Abstract
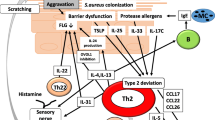
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease known for its complex pathophysiology involving several immune pathways. In the lesion, signals from barrier disruption, allergens, and microbial colonization are integrated and transmitted to diverse immune cell types, which initiate and maintain the disease. Cytokines are critical in the allergic intercellular communication networks. This review focuses on up-to-date knowledge on the role of cytokines in AD, including recently described functions as well as novel cellular sources. We propose three modules defined as the cellular source of groups of cytokines: (1) keratinocytes, (2) innate immune cells, and (3) T cells. This view enables to better position the function of novel cytokine players, such as thymic stromal lymphopoetin, IL-21, IL-25, and IL-33, in linking different modules and ultimately leading to the allergic inflammatory phenotype. Persistent efforts in the detailed characterization of cytokine networks will be fundamental for the understanding of the complex pathogenic mechanisms of the disease and for guiding targeted therapeutic interventions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leung DY, Bieber T (2003) Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 361(9352):151–160
Leung DY, Boguniewicz M, Howell MD, Nomura I, Hamid QA (2004) New insights into atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest 113(5):651–657
Leung DY (2000) Atopic dermatitis: new insights and opportunities for therapeutic intervention. J Allergy Clin Immunol 105(5):860–876
Soumelis V, Reche PA, Kanzler H, Yuan W, Edward G, Homey B et al (2002) Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat Immunol 3(7):673–680
Yoo J, Omori M, Gyarmati D, Zhou B, Aye T, Brewer A et al (2005) Spontaneous atopic dermatitis in mice expressing an inducible thymic stromal lymphopoietin transgene specifically in the skin. J Exp Med 202(4):541–549
Zhou B, Comeau MR, De Smedt T, Liggitt HD, Dahl ME, Lewis DB et al (2005) Thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a key initiator of allergic airway inflammation in mice. Nat Immunol 6(10):1047–1053
Gao PS, Rafaels NM, Mu D, Hand T, Murray T, Boguniewicz M et al (2010) Genetic variants in thymic stromal lymphopoietin are associated with atopic dermatitis and eczema herpeticum. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125(6):1403–1407
Wang YH, Angkasekwinai P, Lu N, Voo KS, Arima K, Hanabuchi S et al (2007) IL-25 augments type 2 immune responses by enhancing the expansion and functions of TSLP-DC-activated Th2 memory cells. J Exp Med 204(8):1837–1847
Shimizu M, Matsuda A, Yanagisawa K, Hirota T, Akahoshi M, Inomata N et al (2005) Functional SNPs in the distal promoter of the ST2 gene are associated with atopic dermatitis. Hum Mol Genet 14(19):2919–2927
Moritz DR, Rodewald HR, Gheyselinck J, Klemenz R (1998) The IL-1 receptor-related T1 antigen is expressed on immature and mature mast cells and on fetal blood mast cell progenitors. J Immunol 161(9):4866–4874
Xu D, Chan WL, Leung BP, Huang F, Wheeler R, Piedrafita D et al (1998) Selective expression of a stable cell surface molecule on type 2 but not type 1 helper T cells. J Exp Med 187(5):787–794
Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan TK et al (2005) IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 23(5):479–490
Angelova-Fischer I, Fernandez IM, Donnadieu MH, Bulfone-Paus S, Zillikens D, Fischer TW et al (2010) Injury to the stratum corneum induces in vivo expression of human thymic stromal lymphopoietin in the epidermis. J Invest Dermatol 130(10):2505–2507
Miyata M, Hatsushika K, Ando T, Shimokawa N, Ohnuma Y, Katoh R et al (2008) Mast cell regulation of epithelial TSLP expression plays an important role in the development of allergic rhinitis. Eur J Immunol 38(6):1487–1492
Bogiatzi SI, Fernandez I, Bichet JC, Marloie-Provost MA, Volpe E, Sastre X et al (2007) Cutting edge: proinflammatory and Th2 cytokines synergize to induce thymic stromal lymphopoietin production by human skin keratinocytes. J Immunol 178(6):3373–3377
Allakhverdi Z, Comeau MR, Jessup HK, Delespesse G (2009) Thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a mediator of crosstalk between bronchial smooth muscles and mast cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123(4):958–960, e2
Vu AT, Baba T, Chen X, Le TA, Kinoshita H, Xie Y et al (2010) Staphylococcus aureus membrane and diacylated lipopeptide induce thymic stromal lymphopoietin in keratinocytes through the Toll-like receptor 2-Toll-like receptor 6 pathway. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126(5):985–993
Ito T, Wang YH, Duramad O, Hori T, Delespesse GJ, Watanabe N et al (2005) TSLP-activated dendritic cells induce an inflammatory T helper type 2 cell response through OX40 ligand. J Exp Med 202(9):1213–1223
Allakhverdi Z, Comeau MR, Jessup HK, Yoon BR, Brewer A, Chartier S et al (2007) Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is released by human epithelial cells in response to microbes, trauma, or inflammation and potently activates mast cells. J Exp Med 204(2):253–258
Al-Shami A, Spolski R, Kelly J, Keane-Myers A, Leonard WJ (2005) A role for TSLP in the development of inflammation in an asthma model. J Exp Med 202(6):829–839
He R, Oyoshi MK, Garibyan L, Kumar L, Ziegler SF, Geha RS (2008) TSLP acts on infiltrating effector T cells to drive allergic skin inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(33):11875–11880
Lu N, Wang YH, Arima K, Hanabuchi S, Liu YJ (2009) TSLP and IL-7 use two different mechanisms to regulate human CD4+ T cell homeostasis. J Exp Med 206(10):2111–2119
Fort MM, Cheung J, Yen D, Li J, Zurawski SM, Lo S et al (2001) IL-25 induces IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and Th2-associated pathologies in vivo. Immunity 15(6):985–995
Angkasekwinai P, Park H, Wang YH, Chang SH, Corry DB, Liu YJ et al (2007) Interleukin 25 promotes the initiation of proallergic type 2 responses. J Exp Med 204(7):1509–1517
Ikeda K, Nakajima H, Suzuki K, Kagami S, Hirose K, Suto A et al (2003) Mast cells produce interleukin-25 upon Fc epsilon RI-mediated activation. Blood 101(9):3594–3596
Hvid M, Vestergaard C, Kemp K, Christensen GB, Deleuran B, Deleuran M (2010) IL-25 in atopic dermatitis: a possible link between Inflammation and skin barrier dysfunction? J Invest Dermatol 131(1):150–157
Basham TY, Nickoloff BJ, Merigan TC, Morhenn VB (1985) Recombinant gamma interferon differentially regulates class II antigen expression and biosynthesis on cultured normal human keratinocytes. J Interferon Res 5(1):23–32
O’Regan GM, Irvine AD (2010) The role of filaggrin in the atopic diathesis. Clin Exp Allergy 40(7):965–972
Allakhverdi Z, Smith DE, Comeau MR, Delespesse G (2007) Cutting edge: the ST2 ligand IL-33 potently activates and drives maturation of human mast cells. J Immunol 179(4):2051–2054
Mekori YA, Metcalfe DD (2000) Mast cells in innate immunity. Immunol Rev 173:131–140
Navi D, Saegusa J, Liu FT (2007) Mast cells and immunological skin diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 33(1–2):144–155
Schreibelt G, Tel J, Sliepen KH, Benitez-Ribas D, Figdor CG, Adema GJ et al (2010) Toll-like receptor expression and function in human dendritic cell subsets: implications for dendritic cell-based anti-cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 59(10):1573–1582
Kang JY, Nan X, Jin MS, Youn SJ, Ryu YH, Mah S et al (2009) Recognition of lipopeptide patterns by Toll-like receptor 2-Toll-like receptor 6 heterodimer. Immunity 31(6):873–884
Jin MS, Kim SE, Heo JY, Lee ME, Kim HM, Paik SG et al (2007) Crystal structure of the TLR1-TLR2 heterodimer induced by binding of a tri-acylated lipopeptide. Cell 130(6):1071–1082
Grewe M, Gyufko K, Schopf E, Krutmann J (1994) Lesional expression of interferon-gamma in atopic eczema. Lancet 343(8888):25–26
Johnson-Huang LM, McNutt NS, Krueger JG, Lowes MA (2009) Cytokine-producing dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of inflammatory skin diseases. J Clin Immunol 29(3):247–256
Wang B, Feliciani C, Howell BG, Freed I, Cai Q, Watanabe H et al (2002) Contribution of Langerhans cell-derived IL-18 to contact hypersensitivity. J Immunol 168(7):3303–3308
Gracie JA, Robertson SE, McInnes IB (2003) Interleukin-18. J Leukoc Biol 73(2):213–224
Homey B, Steinhoff M, Ruzicka T, Leung DY (2006) Cytokines and chemokines orchestrate atopic skin inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 118(1):178–189
Nakanishi K, Tsutsui H, Yoshimoto T (2010) Importance of IL-18-induced super Th1 cells for the development of allergic inflammation. Allergol Int 59(2):137–141
Sugimoto T, Ishikawa Y, Yoshimoto T, Hayashi N, Fujimoto J, Nakanishi K (2004) Interleukin 18 acts on memory T helper cells type 1 to induce airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in a naive host mouse. J Exp Med 199(4):535–545
Yoshimoto T, Tsutsui H, Tominaga K, Hoshino K, Okamura H, Akira S et al (1999) IL-18, although antiallergic when administered with IL-12, stimulates IL-4 and histamine release by basophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(24):13962–13966
Yoshimoto T, Min B, Sugimoto T, Hayashi N, Ishikawa Y, Sasaki Y et al (2003) Nonredundant roles for CD1d-restricted natural killer T cells and conventional CD4+ T cells in the induction of immunoglobulin E antibodies in response to interleukin 18 treatment of mice. J Exp Med 197(8):997–1005
Matsui K, Wirotesangthong M, Nishikawa A (2008) Peptidoglycan from Staphylococcus aureus induces IL-4 production from murine spleen cells via an IL-18-dependent mechanism. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 146(3):262–266
Swain SL, Weinberg AD, English M, Huston G (1990) IL-4 directs the development of Th2-like helper effectors. J Immunol 145(11):3796–3806
Renauld JC (2001) New insights into the role of cytokines in asthma. J Clin Pathol 54(8):577–589
Hamelmann E, Gelfand EW (2001) IL-5-induced airway eosinophilia—the key to asthma? Immunol Rev 179:182–191
Jin H, Oyoshi MK, Le Y, Bianchi T, Koduru S, Mathias CB et al (2009) IL-21R is essential for epicutaneous sensitization and allergic skin inflammation in humans and mice. J Clin Invest 119(1):47–60
Wurster AL, Rodgers VL, Satoskar AR, Whitters MJ, Young DA, Collins M et al (2002) Interleukin 21 is a T helper (Th) cell 2 cytokine that specifically inhibits the differentiation of naive Th cells into interferon gamma-producing Th1 cells. J Exp Med 196(7):969–977
Nurieva R, Yang XO, Martinez G, Zhang Y, Panopoulos AD, Ma L et al (2007) Essential autocrine regulation by IL-21 in the generation of inflammatory T cells. Nature 448(7152):480–483
Sarra M, Monteleone I, Stolfi C, Fantini MC, Sileri P, Sica G et al (2010) Interferon-gamma-expressing cells are a major source of interleukin-21 in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis 16(8):1332–1339
Chtanova T, Tangye SG, Newton R, Frank N, Hodge MR, Rolph MS et al (2004) T follicular helper cells express a distinctive transcriptional profile, reflecting their role as non-Th1/Th2 effector cells that provide help for B cells. J Immunol 173(1):68–78
Peluso I, Fantini MC, Fina D, Caruso R, Boirivant M, MacDonald TT et al (2007) IL-21 counteracts the regulatory T cell-mediated suppression of human CD4+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol 178(2):732–739
Costanzo A, Chimenti MS, Botti E, Caruso R, Sarra M, Monteleone G (2010) IL-21 in the pathogenesis and treatment of skin diseases. J Dermatol Sci 60(2):61–66
Konforte D, Simard N, Paige CJ (2009) IL-21: an executor of B cell fate. J Immunol 182(4):1781–1787
Dillon SR, Sprecher C, Hammond A, Bilsborough J, Rosenfeld-Franklin M, Presnell SR et al (2004) Interleukin 31, a cytokine produced by activated T cells, induces dermatitis in mice. Nat Immunol 5(7):752–760
Sonkoly E, Muller A, Lauerma AI, Pivarcsi A, Soto H, Kemeny L et al (2006) IL-31: a new link between T cells and pruritus in atopic skin inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 117(2):411–417
Bilsborough J, Leung DY, Maurer M, Howell M, Boguniewicz M, Yao L et al (2006) IL-31 is associated with cutaneous lymphocyte antigen-positive skin homing T cells in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 117(2):418–425
Raap U, Wichmann K, Bruder M, Stander S, Wedi B, Kapp A et al (2008) Correlation of IL-31 serum levels with severity of atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122(2):421–423
Cheung PF, Wong CK, Ho AW, Hu S, Chen DP, Lam CW (2010) Activation of human eosinophils and epidermal keratinocytes by Th2 cytokine IL-31: implication for the immunopathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Int Immunol 22(6):453–467
Antonysamy MA, Fanslow WC, Fu F, Li W, Qian S, Troutt AB et al (1999) Evidence for a role of IL-17 in organ allograft rejection: IL-17 promotes the functional differentiation of dendritic cell progenitors. J Immunol 162(1):577–584
Milovanovic M, Drozdenko G, Weise C, Babina M, Worm M (2010) Interleukin-17A promotes IgE production in human B cells. J Invest Dermatol 130(11):2621–2628
Toda M, Leung DY, Molet S, Boguniewicz M, Taha R, Christodoulopoulos P et al (2003) Polarized in vivo expression of IL-11 and IL-17 between acute and chronic skin lesions. J Allergy Clin Immunol 111(4):875–881
Koga C, Kabashima K, Shiraishi N, Kobayashi M, Tokura Y (2008) Possible pathogenic role of Th17 cells for atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol 128(11):2625–2630
Guttman-Yassky E, Lowes MA, Fuentes-Duculan J, Zaba LC, Cardinale I, Nograles KE et al (2008) Low expression of the IL-23/Th17 pathway in atopic dermatitis compared to psoriasis. J Immunol 181(10):7420–7427
Lee FE, Georas SN, Beck LA (2010) IL-17: important for host defense, autoimmunity, and allergy? J Invest Dermatol 130(11):2540–2542
Ferretti S, Bonneau O, Dubois GR, Jones CE, Trifilieff A (2003) IL-17, produced by lymphocytes and neutrophils, is necessary for lipopolysaccharide-induced airway neutrophilia: IL-15 as a possible trigger. J Immunol 170(4):2106–2112
Uhlig HH, McKenzie BS, Hue S, Thompson C, Joyce-Shaikh B, Stepankova R et al (2006) Differential activity of IL-12 and IL-23 in mucosal and systemic innate immune pathology. Immunity 25(2):309–318
Cua DJ, Tato CM (2010) Innate IL-17-producing cells: the sentinels of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 10(7):479–489
Hueber AJ, Asquith DL, Miller AM, Reilly J, Kerr S, Leipe J et al (2010) Mast cells express IL-17A in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. J Immunol 184(7):3336–3340
Wang YH, Voo KS, Liu B, Chen CY, Uygungil B, Spoede W et al (2010) A novel subset of CD4(+) T(H)2 memory/effector cells that produce inflammatory IL-17 cytokine and promote the exacerbation of chronic allergic asthma. J Exp Med 207(11):2479–2491
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carmi-Levy, I., Homey, B. & Soumelis, V. A Modular View of Cytokine Networks in Atopic Dermatitis. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 41, 245–253 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-010-8239-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-010-8239-6