Abstract
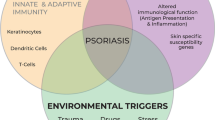
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease characterized by an excessively aberrant hyperproliferation of keratinocytes. The pathogenesis of psoriasis is complex and the exact mechanism remains elusive. However, psoriasis is thought to result from a combination of genetic, epigenetic, and environmental influences. Recent studies have identified that epigenetic factors including dysregulated DNA methylation levels, abnormal histone modification and microRNAs expressions are involved in the development of psoriasis. The interplay of immune cells and cytokines is another critical factor in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. These factors or pathways include Th1/Th2 homeostasis, the Th17/Treg balance and the IL-23/Th17 axis. Th17 is believed particularly important in psoriasis due to its pro-inflammatory effects and its involvement in an integrated inflammatory loop with dendritic cells and keratinocytes, contributing to an overproduction of antimicrobial peptides, inflammatory cytokines, and chemokines that leads to amplification of the immune response. In addition, other pathways and signaling molecules have been found to be involved, including Th9, Th22, regulatory T cells, γδ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and their related cytokines. Understanding the pathogenesis of psoriasis will allow us to develop increasingly efficient targeted treatment by blocking relevant inflammatory signaling pathways and molecules. There is no cure for psoriasis at the present time, and much of the treatment involves managing the symptoms. The biologics, while lacking the adverse effects associated with some of the traditional medications such as corticosteroids and methotrexate, have their own set of side effects, which may include reactivation of latent infections. Significant challenges remain in developing safe and efficacious novel targeted therapies that depend on a better understanding of the immunological dysfunction in psoriasis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seldin MF (2015) The genetics of human autoimmune disease: a perspective on progress in the field and future directions. J Autoimmun 64:1–12
Yang CA, Chiang BL (2015) Inflammasomes and human autoimmunity: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun 61:1–8
Chang C (2014) Autoimmunity: from black water fever to regulatory function. J Autoimmun 48–49:1–9
Duffin KC, Chandran V, Gladman DD, Krueger GG, Elder JT, Rahman P (2008) Genetics of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: update and future direction. J Rheumatol 35:1449–1453
Lu FT, Yang W, Wang YH, Ma HD, Tang W, Yang JB et al (2015) Thymic B cells promote thymus-derived regulatory T cell development and proliferation. J Autoimmun 61:62–72
Boehncke W-H, Schön MP (2015) Disease burden and epidemiology. Lancet 386:983–994
Mahil SK, Capon F, Barker JN (2015) Genetics of psoriasis. Dermatol Clin 33:1–11
Liu Y, Helms C, Liao W, Zaba LC, Duan S, Gardner J et al (2008) A genome-wide association study of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis identifies new disease loci. Plos Genet 4(3):e100041
Tsoi LC, Spain SL, Knight J, Ellinghaus E, Stuart PE, Capon F et al (2012) Identification of 15 new psoriasis susceptibility loci highlights the role of innate immunity. Nat Genet 44:1341–1348
Telfer NR, Chalmers RJG, Whale K, Colman G (1992) The role of streptococcal infection in the initiation of guttate psoriasis. Arch Dermatol 128:39–42
Gudjonsson JE, Thorarinsson AM, Sigurgeirsson B, Kristinsson KG, Valdimarsson H (2003) Streptococcal throat infections and exacerbation of chronic plaque psoriasis: a prospective study. Br J Dermatol 149:530–534
Baker BS, Laman JD, Powles A, van der Fits L, Voerman JSA, Melief MJ et al (2006) Peptidoglycan and peptidoglycan-specific Th1 cells in psoriatic skin lesions. J Pathol 209:174–181
Dziarski R (2004) Peptidoglycan recognition proteins (PGRPs). Mol Immunol 40:877–886
Cai Y, Fleming C, Yan J (2012) New insights of T cells in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Cell Mol Immunol 9:302–309
Baker BS, Powles A, Fry L (2006) Peptidoglycan: a major aetiological factor for psoriasis? Trends Immunol 27:545–551
Raychaudhuri SK, Maverakis E, Raychaudhuri SP (2014) Diagnosis and classification of psoriasis. Autoimmun Rev 13:490–495
Schön MP, Ruzicka T (2001) Psoriasis: the plot thickens. Nat Immunol 2:91
Allione A, Marcon F, Fiorito G, Guarrera S, Siniscalchi E, Zijno A et al (2015) Novel epigenetic changes unveiled by monozygotic twins discordant for smoking habits. PLoS One 10:e0128265
Farber EM, Nall ML (1974) The natural history of psoriasis in 5,600 patients. Dermatology 148:1–18
Nair RP, Stuart PE, Nistor I, Hiremagalore R, Chia NVC, Jenisch S et al (2006) Sequence and haplotype analysis supports HLA-C as the psoriasis susceptibility 1 gene. Am J Hum Genet 78:827–851
Park J-H, Wacholder S, Gail MH, Peters U, Jacobs KB, Chanock SJ et al (2010) Estimation of effect size distribution from genome-wide association studies and implications for future discoveries. Nat Genet 42:570–575
Lowes MA, Suárez-Fariñas M, Krueger JG (2014) Immunology of psoriasis. Annu Rev Immunol 32:227
Alwan W, Nestle FO (2015) Pathogenesis and treatment of psoriasis: exploiting pathophysiological pathways for precision medicine. Clin Exp Rheumatol 33:2
de Cid R, Riveira-Munoz E, Zeeuwen PLJM, Robarge J, Liao W, Dannhauser EN et al (2009) Deletion of the late cornified envelope LCE3B and LCE3C genes as a susceptibility factor for psoriasis. Nat Genet 41:211–215
Zhang X-J, Huang W, Yang S, Sun L-D, Zhang F-Y, Zhu Q-X et al (2009) Psoriasis genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility variants within LCE gene cluster at 1q21. Nat Genet 41:205–210
Ellinghaus E, Ellinghaus D, Stuart PE, Nair RP, Debrus S, Raelson JV et al (2010) Genome-wide association study identifies a psoriasis susceptibility locus at TRAF3IP2. Nat Genet 42:991–995
Di Meglio P, Villanova F, Nestle FO. Psoriasis. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine, 2014;4
Elder JT (2006) PSORS1: linking genetics and immunology. J Investig Dermatol 126:1205–1206
Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis C, the Wellcome Trust Case Control C (2010) A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat Genet 42:985–990
Nair RP, Duffin KC, Helms C, Ding J, Stuart PE, Goldgar D et al (2009) Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-κB pathways. Nat Genet 41:199–204
Nair RP, Ruether A, Stuart PE, Jenisch S, Tejasvi T, Hiremagalore R et al (2008) Polymorphisms of the IL12B and IL23R genes are associated with psoriasis. J Investig Dermatol 128:1653–1661
Di Meglio P, Di Cesare A, Laggner U, Chu C-C, Napolitano L, Villanova F et al (2011) The IL23R R381Q gene variant protects against immune-mediated diseases by impairing IL-23-induced Th17 effector response in humans. PLoS One 6:e17160
Elder JT, Bruce AT, Gudjonsson JE, Johnston A, Stuart PE, Tejasvi T et al (2010) Molecular dissection of psoriasis: integrating genetics and biology. J Investig Dermatol 130:1213–1226
Hoesel B, Schmid JA (2013) The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer 12:1
Han J-W, Zheng H-F, Cui Y, Sun L-D, Ye D-Q, Hu Z et al (2009) Genome-wide association study in a Chinese Han population identifies nine new susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 41:1234–1237
Stahl EA, Raychaudhuri S, Remmers EF, Xie G, Eyre S, Thomson BP et al (2010) Genome-wide association study meta-analysis identifies seven new rheumatoid arthritis risk loci. Nat Genet 42:508–514
Mauro C, Pacifico F, Lavorgna A, Mellone S, Iannetti A, Acquaviva R et al (2006) ABIN-1 binds to NEMO/IKKγ and co-operates with A20 in inhibiting NF-κB. J Biol Chem 281:18482–18488
Hüffmeier U, Uebe S, Ekici AB, Bowes J, Giardina E, Korendowych E et al (2010) Common variants at TRAF3IP2 are associated with susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Nat Genet 42:996–999
Harden JL, Lewis SM, Pierson KC, Suárez-Fariñas M, Lentini T, Ortenzio FS et al (2014) CARD14 expression in dermal endothelial cells in psoriasis. PLoS One 9:e111255
Scudiero I, Zotti T, Ferravante A, Vessichelli M, Vito P (2011) Alternative splicing of CARMA2/CARD14 transcripts generates protein variants with differential effect on NF-κB activation and endoplasmic reticulum stress‐induced cell death. J Cell Physiol 226:3121–3131
Hou R, Yin G, An P, Wang C, Liu R, Yang Y et al (2013) DNA methylation of dermal MSCs in psoriasis: identification of epigenetically dysregulated genes. J Dermatol Sci 72:103–109
Chandra A, Ray A, Senapati S, Chatterjee R (2015) Genetic and epigenetic basis of psoriasis pathogenesis. Mol Immunol 64:313–323
Trowbridge RM, Pittelkow MR (2014) Epigenetics in the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of psoriasis vulgaris. J Drugs Dermatol 13:111–118
Han J, Park S-G, Bae J-B, Choi J, Lyu J-M, Park SH et al (2012) The characteristics of genome-wide DNA methylation in naive CD4+ T cells of patients with psoriasis or atopic dermatitis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 422:157–163
Birney E, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Dutta A, Guigó R, Gingeras TR, Margulies EH et al (2007) Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature 447:799–816
Zhang K, Zhang R, Li X, Yin G, Niu X (2009) Promoter methylation status of p15 and p21 genes in HPP-CFCs of bone marrow of patients with psoriasis. Eur J Dermatol 19:141–146
Chen M, Chen ZQ, Cui PG, Yao X, Li YM, Li AS et al (2008) The methylation pattern of p16INK4a gene promoter in psoriatic epidermis and its clinical significance. Br J Dermatol 158:987–993
Zhang P, Su Y, Chen H, Zhao M, Lu Q (2010) Abnormal DNA methylation in skin lesions and PBMCs of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Dermatol Sci 60:40–42
Zhang P, Su Y, Zhao M, Huang W, Lu Q (2011) Abnormal histone modifications in PBMCs from patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Eur J Dermatol 21:552–557
Wu GC, Pan HF, Leng RX, Wang DG, Li XP, Li XM et al (2015) Emerging role of long noncoding RNAs in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev 14:798–805
Kubo M, Hanada T, Yoshimura A (2003) Suppressors of cytokine signaling and immunity. Nat Immunol 4:1169–1176
Zhao M, Wang L-t, Liang G-p, Zhang P, Deng X-j, Tang Q et al (2014) Up-regulation of microRNA-210 induces immune dysfunction via targeting FOXP3 in CD4+ T cells of psoriasis vulgaris. Clin Immunol 150:22–30
Zibert JR, Løvendorf MB, Litman T, Olsen J, Kaczkowski B, Skov L (2010) MicroRNAs and potential target interactions in psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci 58:177–185
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang K-J, Baltimore D (2006) NF-κB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:12481–12486
Tili E, Michaille J-J, Cimino A, Costinean S, Dumitru CD, Adair B et al (2007) Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following lipopolysaccharide/TNF-α stimulation and their possible roles in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J Immunol 179:5082–5089
Yan S, Xu Z, Lou F, Zhang L, Ke F, Bai J et al. NF-κB-induced microRNA-31 promotes epidermal hyperplasia by repressing protein phosphatase 6 in psoriasis. Nature communications, 2015;6.
Løvendorf MB, Mitsui H, Zibert JR, Røpke MA, Hafner M, Dyring-Andersen B et al (2015) Laser capture microdissection followed by next‐generation sequencing identifies disease‐related microRNAs in psoriatic skin that reflect systemic microRNA changes in psoriasis. Exp Dermatol 24:187–193
Schцn MP, Henning W, Boehncke MD (2005) Medical progress. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med 352:1899–1912
Johnson-Huang LM, Suárez-Fariñas M, Pierson KC, Fuentes-Duculan J, Cueto I, Lentini T et al (2012) A single intradermal injection of IFN-γ induces an inflammatory state in both non-lesional psoriatic and healthy skin. J Investig Dermatol 132:1177–1187
Madonna S, Scarponi C, Sestito R, Pallotta S, Cavani A, Albanesi C (2010) The IFN-γ-dependent suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 promoter activity is positively regulated by IFN regulatory factor-1 and Sp1 but repressed by growth factor independence-1b and Krüppel-like factor-4, and it is dysregulated in psoriatic keratinocytes. J Immunol 185:2467–2481
Abdallah MA, Abdel-Hamid MF, Kotb AM, Mabrouk EA (2009) Serum interferon-g is a psoriasis severity and prognostic marker. Cutis 84:163–168
Goldminz AM, Au SC, Kim N, Gottlieb AB, Lizzul PF (2013) NF-κB: an essential transcription factor in psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci 69:89–94
Zaba LC, Cardinale I, Gilleaudeau P, Sullivan-Whalen M, Suárez-Fariñas M, Fuentes-Duculan J et al (2007) Amelioration of epidermal hyperplasia by TNF inhibition is associated with reduced Th17 responses. J Exp Med 204:3183–3194
Shiga T, Sato K, Kataoka S, Sano S (2015) TNF inhibitors directly target Th17 cells via attenuation of autonomous TNF/TNFR2 signalling in psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci 77:79–81
Papagoras C, Voulgari PV, Drosos AA (2014) Golimumab, the newest TNF-α blocker, comes of age. Clin Exp Rheumatol 33:570–577
Ahn CS, Gustafson CJ, Sandoval LF, Davis SA, Feldman SR (2013) Cost effectiveness of biologic therapies for plaque psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol 14:315–326
Rozenblit M, Lebwohl M (2009) New biologics for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Dermatol Ther 22:56–60
Papp K (2010) Clinical development of onercept, a tumor necrosis factor binding protein, in psoriasis. Curr Med Res Opin 26:2287–2300
Semble AL, Davis SA, Feldman SR (2014) Safety and tolerability of tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors in psoriasis: a narrative review. Am J Clin Dermatol 15:37–43
Johansen C, Usher PA, Kjellerup RB, Lundsgaard D, Iversen L, Kragballe K (2009) Characterization of the interleukin-17 isoforms and receptors in lesional psoriatic skin. Br J Dermatol 160:319–324
Cua DJ, Tato CM (2010) Innate IL-17-producing cells: the sentinels of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 10:479–489
Isailovic N, Daigo K, Mantovani A, Selmi C (2015) Interleukin-17 and innate immunity in infections and chronic inflammation. J Autoimmun 60:1–11
Hou MS, Huang ST, Tsai MH, Yen CC, Lai YG, Liou YH et al (2015) The interleukin-15 system suppresses T cell-mediated autoimmunity by regulating negative selection and nT(H)17 cell homeostasis in the thymus. J Autoimmun 56:118–129
Lai Y, Li D, Li C, Muehleisen B, Radek KA, Park HJ et al (2012) The antimicrobial protein REG3A regulates keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation after skin injury. Immunity 37:74–84
Ramirez-Carrozzi V, Sambandam A, Luis E, Lin Z, Jeet S, Lesch J et al (2011) IL-17C regulates the innate immune function of epithelial cells in an autocrine manner. Nat Immunol 12:1159–1166
Harper EG, Guo C, Rizzo H, Lillis JV, Kurtz SE, Skorcheva I et al (2009) Th17 cytokines stimulate CCL20 expression in keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo: implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. J Investig Dermatol 129:2175–2183
Hueber W, Patel DD, Dryja T, Wright AM, Koroleva I, Bruin G et al (2010) Effects of AIN457, a fully human antibody to interleukin-17A, on psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and uveitis. Sci Transl Med 2:52ra72–52ra72
Krueger JG, Fretzin S, Suárez-Fariñas M, Haslett PA, Phipps KM, Cameron GS et al (2012) IL-17A is essential for cell activation and inflammatory gene circuits in subjects with psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 130:145–54
Kanda N, Koike S, Watanabe S (2005) IL-17 suppresses TNF-α-induced CCL27 production through induction of COX-2 in human keratinocytes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 116:1144–1150
Stockinger B, Veldhoen M (2007) Differentiation and function of Th17 T cells. Curr Opin Immunol 19:281–286
Lee E, Trepicchio WL, Oestreicher JL, Pittman D, Wang F, Chamian F et al (2004) Increased expression of interleukin 23 p19 and p40 in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Exp Med 199:125–130
Yawalkar N, Tscharner GG, Hunger RE, Hassan AS (2009) Increased expression of IL-12p70 and IL-23 by multiple dendritic cell and macrophage subsets in plaque psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci 54:99–105
Cargill M, Schrodi SJ, Chang M, Garcia VE, Brandon R, Callis KP et al (2007) A large-scale genetic association study confirms IL12B and leads to the identification of IL23R as psoriasis-risk genes. Am J Hum Genet 80:273–290
Zheng Y, Danilenko DM, Valdez P, Kasman I, Eastham-Anderson J, Wu J et al (2007) Interleukin-22, a TH17 cytokine, mediates IL-23-induced dermal inflammation and acanthosis. Nature 445:648–651
Wolk K, Witte E, Wallace E, Döcke WD, Kunz S, Asadullah K et al (2006) IL-22 regulates the expression of genes responsible for antimicrobial defense, cellular differentiation, and mobility in keratinocytes: a potential role in psoriasis. Eur J Immunol 36:1309–1323
Mashiko S, Bouguermouh S, Rubio M, Baba N, Bissonnette R, Sarfati M (2015) Human mast cells are major IL-22 producers in patients with psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 136(2):351–9
Becher B, Pantelyushin S (2012) Hiding under the skin: interleukin-17-producing γδ T cells go under the skin? Nat Med 18:1748–1750
Singh TP, Schön MP, Wallbrecht K, Gruber-Wackernagel A, Wang X-J, Wolf P (2013) Involvement of IL-9 in Th17-associated inflammation and angiogenesis of psoriasis. PLoS One 8:e51752
Elyaman W, Bradshaw EM, Uyttenhove C, Dardalhon V, Awasthi A, Imitola J et al (2009) IL-9 induces differentiation of TH17 cells and enhances function of FoxP3+ natural regulatory T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:12885–12890
Witte E, Kokolakis G, Witte K, Philipp S, Doecke W-D, Babel N et al (2014) IL-19 is a component of the pathogenetic IL-23/IL-17 cascade in psoriasis. J Investig Dermatol 134:2757–2767
Noguchi E, Shibasaki M, Arinami T, Takeda K, Maki T, Miyamoto T et al (1997) Evidence for linkage between asthma/atopy in childhood and chromosome 5q31-q33 in a Japanese population. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156:1390–1393
Schlaak JF, Buslau M, Jochum W, Hermann E, Girndt M, Gallati H et al (1994) T cells involved in psoriasis vulgaris belong to the Th1 subset. J Investig Dermatol 102:145–149
Austin LM, Ozawa M, Kikuchi T, Walters IB, Krueger JG (1999) The majority of epidermal T cells in psoriasis vulgaris lesions can produce type 1 cytokines, interferon-γ, interleukin-2, and tumor necrosis factor-α, defining TC1 (cytotoxic T lymphocyte) and TH1 effector populations: a type 1 differentiation bias is also measured in circulating blood T cells in psoriatic patients. J Investig Dermatol 113:752–759
Aydogan K, Tore O, Akcaglar S, Oral B, Ener B, Tunalı S et al (2013) Effects of Malassezia yeasts on serum Th1 and Th2 cytokines in patients with guttate psoriasis. Int J Dermatol 52:46–52
Szabo SK, Hammerberg C, Yoshida Y, Bata-Csorgo Z, Cooper KD (1998) Identification and quantitation of interferon-γ producing T cells in psoriatic lesions: localization to both CD4+ and CD8+ subsets. J Investig Dermatol 111:1072–1078
Uyemura K, Yamamura M, Fivenson DF, Modlin RL, Nickoloff BJ (1993) The cytokine network in lesional and lesion-free psoriatic skin is characterized by a T helper type 1 cell-mediated response. J Investig Dermatol 101:701–705
Onderdijk AJ, Baerveldt EM, Kurek D, Kant M, Florencia EF, Debets R et al (2015) IL-4 downregulates IL-1β and IL-6 and induces GATA3 in psoriatic epidermal cells: route of action of a Th2 cytokine. J Immunol 195:1744–1752
Debets R, Hegmans JPJJ, Troost RJJ, Benner R, Prens EP (1995) Enhanced production of biologically active interleukin-1α and interleukin-1β by psoriatic epidermal cells ex vivo: evidence of increased cytosolic interleukin-1β levels and facilitated interleukin-1 release. Eur J Immunol 25:1624–1630
Wei L, Debets R, Hegmans JJ, Benner R, Prens EP (1999) IL-1β and IFN-γ induce the regenerative epidermal phenotype of psoriasis in the transwell skin organ culture system. IFN-γ upregulates the expression of keratin 17 and keratinocyte transglutaminase via endogenous IL-1 production. J Pathol 187:358–364
Debets R, Timans JC, Homey B, Zurawski S, Sana TR, Lo S et al (2001) Two novel IL-1 family members, IL-1δ and IL-1ε, function as an antagonist and agonist of NF-κB activation through the orphan IL-1 receptor-related protein 2. J Immunol 167:1440–1446
Campanati A, Orciani M, Consales V, Lazzarini R, Ganzetti G, Di Benedetto G et al (2014) Characterization and profiling of immunomodulatory genes in resident mesenchymal stem cells reflect the Th1-Th17/Th2 imbalance of psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res 306:915–920
Zhang P, Chen H-X, Duan Y-Q, Wang W-Z, Zhang T-Z, Li J-W et al (2014) Analysis of Th1/Th2 response pattern for erythrodermic psoriasis. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci 34:596–601
Kryczek I, Bruce AT, Gudjonsson JE, Johnston A, Aphale A, Vatan L et al (2008) Induction of IL-17+ T cell trafficking and development by IFN-γ: mechanism and pathological relevance in psoriasis. J Immunol 181:4733–4741
Dinarello CA (1999) IL-18: a TH1-inducing, proinflammatory cytokine and new member of the IL-1 family. J Allergy Clin Immunol 103:11–24
Chung Y, Chang SH, Martinez GJ, Yang XO, Nurieva R, Kang HS et al (2009) Critical regulation of early Th17 cell differentiation by interleukin-1 signaling. Immunity 30:576–587
Anderson AC, Sullivan JM, Tan DJ, Lee DH, Kuchroo VK (2015) A T cell extrinsic mechanism by which IL-2 dampens Th17 differentiation. J Autoimmun 59:38–42
Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, Tadokoro CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ et al (2006) The orphan nuclear receptor RORγt directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell 126:1121–1133
Yang XO, Pappu BP, Nurieva R, Akimzhanov A, Kang HS, Chung Y et al (2008) T helper 17 lineage differentiation is programmed by orphan nuclear receptors RORα and RORγ. Immunity 28:29–39
Fujishima S, Watanabe H, Kawaguchi M, Suzuki T, Matsukura S, Homma T et al (2010) Involvement of IL-17F via the induction of IL-6 in psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res 302:499–505
Chizzolini C, Chicheportiche R, Alvarez M, De Rham C, Roux-Lombard P, Ferrari-Lacraz S et al (2008) Prostaglandin E2 synergistically with interleukin-23 favors human Th17 expansion. Blood 112:3696–3703
Ottaviani C, Nasorri F, Bedini C, de Pità O, Girolomoni G, Cavani A (2006) CD56brightCD16(−) NK cells accumulate in psoriatic skin in response to CXCL10 and CCL5 and exacerbate skin inflammation. Eur J Immunol 36:118–128
Kaštelan M, Prpić Massari L, Gruber F, Zamolo G, Žauhar G, Čoklo M et al (2004) Perforin expression is upregulated in the epidermis of psoriatic lesions. Br J Dermatol 151:831–836
Büchau AS, Gallo RL (2007) Innate immunity and antimicrobial defense systems in psoriasis. Clin Dermatol 25:616–624
van der Fits L, Mourits S, Voerman JSA, Kant M, Boon L, Laman JD et al (2009) Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J Immunol 182:5836–5845
Tonel G, Conrad C, Laggner U, Di Meglio P, Grys K, McClanahan TK et al (2010) Cutting edge: a critical functional role for IL-23 in psoriasis. J Immunol 185:5688–5691
Chan JR, Blumenschein W, Murphy E, Diveu C, Wiekowski M, Abbondanzo S et al (2006) IL-23 stimulates epidermal hyperplasia via TNF and IL-20R2-dependent mechanisms with implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. J Exp Med 203:2577–2587
Bell CJ, Sun Y, Nowak UM, Clark J, Howlett S, Pekalski ML et al (2015) Sustained in vivo signaling by long-lived IL-2 induces prolonged increases of regulatory T cells. J Autoimmun 56:66–80
Campbell DJ, Koch MA (2011) Phenotypical and functional specialization of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells. Nat Rev Immunol 11:119–130
MacHugh RS, Piccirilo C, Young DA, Shevach EM, Collins M, Byrne C (2002) CD4CD25 immunoregulatory T cells: gene expression analysis reveals a functional role for the glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor. Immunity 16:311–323
Ellis SD, Carthy ER, Notley CA (2014) Advances on regulatory T cells from the 15th International Congress of Immunology. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 10:203–205
Pasare C, Medzhitov R (2003) Toll pathway-dependent blockade of CD4+ CD25+ T cell-mediated suppression by dendritic cells. Science 299:1033–1036
Dhaeze T, Stinissen P, Liston A, Hellings N (2015) Humoral autoimmunity: a failure of regulatory T cells? Autoimmun Rev 14:735–741
Sugiyama H, Gyulai R, Toichi E, Garaczi E, Shimada S, Stevens SR et al (2005) Dysfunctional blood and target tissue CD4+ CD25high regulatory T cells in psoriasis: mechanism underlying unrestrained pathogenic effector T cell proliferation. J Immunol 174:164–173
Wang H, Peters T, Sindrilaru A, Kess D, Oreshkova T, Yu X-Z et al (2008) TGF-β-dependent suppressive function of Tregs requires wild-type levels of CD18 in a mouse model of psoriasis. J Clin Invest 118:2629
Kim C-H, Kim J-Y, Lee A-Y (2015) Therapeutic and immunomodulatory effects of glucosamine in combination with low-dose cyclosporine A in a murine model of imiquimod-induced psoriasis. Eur J Pharmacol 756:43–51
Zhang K, Li X, Yin G, Liu Y, Niu X, Hou R (2008) Functional characterization of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells differentiated in vitro from bone marrow-derived haematopoietic cells of psoriasis patients with a family history of the disorder. Br J Dermatol 158:298–305
Cai Y, Fleming C, Yan J (2013) Dermal γδ T cells—a new player in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Int Immunopharmacol 16:388–391
Martin B, Hirota K, Cua DJ, Stockinger B, Veldhoen M (2009) Interleukin-17-producing γδ T cells selectively expand in response to pathogen products and environmental signals. Immunity 31:321–330
Cai Y, Shen X, Ding C, Qi C, Li K, Li X et al (2011) Pivotal role of dermal IL-17-producing γδ T cells in skin inflammation. Immunity 35:596–610
Mabuchi T, Takekoshi T, Hwang ST (2011) Epidermal CCR6+ γδ T cells are major producers of IL-22 and IL-17 in a murine model of psoriasiform dermatitis. J Immunol 187:5026–5031
Pantelyushin S, Haak S, Ingold B, Kulig P, Heppner FL, Navarini AA et al (2012) Rorγt+ innate lymphocytes and γδ T cells initiate psoriasiform plaque formation in mice. J Clin Invest 122:2252–2256
Laggner U, Di Meglio P, Perera GK, Hundhausen C, Lacy KE, Ali N et al (2011) Identification of a novel proinflammatory human skin-homing Vγ9Vδ2 T cell subset with a potential role in psoriasis. J Immunol 187:2783–2793
Lowes MA, Suárez-Fariñas M, Krueger JG (2013) Immunology of psoriasis. Annu Rev Immunol 32:227–255
Prinz JC (2004) Disease mimicry—a pathogenetic concept for T cell-mediated autoimmune disorders triggered by molecular mimicry? Autoimmun Rev 3:10–15
Johnston A, Gudjonsson JE, Sigmundsdottir H, Love TJ, Valdimarsson H (2004) Peripheral blood T cell responses to keratin peptides that share sequences with streptococcal M proteins are largely restricted to skin-homing CD8+ T cells. Clin Exp Immunol 138:83–93
Kastelan M, Massari LP, Peternel S (2009) The role of perforin mediated cell cytotoxicity in psoriasis. Lijec Vjesn 132:361–364
Liu J, Cao X (2015) Regulatory dendritic cells in autoimmunity: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun 63:1–12
Zaba LC, Krueger JG, Lowes MA (2009) Resident and “inflammatory” dendritic cells in human skin. J Investig Dermatol 129:302–308
Collin M, McGovern N, Haniffa M (2013) Human dendritic cell subsets. Immunology 140:22–30
Nestle FO, Turka LA, Nickoloff BJ (1994) Characterization of dermal dendritic cells in psoriasis. Autostimulation of T lymphocytes and induction of Th1 type cytokines. J Clin Investig 94:202
Gilliet M, Conrad C, Geiges M, Cozzio A, Thürlimann W, Burg G et al (2004) Psoriasis triggered by toll-like receptor 7 agonist imiquimod in the presence of dermal plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursors. Arch Dermatol 140:1490–1495
Nestle FO, Conrad C, Tun-Kyi A, Homey B, Gombert M, Boyman O et al (2005) Plasmacytoid predendritic cells initiate psoriasis through interferon-α production. J Exp Med 202:135–143
Acosta-Rodriguez EV, Rivino L, Geginat J, Jarrossay D, Gattorno M, Lanzavecchia A et al (2007) Surface phenotype and antigenic specificity of human interleukin 17-producing T helper memory cells. Nat Immunol 8:639–646
Leonardi CL, Powers JL, Matheson RT, Goffe BS, Zitnik R, Wang A et al (2003) Etanercept as monotherapy in patients with psoriasis. N Engl J Med 349:2014–2022
Lowes MA, Chamian F, Abello MV, Fuentes-Duculan J, Lin S-L, Nussbaum R et al (2005) Increase in TNF-α and inducible nitric oxide synthase-expressing dendritic cells in psoriasis and reduction with efalizumab (anti-CD11a). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:19057–19062
Dunphy S, Gardiner CM. 2011 NK cells and psoriasis. BioMed Research International, 2011.
Terui T, Ozawa M, Tagami H (2000) Role of neutrophils in induction of acute inflammation in T-cell-mediated immune dermatosis, psoriasis: a neutrophil-associated inflammation-boosting loop. Exp Dermatol 9:1–10
Knight JS, Carmona-Rivera C, Kaplan MJ. (2012) Proteins derived from neutrophil extracellular traps may serve as self-antigens and mediate organ damage in autoimmune diseases. Frontiers in immunology, 3.
Fuentes-Duculan J, Suárez-Fariñas M, Zaba LC, Nograles KE, Pierson KC, Mitsui H et al (2010) A subpopulation of CD163-positive macrophages is classically activated in psoriasis. J Investig Dermatol 130:2412–2422
Novelli L, Chimenti MS, Chiricozzi A, Perricone R (2014) The new era for the treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: perspectives and validated strategies. Autoimmun Rev 13:64–69
Garzorz N, Eyerich K (2015) NOS2 and CCL27: clinical implications for psoriasis and eczema diagnosis and management. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 11:167–169
Chong M, Fonacier L. (2015) Treatment of eczema: corticosteroids and beyond. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol.
Smith CH, Barker J (2006) Psoriasis and its management. Br Med J 7564:380
Boehncke W-H (2003) Immunomodulatory drugs for psoriasis: new “biologics” offer much promise. BMJ Br Med J 327:634
Griffiths CE, Clark CM, Chalmers RJ, Li WPA, Williams HC (1999) A systematic review of treatments for severe psoriasis. Health Technol Assess 4:1–125
Heydendael VMR, Spuls PI, Opmeer BC, de Borgie CAJM, Reitsma JB, Goldschmidt WFM et al (2003) Methotrexate versus cyclosporine in moderate-to-severe chronic plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med 349:658–665
Chighizola CB, Favalli EG, Meroni PL (2014) Novel mechanisms of action of the biologicals in rheumatic diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 47:6–16
Strohal R, Chimenti S, Vena GA, Girolomoni G (2013) Etanercept provides an effective, safe and flexible short-and long-term treatment regimen for moderate-to-severe psoriasis: a systematic review of current evidence. J Dermatol Treat 24:199–208
Gilbert KE, Manalo IF, Wu JJ (2015) Efficacy and safety of etanercept and adalimumab with and without a loading dose for psoriasis: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol 73:329–331
Feldman SR, Zhao Y, Navaratnam P, Friedman HS, Lu J, Tran MH (2015) Patterns of medication utilization and costs associated with the use of etanercept, adalimumab, and ustekinumab in the management of moderate-to-severe psoriasis. J Managed Care Specialty Pharm 21:201–209
Gottlieb AB, Langley RG, Strober BE, Papp KA, Klekotka P, Creamer K et al (2012) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the addition of methotrexate to etanercept in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 167:649–657
Schett G, Wollenhaupt J, Papp K, Joos R, Rodrigues JF, Vessey AR et al (2012) Oral apremilast in the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arth Rheum 64:3156–3167
Bachelez H, van de Kerkhof PCM, Strohal R, Kubanov A, Valenzuela F, Lee J-H et al (2015) Tofacitinib versus etanercept or placebo in moderate-to-severe chronic plaque psoriasis: a phase 3 randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet 386:552–561
Nast A, Boehncke WH, Mrowietz U, Ockenfels HM, Philipp S, Reich K et al (2012) S3—guidelines on the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris (English version). Update. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 10:S1–s95
Bachmann F, Nast A, Sterry W, Philipp S. Safety and efficacy of the tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Seminars in cutaneous medicine and surgery: WB Saunders; 2010, p. 35–47.
Bustamante J, Boisson-Dupuis S, Jouanguy E, Picard C, Puel A, Abel L et al (2008) Novel primary immunodeficiencies revealed by the investigation of paediatric infectious diseases. Curr Opin Immunol 20:39–48
Godinez I, Keestra AM, Spees A, Bäumler AJ (2011) The IL-23 axis in Salmonella gastroenteritis. Cell Microbiol 13:1639–1647
Akahoshi M, Nakashima H, Miyake K, Inoue Y, Shimizu S, Tanaka Y et al (2003) Influence of interleukin-12 receptor β1 polymorphisms on tuberculosis. Hum Genet 112:237–243
Kalb RE, Fiorentino DF, Lebwohl MG, Toole J, Poulin Y, Cohen AD et al (2015) Risk of serious infection with biologic and systemic treatment of psoriasis: results from the Psoriasis Longitudinal Assessment and Registry (PSOLAR). JAMA Dermatol 151:961–969
Ahlehoff O, Skov L, Gislason G, Lindhardsen J, Kristensen SL, Iversen L et al (2013) Cardiovascular disease event rates in patients with severe psoriasis treated with systemic anti-inflammatory drugs: a Danish real-world cohort study. J Intern Med 273:197–204
Ryan C, Leonardi CL, Krueger JG, Kimball AB, Strober BE, Gordon KB et al (2011) Association between biologic therapies for chronic plaque psoriasis and cardiovascular events: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. JAMA 306:864–871
Alshaker HA, Matalka KZ (2011) IFN-γ, IL-17 and TGF-β involvement in shaping the tumor microenvironment: the significance of modulating such cytokines in treating malignant solid tumors. Cancer Cell Int 11:1
López-Ferrer A, Vilarrasa E, Puig L (2015) Secukinumab (AIN457) for the treatment of psoriasis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 11:1177–1188
Brown SL, Greene MH, Gershon SK, Edwards ET, Braun MM (2002) Tumor necrosis factor antagonist therapy and lymphoma development: twenty-six cases reported to the Food and Drug Administration. Arth Rheum 46:3151–3158
Nesher G (2014) Polymyalgia rheumatica—diagnosis and classification. J Autoimmun 48–49:76–78
Lu Q (2014) Unmet needs in autoimmunity and potential new tools. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 47:111–118
Petrillo MG, Ronchetti S, Ricci E, Alunno A, Gerli R, Nocentini G et al (2015) GITR+ regulatory T cells in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev 14:117–126
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81220108017, 81430074, 81270024, and 30972745).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Y., Chang, C. & Lu, Q. The Inflammatory Response in Psoriasis: a Comprehensive Review. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 50, 377–389 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-016-8535-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-016-8535-x