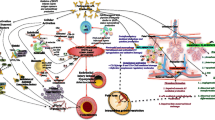
Abstract
Recurrent fetal loss affects 1–5% of women of childbearing age. Immunological mechanisms may account for 40% of recurrent miscarriages, and in particular, the antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) appears to be implicated in 7–25% of the cases. Because antiphospholipid (aPL) antibodies have thrombogenic properties, fetal loss in patients with APS has been ascribed to thrombosis of placental vessels. However, we have shown that inflammation, specifically activation of complement with generation of the anaphylotoxin C5a, is an essential trigger of fetal injury. Thrombosis and inflammation are linked in many clinical conditions. Tissue factor (TF), the major cellular initiator of the coagulation protease cascade, plays important roles in both thrombosis and inflammation, and its expression is increased in patients with APS. Here we describe how TF, acting as a proinflammatory molecule, induces trophoblast injury and fetal death in a mouse model of APS. Importantly, we will discuss how TF contributes to C5a-induced oxidative burst in neutrophils leading to trophoblasts and fetal injury in APS. The finding that TF is an important effector in aPL-induced inflammation may allow the development of new therapies to abrogate the inflammatory loop caused by tissue factor and improve pregnancy outcomes in patients with aPL antibodies. Statins downregulate TF-induced inflammation and rescued the pregnancies in aPL-treated mice, suggesting they may be a good treatment for women with aPL-induced pregnancy complications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaumont JL (1954) Syndrome hemorrragique acquis du a un anticoagulant circulant. Sang 25:1–15
Nilsson IM, Astedt B, Hedner U, Berezin D (1975) Intrauterine death and circulating anticoagulant (‘antithromboplastin’). Acta Med Scand 197:153–159
Firkin BG, Howard MA, Radford N (1980) Possible relationship between lupus inhibitor and recurrent abortion in young women. Lancet ii:366
Loizou S, Byron MA, Englert HJ, David J, Hughes GV, Walport MJ (1988) Association of quantitative anticardiolipin antibody levels with fetal loss and time of loss in systemic lupus erythematosus. Q J Med 68:525–531
Derksen RH, de Groot PG (2008) The obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome. J Reprod Immunol 77(1):41–50
Tincani A, Bazzani C, Zingarelli S, Lojacono A (2008) Lupus and the antiphospholipid syndrome in pregnancy and obstetrics: clinical characteristics, diagnosis, pathogenesis, and treatment. Semin Thromb Hemost 34(3):267–273
Blank M, Shoenfeld Y (2009) Antiphospholipid antibody-mediated reproductive failure in antiphospholipid syndrome. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol (in press)
Yetman DL, Kutteh WH (1996) Antiphospholipid antibody panels and recurrent pregnancy loss: prevalence of anticardiolipin antibodies compared with other antiphospholipid antibodies. Fertil Steril 66:540–546
Stephenson MD (1996) Frequency of factors associated with habitual abortion in 197 couples. Fertil Steril 66:24–29
Wilson WA, Gharavi AE, Koike T, Lockshin MD, Branch DW, Piette JC et al (1999) International consensus statement on preliminary classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 42:1309–1311
Lockshin MD, Sammaritano LS, Schwartzman SS (2000) Validation of the Sapporo criteria for antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 43:440–443
Kutteh WH (1996) Antiphospholipid antibody-associated recurrent pregnancy loss: treatment with heparin and low-dose aspirin is superior to low-dose aspirin alone. Am J Obstet Gynecol 174:1584–1589
Rai R, Cohen H, Dave M, Regan L (1997) Randomized controlled trial of aspirin and aspirin plus heparin in pregnant women with recurrent miscarriage associated with phospholipid antibodies. J Brit Med 314:253–257
Zhang Y, Deng T, Luther M et al (1994) Tissue factor controls the balance of angiogenic and antiangiogenic properties of tumor cells in mice. J Clin Invest 94:1320–1327
Soifer SJ, Peters KG, O’Keefe J, Coughlin SR (1994) Disparate temporal expression of the prothrombin and thrombin receptor genes during mouse development. Am J Pathol 144:60–69
Bugge TH, Xiao Q, Kombrinck KW et al (1996) Fatal embryonic bleeding events in mice lacking tissue factor, the cell-associated initiator of blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:6258–6263
Parry GC, Erlich JH, Carmeliet P, Luther T, Mackman N (1998) Low levels of tissue factor are compatible with development and hemostasis in mice. J Clin Invest 101:560–569
Carmeliet P, Mackman N, Moons L et al (1996) Role of tissue factor in embryonic blood vessel development. Nature 383:73–75
Osterud B, Flæstad T (1983) Increased tissue thromboplastin activity in monocytes of patients with meningococcal infection: related to an unfavorable prognosis. Thromb Haemost 49:5–7
Edwards RL, Rickles FR, Cronlund M (1981) Abnormalities of blood coagulation in patients with cancer. J Lab Clin Med 98:917–928
Leatham E, Bath P, Tooze J, Camm A (1995) Increased monocyte tissue factor expression in coronary disease. Br Heart J 73:10–13
Monroe DM, Key NS (2007) The tissue factor-factor VIIa complex: procoagulant activity, regulation, and multitasking. J Thromb Haemost 5:1097–1105
Camerer E, Huang W, Coughlin SR (2000) Tissue factor- and factor X-dependent activation of protease-activated receptor 2 by factor VIIa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5255–5260
Ruf W, Dorfleutner A, Riewald M (2003) Specificity of coagulation factor signaling. J Thromb Haemost 1:1495–1503
Mueller BM, Reisfeld RA, Edgington TS, Ruf W (1992) Expression of tissue factor by melanoma cells promotes efficient hematogenous metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1–6
Cuadrado MJ, López-Pedrera C, Khamashta MA et al (1997) Thrombosis in primary antiphospholipid syndrome: a pivotal role for monocyte tissue factor expression. Arthritis Rheum 40:834–841
Dobado-Berrios PM, Lopez-Pedrera C, Velasco F, Aguirre MA, Torres A, Cuadrado M (1999) Increased levels of tissue factor mRNA in mononuclear blood cells of patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb Haemost 82:1578–1582
Reverter JC, Tassies D, Font J et al (1996) Hypercoagulable state in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome is related to high induced tissue factor expression on monocytes and to low free protein S. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 16:1319–1326
Nojima J, Masuda Y, Iwatani Y et al (2008) Tissue factor expression on monocytes induced by anti-phospholipid antibodies as a strong risk factor for thromboembolic complications in SLE patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 365:195–200
Reverter JC, Tàssies D, Font J et al (1998) Effects of human monoclonal anticardiolipin antibodies on platelet function and on tissue factor expression on monocytes. Arthritis Rheum 41:1420–1427
Amengual O, Atsumi T, Khamashta MA, Hughes GRV (1998) The role of the tissue factor pathway in the hypercoagulable state in patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb Haemost 79:276–281
Zhou H, Walberg AS, Roubey RAS (2004) Characterization of monocyte tissue factor activity induced by IgG antiphospholipid antibodies and inhibition by dilazep. Blood 104:2353–2358
Roubey RA, Pratt CW, Buyon JP, Winfield JB (1992) Lupus anticoagulant activity of autoimmune antiphospholipid antibodies is dependent upon beta 2-glycoprotein I. J Clin Invest 90:1100–1104
Vega-Ostertag M, Casper K, Swerlick R, Ferrara D, Harris EN, Pierangeli SS (2005) Involvement of p38 MAPK in the up-regulation of tissue factor on endothelial cells by antiphospholipid antibodies. Arthritis Rheum 52:1545–1554
Lopez-Pedrera C, Buendia P, Barbarroja N, Siendones E, Velasco F, Cuadrado MJ (2006) Antiphospholipid-mediated thrombosis: interplay between anticardiolipin antibodies and vascular cells. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 12:41–45
Kornberg A, Renaudineau Y, Blank M, Youinou P, Sheffield Y (2000) Anti-beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies and anti-endothelial cell antibodies induce tissue factor in endothelial cells. Isr Med Assoc J 2:27–31
Vega-Ostertag ME, Ferrara DE, Romay-Penabad Z et al (2007) Role of p38 mutagen-activated protein kinas in antiphospholipid antibodymediated thrombosis and endothelial cell activation. J Thromb Haemost 5:1828–1834
Ritis K, Doumas M, Mastellos D et al (2006) A novel C5a receptor-tissue factor cross-talk in neutrophils links innate immunity to coagulation pathways. J Immunol 177:4794–4802
Girardi G, Berman J, Redecha P et al (2003) Complement C5a receptors and neutrophils mediate fetal injury in the antiphospholipid syndrome. J Clin Invest 112:1644–1654
Girardi G, Redecha P, Salmon JE (2004) Heparin prevents antiphospholipid antibody-induced fetal loss by inhibiting complement activation. Nat Med 10:1222–1226
Redecha P, Tilley R, Tencati M et al (2007) Tissue factor: a link between C5a and neutrophil activation in antiphospholipid antibody induced fetal injury. Blood 110:2423–2431
Bunnett NW (2006) Protease-activated receptors: how proteases signal to cells to cause inflammation and pain. Semin Thromb Hemost 32:39–48
Chin AC, Lee WY, Nusrat A, Vergnolle N, Parkos CA (2008) Neutrophil-mediated activation of epithelial protease-activated receptors-1 and -2 regulates barrier function and transepithelial migration. J Immunol 181:5702–5710
Shpacovitch VM, Seeliger S, Huber-Lang M et al (2007) Agonists of proteinase-activated receptor-2 affect transendothelial migration and apoptosis of human neutrophils. Exp Dermatol 16:799–806
Redecha P, Franzke CW, Ruf W, Mackman N, Girardi G (2008) Neutrophil activation by the tissue factor/Factor VIIa/PAR2 axis mediates fetal death in a mouse model of antiphospholipid syndrome. J Clin Invest 118:3453–3461
Takemoto M, Liao JK (2001) Pleiotropic effects of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21:1712–1719
Rosenson R, Tangney C (1998) Antiatherosclerotic properties of statins. JAMA 279:1643–1650
Paraskevas KI, Stathopoulos V, Mikhailidis DP (2007) Emerging indications for statins: a pluripotent family of agents with several potential applications. Curr Pharm Des 13:3622–3636
Pierangeli SS, Ferrara DE (2005) More on: fluvastatin inhibits up-regulation of tissue factor expression by antiphospholipid antibodies on endothelial cells. J Thromb Haemost 3:1112–1113
Kunieda Y, Nakagawa K, Nishimura H et al (2003) HMG CoA reductase inhibitor suppresses the expression of tissue factor and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induced by angiotensin II in cultured rat aortic endothelial cells. Thromb Res 110:227–234
Pollack PS, Shields KE, Burnett DM, Osborne MJ, Cunningham ML, Stepanavage ME (2005) Pregnancy outcomes after maternal exposure to simvastatin and lovastatin. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 73:888–896
Edison RJ, Muenke M (2005) Mechanistic and epidemiologic considerations in the evaluation of adverse birth outcomes following gestational exposure to statins. Am J Med Genet A 135:230–231
Contrino J, Hair G, Kreutzer DL, Rickles FR (1996) In situ detection of tissue factor in vascular endothelial cells: correlation with the malignant phenotype of human breast disease. Nat Med 2:209–215
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Girardi, G. Role of Tissue Factor in the Maternal Immunological Attack of the Embryo in the Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 39, 160–165 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-009-8187-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-009-8187-1