a water gradient. In this communication, we describe the results of a functional 1H proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (fMRS) study, and provide evidence that in the human visual cortex, over a 10-min period of visual stimulation, there are stimulation-induced graded changes in the NAA MRS signal from that of a preceding 10-min baseline period with a decline in the NAA signal of 13.1% by the end of the 10-min stimulation period. Upon cessation of visual stimulation, the NAA signal gradually increases during a 10-min recovery period and once again approaches the baseline level. Because the NAA MRS signal reflects the NAA concentration, these changes indicate rapid focal changes in its concentration, and transient changes in its intercompartmental metabolism. These include its rates of synthesis and efflux from neurons and its hydrolysis by oligodendrocytes. During stimulation, the apparent rate of NAA efflux and hydrolysis increased 14.2 times, from 0.55 to 7.8 μmol g−1 h−1. During recovery, the apparent rate of synthesis increased 13.3 times, from 0.55 to 7.3 μmol g−1 h−1. The decline in the NAA signal during stimulation suggests that a rapid increase in the rate of NAA-obligated water release to extracellular fluid (ECF) is the initial and seminal event in response to neurostimulation. It is concluded that the NAA metabolic cycle in the visual cortex is intimately linked to rates of neuronal signaling, and that the functional cycle of NAA is associated with its release to ECF, thus supporting the hypothesis that an important function of the NAA metabolic cycle is that of an efflux MWP.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ac:
-
acetate
- AcCoA:
-
acetyl-coenzyme A
- Asp:
-
aspartic acid
- ATP:
-
adenosine triphosphate
- AQP4:
-
aquaporin 4
- BOLD:
-
blood oxygen level-dependent imaging
- CI:
-
confidence interval
- ECF:
-
extracellular fluid
- ECS:
-
extracellular space
- fMRS:
-
functional magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- Glc:
-
glucose
- GLUT 1:
-
Glc transporter 1
- 1H MRS:
-
proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- MRS:
-
magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- NAA:
-
N-acetyl-l-aspartic acid
- NAAG:
-
N-acetylaspartylglutamic acid
- NMR:
-
nuclear magnetic resonance
- tNAA:
-
total NAA + NAAG
- ROI:
-
region of interest
- SNR:
-
signal to noise ratio
References
Baslow, M. H. (1999). The existence of molecular water pumps in the nervous system. A review of the evidence. Neurochemistry International, 34, 77–90.
Baslow, M. H. (2000). Functions of N-acetyl-L-aspartate and N-acetyl-L-aspartylglutamate in the vertebrate brain. Role in glial cell-specific signaling. Journal of Neurochemistry, 75, 453–459.
Baslow, M. H. (2002). Evidence supporting a role for N-acetyl-L-aspartate as a molecular water pump in myelinated neurons in the central nervous system. An analytical review. Neurochemistry International, 40(4), 295–300.
Baslow, M. H. (2003). N-acetylaspartate in the vertebrate brain: Metabolism and function. Neurochemical Research, 28(6), 941–953.
Baslow, M. H., & Guilfoyle, D. N. (2002). Effect of N-acetylaspartic acid on the diffusion coefficient of water: A proton magnetic resonance phantom method for measurement of osmolyte-obligated water. Analytical Biochemistry, 311(2), 133–138.
Baslow, M. H., & Guilfoyle, D. N. (2006). Functions of N-acetylaspartate and N-acetylaspartylglutamate in brain: Evidence of a role in maintenance of higher brain integrative activities of information processing and cognition. Advances in Experimental Medicine & Biology, 576, 95–112.
Baslow, M. H., & Guilfoyle, D. N. (2006). Using proton magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy to understand brain “activation.” Brain and Language (in press). DOI 10.1016/s.band1.2006.06.119.
Battistuta, J., Bjartmar, C., & Trapp, B. D. (2001). Postmortem degradation of N-acetyl aspartate and N-acetyl aspartylglutamate: An HPLC analysis of different rat CNS regions. Neurochemical Research, 26, 695–702.
Bottomley, P. A. (1987). Spatial localization in NMR spectroscopy in vivo. Annals of the New York Academy of Science, 508, 333–348.
Boucard, C. C., Mostert, J. P., Cornelissen, F. W., De Keyser, J., Oudkerk, M., & Sijens, P. E. (2005). Visual stimulation, 1H MR spectroscopy and fMRI of the human visual pathways. European Radiology, 15, 47–52.
Chen, W., Novotny, E. J., Zhu, X.-H., Rothman, D. L., & Shulman, R. G. (1993). Localized 1H NMR measurement of glucose consumption in the human brain during visual stimulation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 90, 9896–9900.
Duc, C. O., Weber, O. M., Trabesinger, A. H., Meier, D., & Boesiger, P. (1998). Quantitative 1H MRS of the human brain in vivo based on the simulation phantom calibration strategy. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 39, 491–496.
Escartin, C., Valette, J., Lebon, V., & Bonvento, G. (2006). Neuron–astrocyte interactions in the regulation of brain energy metabolism: A focus on NMR spectroscopy. Journal of Neurochemistry, 99, 393–401.
Fatouros, P. P., Heath, D. L., Beaumont, A., Corwin, F. D., Signoretti, S., Al-Samsam, R. H., et al. (2000). Comparison of NAA measures by MRS and HPLC. Acta Neurochirurgica, 76, 35–37.
Frahm, J., Kruger, G., Merboldt, K. D., & Kleinschmidt, A. (1996). Dynamic uncoupling and recoupling of perfusion and oxidative metabolism during focal brain activation in man. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 35, 143–148.
Katz-Brull, R., Alsop, D. C., Marquis, R. P., & Lenkinski, R. E. (2006). Limits on activation-induced temperature and metabolic changes in the human primary visual cortex. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 56, 348–355.
Kaul, R., Casanova, J., Johnson, A. B., Tang, P., & Matalon, R. (1991). Purification, characterization, and localization of aspartoacylase from bovine brain. Journal of Neurochemistry, 56, 129–135.
Kimelberg, H. K. (2004). Water homeostasis in the brain: Basic concepts. Neuroscience, 129, 851–860.
Kobayashi, H., Minami, S.-I., Itoh, S., Shiraishi, S., Yokoo, H., Yanagita, T., et al. (2001). Aquaporin subtypes in rat cerebral microvessels. Neuroscience Letters, 297, 163–166.
Le Bihan, D., Urayama, S.-I., Aso, T., Hanakawa, T., & Fukuyama, H. (2006). Direct and fast detection of neuronal activation in the human brain with diffusion MRI. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(21), 8263–8268.
Maddock, R. J., Buonocore, M. H., Lavoie, S. P., Copeland, L. E., Kile, S. J., Richards, A. L., et al. (2006). Brain lactate responses during visual stimulation in fasting and hyperglycemic subjects: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study at 1.5 Tesla. Psychiatry Research, 148, 47–54.
Masson, J.-B., Sauviat, M.-P., Martin, J.-L., & Gallot, G. (2006). Ionic contrast terahertz near-field imaging of axonal water fluxes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(13), 4808–4812.
Meinild, A.-K., Klaerke, D. A., Loo, D. D. F., Wright, E. M., & Zeuthen, T. (l998). The human Na+-glucose cotransporter is a molecular water pump. Journal of Physiology, 508(1), l5–21.
Merboldt, K. D., Bruhn, H., Hanicke, W., Michaelis, T., & Frahm, J. (1992). Decrease of glucose in the human visual cortex during photic stimulation. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 25, 187–194.
Moffett, J. R., Ross, B., Arun, P., Madhavarao, C.N., & Namboodiri, A. M. A. (2007). N-acetylaspartate in the CNS: From neurodiagnostics to neurobiology. Progress Neurobiology, 81, 89–131.
Patel, A. B., de Graaf, R. A., Mason, G. F., Kanamatsu, T., Rothman, D. L., Shulman, R. G., et al. (2004). Glutamatergic neurotransmission and neuronal glucose oxidation are coupled during intense neuronal activation. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 24(9), 972–985.
R Development Core Team (2006). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing, ISBN 3-900051-07-0.
Sager, T. N., Laursen, H., Fink-Jensen, A., Topp, S., Stennsgaard, A., Hedehus, M., et al. (1999). N-acetylaspartate distribution in rat brain striatum during acute brain ischemia. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 19, 164–172.
Sarchielli, P., Tarducci, R., Presciutti, O., Gobbi, G., Pelliccioli, G. P., Stipa, G., et al. (2005) Functional 1H-MRS findings in migraine patients with and without aura assessed interictally. Neuroimage, 24, 1025–1031.
Traber, F., Block, W., Freymann, N., Gur, O., Kucinski, T., Hammen, T., et al. (2006). A multicenter reproducibility study of single-voxel 1H-MRS of the medial temporal lobe. European Radiology, 16, 1096–1103.
Urrila, A. S., Hakkarainen, A., Heikkinen, S., Huhdankoski, O., Kuusi, T., Stenberg, D., et al. (2006). Preliminary findings of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in occipital cortex during sleep deprivation. Psychiatry Research, 147, 41–46.
Vrenken, H., Barkhof, F., Uitdehaag, B. M. J., Castelijns, J. A., Polman, C. H., & Pouwels, P. J. W. (2005). MR spectroscopic evidence for glial increase but not for neuro-axonal damage in MS normal-appearing white matter. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 53, 256–266.
Wellard, R. M., Briellmann, R. S., Jennings, C., & Jackson, G. D. (2005). Physiologic variability of single-voxel proton MR spectroscopic measurements at 3T. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 26, 585–590.
Zhu, X.-H., & Chen, W. (2001). Observed BOLD effects on cerebral metabolite resonances in human visual cortex during visual stimulation: A functional 1H MRS study at 4 T. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 46, 841–847.
Acknowledgement
This study was supported in part by a grant from the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (1 R21 EB004727-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baslow, M.H., Hrabe, J. & Guilfoyle, D.N. Dynamic Relationship Between Neurostimulation and N-Acetylaspartate Metabolism in the Human Visual Cortex. J Mol Neurosci 32, 235–245 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-007-0049-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-007-0049-9