Abstract
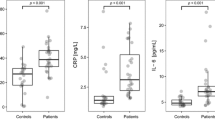
This study was aimed to analyse the prevalence of antinuclear antibodies in patients with psoriasis after treatment with infliximab and correlates the development of antibodies with both response to treatment and adipokines levels. Serum levels of ANA, anti-dsDNA, anti-histone, anti-nucleosome and anti-ENA antibodies at baseline after 2 and 12 months of treatment with infliximab were measured in 27 patients with psoriasis, as well as in 27 matched controls. Serum C-reactive protein (CRP), chemerin, visfatin and resistin were also assessed. The prevalence of ANA increased from 22 to 37 % and 63 % (p < 0.01) during treatment with infliximab, with a gradual progressive increase both in ANA titre and in percentage of ANA pattern. The prevalence of other antibodies also increased from 7 to 30 % and 48 % (p < 0.01) for anti-ds-DNA and from 7 to 26 % and 37 % for anti-nucleosome antibodies (p < 0.05), whereas the prevalence of anti-histone and anti-ENA antibodies was unchanged throughout the study period. Basal chemerin, resistin and CRP levels were higher in patients than in controls, and their levels progressively normalized during treatment (p < 0.01). Conversely, visfatin levels gradually increased (p < 0.01). ANA+ patients tended to show a faster decrease in PASI score, CRP and chemerin levels after 2 months, but the PASI score did not differ between ANA+ and ANA− patients at 12 months. A higher increase of visfatin was also found in ANA+ patients at 2 and 12 months. The antinuclear antibody response induced by infliximab was restricted to ANA, anti-dsDNA and anti-nucleosome antibodies. Patients who developed ANA positivity showed a faster clinical, inflammatory and immunological response to infliximab therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reich K, Nestle FO, Papp K, Ortonne JP, Evans R, Guzzo C, et al. Infliximab induction and maintenance therapy for moderate-to-severe psoriasis: a phase III, multicentre, double-blind trial. Lancet. 2005;366:1367–74.
Valesini G, Iannuccelli C, Marocchi E, Pascoli L, Scalzi V, Di Franco M. Biological and clinical effects of anti-TNFalpha treatment. Autoimmun Rev. 2007;7:35–41.
Ingegnoli F, Favalli EG, Meroni PL. Does polymorphysm of genes coding for pro-inflammatory mediators predict the clinical response to tnf alpha blocking agents? A review analysis of literature. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10:460–3.
Elkayam O, Pavelka K. Biologic registries in rheumatology: lessons learned and expectations for the future. Autoimmun Rev. 2012;12:329–36.
Atzeni F, Talotta R, Benucci M, Salaffi F, Cassinotti A, Varisco V et al. Immunogenicity and autoimmunity during anti-TNF therapy. Autoimmun Rev. 2012; doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2012.10.021 [Epub ahead of print].
Poulalhon N, Begon E, Lebbé C, Lioté F, Lahfa M, Bengoufa D, et al. A follow-up study in 28 patients treated with infliximab for severe recalcitrant psoriasis: evidence for efficacy and high incidence of biological autoimmunity. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:329–36.
Pink AE, Fonia A, Allen MH, Smith CH, Barker JN. Antinuclear antibodies associate with loss of response to antitumour necrosis factor-alpha therapy in psoriasis: a retrospective, observational study. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:780–5.
Caramaschi P, Biasi D, Colombatti M, Pieropan S, Martinelli N, Carletto A, et al. Anti-TNFalpha therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmunity. Rheumatol Int. 2006;26:209–14.
De Bandt M, Sibilia J, Le Loët X, Prouzeau S, Fautrel B, Marcelli C, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus induced by anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha therapy: a French national survey. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7:R545–51.
Shen GQ, Shoenfeld Y, Peter JB. Anti-DNA, antihistone, and antinucleosome antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus and drug-induced lupus. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 1998;16:321–34.
Krause I, Valesini G, Scrivo R, Shoenfeld Y. Autoimmune aspects of cytokine and anticytokine therapies. Am J Med. 2003;115:390–7.
Cantaert T, De Rycke L, Mavragani CP, Wijbrandts CA, Niewold TB, Niers T, et al. Exposure to nuclear antigens contributes to the induction of humoral autoimmunity during tumour necrosis factor alpha blockade. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:1022–9.
Smeets TJ, Kraan MC, van Loon ME, Tak PP. Tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade reduces the synovial cell infiltrate early after initiation of treatment, but apparently not by induction of apoptosis in synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:2155–62.
Goedkoop AY, Kraan MC, Teunissen MB, Picavet DI, de Rie MA, Bos JD, et al. Early effects of tumour necrosis factor alpha blockade on skin and synovial tissue in patients with active psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63:769–73.
Lugering A, Schmidt M, Lugering N, Pauels HG, Domschke W, Kucharzik T. Infliximab induces apoptosis in monocytes from patients with chronic active Crohn’s disease by using a caspase-dependent pathway. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:1145–57.
Van den Brande JM, Braat H, van den Brink GR, Versteeg HH, Bauer CA, Hoedemaeker I, et al. Infliximab but not etanercept induces apoptosis in lamina propria T-lymphocytes from patients with Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:1774–85.
Catrina AI, Trollmo C. Af Klint E, Engstrom M, Lampa J, Hermansson Y, et al. Evidence that anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy with both etanercept and infliximab induces apoptosis in macrophages, but not lymphocytes, in rheumatoid arthritis joints: extended report. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:61–72.
Savill J, Dransfield I, Gregory C, Haslett C. A blast from the past: clearance of apoptotic cells regulates immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:965–75.
Cohen PL, Caricchio R, Abraham V, Camenisch TD, Jennette JC, Roubey RA, et al. Delayed apoptotic cell clearance and lupus-like autoimmunity in mice lacking the c-mer membrane tyrosine kinase. J Exp Med. 2002;196:135–40.
Gershow D, Kim S, Brot N, Elkon KB. C-reactive protein binds to apoptotic cells, protect the cells from assembly of the terminal complement components, and sustains an antiinflammatory innate immune response: implications for systemic autoimmunity. J Exp Med. 2000;192:1353–64.
Gerdes S, Rostami-Yazdi M, Mrowietz U. Adipokines and psoriasis. Exp Dermatol. 2011;20:81–7.
Gisondi P, Tessari G, Conti A, Piaserico S, Schianchi S, Peserico A, et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriasis: a hospital-based case–control study. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:68–73.
Nakajima H, Nakajima K, Tarutani M, Morishige R, Sano S. Kinetics of circulating Th17 cytokines and adipokines in psoriasis patients. Arch Dermatol Res. 2011;303:451–5.
Albanesi C, Scarponi C, Pallotta S, Daniele R, Bosisio D, Madonna S, et al. Chemerin expression marks early psoriatic skin lesions and correlates with plasmacytoid dendritic cell recruitment. J Exp Med. 2009;206:249–58.
Albanesi C, Scarponi C, Bosisio D, Sozzani S, Girolomoni G. Immune functions and recruitment of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in psoriasis. Autoimmunity. 2010;43:215–9.
Yoshimura T, Oppenheim JJ. Chemerin reveals its chimeric nature. J Exp Med. 2008;205:2187–90.
Cash JL, Christian AR, Greaves DR. Chemerin peptides promote phagocytosis in a ChemR23- and Syk-dependent manner. J Immunol. 2010;184:5315–24.
Vermi W, Lonardi S, Morassi M, Rossini C, Tardanico R, Venturini M, et al. Cutaneous distribution of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in lupus erythematosus. Selective tropism at the site of epithelial apoptotic damage. Immunobiology. 2009;214:877–86.
Moschen AR, Kaser A, Enrich B, Mosheimer B, Theurl M, Niederegger H, et al. Visfatin, an adipocytokine with proinflammatory and immunomodulating properties. J Immunol. 2007;178:1748–58.
Jia SH, Li Y, Parodo J, Kapus A, Fan L, Rotstein OD, et al. Pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor inhibits neutrophil apoptosis in experimental inflammation and clinical sepsis. J Clin Invest. 2004;113:1318–27.
Filkova M, Haluzik M, Gay S, Senolt L. The role of resistin as a regulator of inflammation: implications for various human pathologies. Clin Immunol. 2009;133:157–70.
Griffiths CE, Barker JN. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet. 2007;370:263–71.
Feldman SR. A quantitative definition of severe psoriasis for use in clinical trials. J Dermatol Treat. 2004;15:27–9.
Taylor W, Gladman D. Helliwell, Marchesoni A, Mease P, Mielants H; CASPAR Study Group. Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2665–73.
Viana VST, Carvalho JF, Moraes JCB, Saad CGS, Ribeiro ACM, Gonçalves C, et al. Autoantibodies in patients with psoriatic arthritis on anti-TNFα therapy. Bras J Rheumatol. 2010;50:225–34.
Charles PJ, Smeenk JF, De Jong J, Feldmann M, Maini RN. Assessment of antibodies to double-stranded DNA in rheumatoid arthritis patients following treatment with Infliximab, a monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor α. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:2383–90.
Eriksson C, Engstrand S, Sundqvist KG, Rantapää-Dahlqvist S. Autoantibody formation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF alpha. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64:403–7.
Villalta D, Tonutti E, Tozzoli R, Bizzaro N. Attività Dnasica, apoptosi e produzione antoanticorpale nel LES. Riv Med Lab. 2004;5:149–51.
Gualtierotti R, Biggioggero M, Penatti AE, Meroni PL. Updating on the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev. 2010;10:3–7.
Agmon-Levin N, Mosca M, Petri M, Shoenfeld Y. Systemic lupus erythematosus one disease or many? Autoimmun Rev. 2012;11:593–5.
Vedove CD, Del Giglio M, Schena D, Girolomoni G. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol Res. 2009;301:99–105.
Gisondi P, Malerba M, Malara G, Puglisi Guerra A, Sala R, Radaeli A. C-reactive protein and markers for thrombophilia in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2010;23:1195–202.
Katz U, Zandman-Goddard G. Drug-induced lupus an update. Autoimmun Rev. 2010;10:46–50.
Pilz S, Mangge H, Obermayer-Pietsch B, März W. Visfatin/pre-B-cell colony-enhancing factor: a protein with various suggested functions. J Endocrinol Invest. 2007;30:138–44.
Ismail SA, Mohamed SA. Serum levels of visfatin and omentin-1 in patients with psoriasis and their relation to disease severity. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:436–9.
Gerdes S, Osadtschy S, Rostami-Yazdi M, Buhles N, Weichenthal M, Mrowietz U. Leptin, adiponectin, visfatin and retinol-binding protein-4—mediators of comorbidities in patients with psoriasis? Exp Dermatol. 2012;21:43–7.
Tilg H, Moschen AR. Role of adiponectin and PBEF/visfatin as regulators of inflammation: involvement in obesity-associated diseases. Clin Sci Lond. 2008;114:275–88.
Kendal-Wright CE, Hubbard D, Bryant-Greenwood GD. Chronic stretching of amniotic epithelial cells increases pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF/visfatin) expression and protects them from apoptosis. Placenta. 2008;29:255–65.
Anaya JM, Corena R, Castiblanco J, Rojas-Villarraga A, Shoenfeld Y. The kaleidoscope of autoimmunity: multiple autoimmune syndromes and familial autoimmunity. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2007;3:623–35.
Lorber M, Gershwin ME, Shoenfeld Y. The coexistence of systemic lupus erythematosus with other autoimmune diseases: the kaleidoscope of autoimmunity. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1994;24:105–13.
Shoenfeld Y, Lorber M, Yucel T, Yazici H. Case report primary antiphospholipid syndrome emerging following thymectomy for myasthenia gravis: additional evidence for the kaleidoscope of autoimmunity. Lupus. 1997;6:474–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lora, V., Bonaguri, C., Gisondi, P. et al. Autoantibody induction and adipokine levels in patients with psoriasis treated with infliximab. Immunol Res 56, 382–389 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-013-8410-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-013-8410-2