Abstract
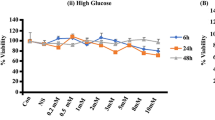
Obesity with excessive levels of circulating free fatty acids (FFAs) is tightly linked to the incidence of type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance of peripheral tissues and pancreatic β-cell dysfunction are two major pathological changes in diabetes and both are facilitated by excessive levels of FFAs and/or glucose. To gain insight into the mitochondrial-mediated mechanisms by which long-term exposure of INS-1 cells to excess FFAs causes β-cell dysfunction, the effects of the unsaturated FFA linoleic acid (C 18:2, n-6) on rat insulinoma INS-1 β cells was investigated. INS-1 cells were incubated with 0, 50, 250 or 500 μM linoleic acid/0.5% (w/v) BSA for 48 h under culture conditions of normal (11.1 mM) or high (25 mM) glucose in serum-free RPMI-1640 medium. Cell viability, apoptosis, glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, Bcl-2, and Bax gene expression levels, mitochondrial membrane potential and cytochrome c release were examined. Linoleic acid 500 μM significantly suppressed cell viability and induced apoptosis when administered in 11.1 and 25 mM glucose culture medium. Compared with control, linoleic acid 500 μM significantly increased Bax expression in 25 mM glucose culture medium but not in 11.1 mM glucose culture medium. Linoleic acid also dose-dependently reduced mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and significantly promoted cytochrome c release from mitochondria in both 11.1 mM glucose and 25 mM glucose culture medium, further reducing glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, which is dependent on normal mitochondrial function. With the increase in glucose levels in culture medium, INS-1 β-cell insulin secretion function was deteriorated further. The results of this study indicate that chronic exposure to linoleic acid-induced β-cell dysfunction and apoptosis, which involved a mitochondrial-mediated signal pathway, and increased glucose levels enhanced linoleic acid-induced β-cell dysfunction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.B. Lowell, G.I. Shulman, Mitochondrial dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Science 307, 384–387 (2005)
C.M. Kusminski, S. Shetty, L. Orci, R.H. Unger, P.E. Scherer, Diabetes and apoptosis: lipotoxicity. Apoptosis 14, 1484–1495 (2009)
P.J. Randle, Regulatory interactions between lipids and carbohydrates: the glucose fatty acid cycle after 35 years. Diabetes Metab. Rev. 14, 263–283 (1998)
L.O. Schulz, P.H. Bennett, E. Ravussin, J.R. Kidd, K.K. Kidd, J. Esparza, M.E. Valencia, Effects of traditional and western environments on prevalence of type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians in Mexico and the U.S. Diabetes Care 29, 1866–1871 (2006)
V. Poitout, R.P. Robertson, Glucolipotoxicity: fuel excess and beta-cell dysfunction. Endocr. Rev. 29, 351–366 (2008)
R.H. Unger, L. Orci, Diseases of liporegulation: new perspective on obesity and related disorders. FASEB J. 15, 312–321 (2001)
R.H. Unger, Lipid overload and overflow: metabolic trauma and the metabolic syndrome. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 14, 398–403 (2003)
E. Lai, G. Bikopoulos, M.B. Wheeler, M. Rozakis-Adcock, A. Volchuk, Differential activation of ER stress and apoptosis in response to chronically elevated free fatty acids in pancreatic beta-cells. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 294, E540–E550 (2008)
J.L. Evans, I.D. Goldfine, B.A. Maddux, G.M. Grodsky, Are oxidative stress-activated signaling pathways mediators of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction? Diabetes 52, 1–8 (2003)
P. Newsholme, E.P. Haber, S.M. Hirabara, E.L. Rebelato, J. Procopio, D. Morgan, H.C. Oliveira-Emilio, A.R. Carpinelli, R. Curi, Diabetes associated cell stress and dysfunction: role of mitochondrial and non-mitochondrial ROS production and activity. J. Physiol. 583, 9–24 (2007)
A.I. Oprescu, G. Bikopoulos, A. Naassan, E.M. Allister, C. Tang, E. Park, H. Uchino, G.F. Lewis, I.G. Fantus, M. Rozakis-Adcock, M.B. Wheeler, A. Giacca, Free fatty acid-induced reduction in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion: evidence for a role of oxidative stress in vitro and in vivo. Diabetes 56, 2927–2937 (2007)
J.L. Evans, B.A. Maddux, I.D. Goldfine, The molecular basis for oxidative stress-induced insulin resistance. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 7, 1040–1052 (2005)
G. Szabadkai, M.R. Duchen, Mitochondria mediated cell death in diabetes. Apoptosis 14, 1405–1423 (2009)
E. Karaskov, C. Scott, L. Zhang, T. Teodoro, M. Ravazzola, A. Volchuk, Chronic palmitate but not oleate exposure induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, which may contribute to INS-1 pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis. Endocrinology 147, 3398–3407 (2006)
I. Kharroubi, L. Ladriere, A.K. Cardozo, Z. Dogusan, M. Cnop, D.L. Eizirik, Free fatty acids and cytokines induce pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis by different mechanisms: role of nuclear factor-kappaB and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Endocrinology 145, 5087–5096 (2004)
K. Eitel, H. Staiger, M.D. Brendel, H. Brandhorst, R.G. Bretzel, H.U. Haring, M. Kellerer, Apoptosis induced by free fatty acids. Med. Klin. 98, 248–252 (2003)
T. Kawai, H. Hirose, Y. Seto, H. Fujita, T. Saruta, Chronic effects of different fatty acids and leptin in INS-1 cells. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 51, 1–8 (2001)
I. Maestre, J. Jordan, S. Calvo, J.A. Reig, V. Cena, B. Soria, M. Prentki, E. Roche, Mitochondrial dysfunction is involved in apoptosis induced by serum withdrawal and fatty acids in the beta-cell line INS-1. Endocrinology 144, 335–345 (2003)
M. Cnop, J.C. Hannaert, D.G. Pipeleers, Troglitazone does not protect rat pancreatic beta cells against free fatty acid-induced cytotoxicity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 63, 1281–1285 (2002)
F.T. Schulthess, S. Katz, A. Ardestani, H. Kawahira, S. Georgia, D. Bosco, A. Bhushan, K. Maedler, Deletion of the mitochondrial flavoprotein apoptosis inducing factor (AIF) induces beta-cell apoptosis and impairs beta-cell mass. PLoS One 4, e4394 (2009)
V. Grishko, L. Rachek, S. Musiyenko, S.P. Ledoux, G.L. Wilson, Involvement of mtDNA damage in free fatty acid-induced apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 38, 755–762 (2005)
L.G. Grunnet, R. Aikin, M.F. Tonnesen, S. Paraskevas, L. Blaabjerg, J. Storling, L. Rosenberg, N. Billestrup, D. Maysinger, T. Mandrup-Poulsen, Proinflammatory cytokines activate the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in beta-cells. Diabetes 58, 1807–1815 (2009)
L.I. Rachek, N.P. Thornley, V.I. Grishko, S.P. LeDoux, G.L. Wilson, Protection of INS-1 cells from free fatty acid-induced apoptosis by targeting hOGG1 to mitochondria. Diabetes 55, 1022–1028 (2006)
L.K. Olson, J. Qian, V. Poitout, Glucose rapidly and reversibly decreases INS-1 cell insulin gene transcription via decrements in STF-1 and C1 activator transcription factor activity. Mol. Endocrinol. 12, 207–219 (1998)
S.P. Cousin, S.R. Hugl, C.E. Wrede, H. Kajio, M.G. Myers Jr., C.J. Rhodes, Free fatty acid-induced inhibition of glucose and insulin-like growth factor I-induced deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in the pancreatic beta-cell line INS-1. Endocrinology 142, 229–240 (2001)
M. Cnop, J.C. Hannaert, A. Hoorens, D.L. Eizirik, D.G. Pipeleers, Inverse relationship between cytotoxicity of free fatty acids in pancreatic islet cells and cellular triglyceride accumulation. Diabetes 50, 1771–1777 (2001)
F. Frigerio, T. Brun, C. Bartley, A. Usardi, D. Bosco, K. Ravnskjaer, S. Mandrup, P. Maechler, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) protects against oleate-induced INS-1E beta cell dysfunction by preserving carbohydrate metabolism. Diabetologia 53, 331–340 (2010)
C. Warnotte, M. Nenquin, J.C. Henquin, Unbound rather than total concentration and saturation rather than unsaturation determine the potency of fatty acids on insulin secretion. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 153, 147–153 (1999)
X. Du, D. Edelstein, S. Obici, N. Higham, M.H. Zou, M. Brownlee, Insulin resistance reduces arterial prostacyclin synthase and eNOS activities by increasing endothelial fatty acid oxidation. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 1071–1080 (2006)
A.K. Cardozo, P. Proost, C. Gysemans, M.C. Chen, C. Mathieu, D.L. Eizirik, IL-1beta and IFN-gamma induce the expression of diverse chemokines and IL-15 in human and rat pancreatic islet cells, and in islets from pre-diabetic NOD mice. Diabetologia 46, 255–266 (2003)
A.M. Brambrink, A. Schneider, H. Noga, A. Astheimer, B. Gotz, I. Korner, A. Heimann, M. Welschof, O. Kempski, Tolerance-Inducing dose of 3-nitropropionic acid modulates bcl-2 and bax balance in the rat brain: a potential mechanism of chemical preconditioning. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 20, 1425–1436 (2000)
J.E. Brown, S.J. Dunmore, Leptin decreases apoptosis and alters BCL-2: Bax ratio in clonal rodent pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 23, 497–502 (2007)
G. Juan, M. Cavazzoni, G.T. Saez, J.E. O’Connor, A fast kinetic method for assessing mitochondrial membrane potential in isolated hepatocytes with rhodamine 123 and flow cytometry. Cytometry 15, 335–342 (1994)
A. Masud, S.A. Lakhani, K. Kuida, G.A. Porter Jr, C.J. Booth, W.Z. Mehal, I. Inayat, R.A. Flavell, Caspases 3 and 7: key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science 311, 847–851 (2006)
A. Gross, J.M. McDonnell, S.J. Korsmeyer, BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev. 13, 1899–1911 (1999)
D.L. Vaux, S.J. Korsmeyer, Cell death in development. Cell 96, 245–254 (1999)
H. Kim, Y.N. Kim, C.W. Kim, Oxidative stress attenuates Fas-mediated apoptosis in Jurkat T cell line through Bfl-1 induction. Oncogene 24, 1252–1261 (2005)
H.J.M. Brady, Apoptosis methods and protocols (Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, 2004)
D. Zhang, C. Lu, M. Whiteman, B. Chance, J.S. Armstrong, The mitochondrial permeability transition regulates cytochrome c release for apoptosis during endoplasmic reticulum stress by remodeling the cristae junction. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 3476–3486 (2008)
T. Eissing, S. Waldherr, F. Allgower, P. Scheurich, E. Bullinger, Response to bistability in apoptosis: roles of bax, bcl-2, and mitochondrial permeability transition pores. Biophys. J. 92, 3332–3334 (2007)
T. Kudo, J. Wu, Y. Ogawa, S. Suga, N. Hasegawa, T. Suda, H. Mizukami, S. Yagihashi, M. Wakui, Novel mechanism of chronic exposure of oleic acid-induced insulin release impairment in rat pancreatic beta-cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 318, 1203–1210 (2006)
A. Sultan, P.M. Sokolove, Free fatty acid effects on mitochondrial permeability: an overview. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 386, 52–61 (2001)
C.J. Nolan, M.S. Madiraju, V. Delghingaro-Augusto, M.L. Peyot, M. Prentki, Fatty acid signaling in the beta-cell and insulin secretion. Diabetes 55(Suppl 2), S16–S23 (2006)
V.A. Bohr, T. Stevnsner, N.C. de Souza-Pinto, Mitochondrial DNA repair of oxidative damage in mammalian cells. Gene 286, 127–134 (2002)
S. Lenzen, Oxidative stress: the vulnerable beta-cell. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 36, 343–347 (2008)
K. Maedler, J. Oberholzer, P. Bucher, G.A. Spinas, M.Y. Donath, Monounsaturated fatty acids prevent the deleterious effects of palmitate and high glucose on human pancreatic beta-cell turnover and function. Diabetes 52, 726–733 (2003)
L.L. Listenberger, X. Han, S.E. Lewis, S. Cases, R.V. Farese Jr., D.S. Ory, J.E. Schaffer, Triglyceride accumulation protects against fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 3077–3082 (2003)
M. Rodriguez-Cruz, A.R. Tovar, M. del Prado, N. Torres, Molecular mechanisms of action and health benefits of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Rev. Invest. Clin. 57, 457–472 (2005)
J.M. Jurgensmeier, Z. Xie, Q. Deveraux, L. Ellerby, D. Bredesen, J.C. Reed, Bax directly induces release of cytochrome c from isolated mitochondria. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 4997–5002 (1998)
D.R. Green, Apoptotic pathways: ten minutes to dead. Cell 121, 671–674 (2005)
H. Kim, M. Rafiuddin-Shah, H.C. Tu, J.R. Jeffers, G.P. Zambetti, J.J. Hsieh, E.H. Cheng, Hierarchical regulation of mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis by BCL-2 subfamilies. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 1348–1358 (2006)
P. Bernardi, The permeability transition pore. Control points of a cyclosporin A-sensitive mitochondrial channel involved in cell death. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1275, 5–9 (1996)
D.R. Green, G. Kroemer, The pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science 305, 626–629 (2004)
P. Maechler, C.B. Wollheim, Mitochondrial signals in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in the beta cell. J. Physiol. 529(Pt 1), 49–56 (2000)
C.B. Wollheim, P. Maechler, Beta-cell mitochondria and insulin secretion: messenger role of nucleotides and metabolites. Diabetes 51(Suppl 1), S37–S42 (2002)
C.M. Kusminski, S. Shetty, L. Orci, R.H. Unger, P.E. Scherer, Diabetes and apoptosis: lipotoxicity. Apoptosis 14, 1484–1495 (2009)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge scientific contribution of Drs SH Lee and F Steyn, and editorial help of Mr M Sinclair. Ya Tuo is a recipient of overseas post-graduate research scholarship from the China Scholarship Council (CSC, China) and subsidy scholarship by the University of Queensland; and research was supported by Australian NHMRC and the University of Queensland
Conflict of interest
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shengbin Li and Chen Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tuo, Y., Wang, D., Li, S. et al. Long-term exposure of INS-1 rat insulinoma cells to linoleic acid and glucose in vitro affects cell viability and function through mitochondrial-mediated pathways. Endocr 39, 128–138 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-010-9432-3
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-010-9432-3