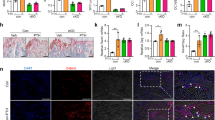
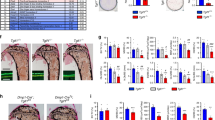
Abstract
The receptor for parathyroid hormone (PTH) and PTH-related peptide (PTH1R) belongs to the class II G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. The calpain small subunit encoded by the gene Capns1 is the second protein and the first enzyme identified by a yeast two-hybrid screen using the intracellular C-terminal tail of the rat PTH1R. The calpain regulatory small subunit forms a heterodimer with the calpain large catalytic subunit and modulates various cellular functions as a cysteine protease. To investigate a physiological role of the calpain small subunit in cells of the osteoblast lineage, we generated osteoblast-specific Capns1 knockout mouse models and characterized their bone phenotype. Molecular mechanisms by which calpain modulates cell proliferation of the osteoblast lineage were further examined in vitro. Moreover, we utilized the mutant mice as a disease model of osteoporosis accompanied with impaired bone resorptive function and suggested a possible clinical translation of our basic research finding.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ducy, P., Amling, M., Takeda, S., Priemel, M., Schilling, A. F., Beil, F. T., et al. (2000). Leptin inhibits bone formation through a hypothalamic relay: A central control of bone mass. Cell, 100, 197–207.
Takeda, S., Elefteriou, F., Levasseur, R., Liu, X., Zhao, L., Parker, K. L., et al. (2002). Leptin regulates bone formation via the sympathetic nervous system. Cell, 111, 305–317.
Elefteriou, F., Ahn, J. D., Takeda, S., Starbuck, M., Yang, X., Liu, X., et al. (2005). Leptin regulation of bone resorption by the sympathetic nervous system and CART. Nature, 434, 514–520.
Yadav, V. K., Oury, F., Suda, N., Liu, Z. W., Gao, X. B., Confavreux, C., et al. (2009). A serotonin-dependent mechanism explains the leptin regulation of bone mass, appetite, and energy expenditure. Cell, 138, 976–989.
Lee, N. K., Sowa, H., Hinoi, E., Ferron, M., Ahn, J. D., Confavreux, C., et al. (2007). Endocrine regulation of energy metabolism by the skeleton. Cell, 130, 456–469.
Hinoi, E., Gao, N., Jung, D. Y., Yadav, V., Yoshizawa, T., Kajimura, D., et al. (2009). An Osteoblast-dependent mechanism contributes to the leptin regulation of insulin secretion. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1173(Suppl 1), E20–E30.
Ferron, M., Wei, J., Yoshizawa, T., Del Fattore, A., DePinho, R. A., Teti, A., et al. (2010). Insulin signaling in osteoblasts integrates bone remodeling and energy metabolism. Cell, 142, 296–308.
Mahon, M. J., Donowitz, M., Yun, C. C., & Segre, G. V. (2002). Na(+)/H(+) exchanger regulatory factor 2 directs parathyroid hormone 1 receptor signalling. Nature, 417, 858–861.
Juppner, H., Abou-Samra, A. B., Freeman, M., Kong, X. F., Schipani, E., Richards, J., et al. (1991). A G protein-linked receptor for parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide. Science, 254, 1024–1026.
Shimada, M., Mahon, M. J., Greer, P. A., & Segre, G. V. (2005). The receptor for parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide is hydrolyzed and its signaling properties are altered by directly binding the calpain small subunit. Endocrinology, 146, 2336–2344.
Goll, D. E., Thompson, V. F., Li, H., Wei, W., & Cong, J. (2003). The calpain system. Physiological Reviews, 83, 731–801.
Sorimachi, H., Hata, S., & Ono, Y. (2011). Calpain chronicle—an enzyme family under multidisciplinary characterization. Proceedings of the Japan Academy-Series B: Physical & Biological Sciences, 87, 287–327.
Arthur, J. S., Elce, J. S., Hegadorn, C., Williams, K., & Greer, P. A. (2000). Disruption of the murine calpain small subunit gene, Capn4: Calpain is essential for embryonic development but not for cell growth and division. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 20, 4474–4481.
Zimmerman, U. J., Boring, L., Pak, J. H., Mukerjee, N., & Wang, K. K. (2000). The calpain small subunit gene is essential: Its inactivation results in embryonic lethality. IUBMB Life, 50, 63–68.
Tram, K. K., Spencer, M. J., Murray, S. S., Lee, D. B., Tidball, J. G., & Murray, E. J. (1993). Identification of calcium-activated neutral protease activity and regulation by parathyroid hormone in mouse osteoblastic cells. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology International, 29, 981–987.
Murray, E. J., Tram, K. K., Murray, S. S., & Lee, D. B. (1995). Parathyroid hormone-induced retraction of MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells is attenuated by the calpain inhibitor N-Ac-Leu–Leu-norleucinal. Metabolism, 44, 141–144.
Murray, E. J., Grisanti, M. S., Bentley, G. V., & Murray, S. S. (1997). E64d, a membrane-permeable cysteine protease inhibitor, attenuates the effects of parathyroid hormone on osteoblasts in vitro. Metabolism, 46, 1090–1094.
Murray, S. S., Grisanti, M. S., Bentley, G. V., Kahn, A. J., Urist, M. R., & Murray, E. J. (1997). The calpain-calpastatin system and cellular proliferation and differentiation in rodent osteoblastic cells. Experimental Cell Research, 233, 297–309.
Shimada, M., Greer, P. A., McMahon, A. P., Bouxsein, M. L., & Schipani, E. (2008). In vivo targeted deletion of calpain small subunit, Capn4, in cells of the osteoblast lineage impairs cell proliferation, differentiation, and bone formation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283, 21002–21010.
Nakashima, K., Zhou, X., Kunkel, G., Zhang, Z., Deng, J. M., Behringer, R. R., et al. (2002). The novel zinc finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell, 108, 17–29.
Dacquin, R., Starbuck, M., Schinke, T., & Karsenty, G. (2002). Mouse alpha1(I)-collagen promoter is the best known promoter to drive efficient Cre recombinase expression in osteoblast. Developmental Dynamics, 224, 245–251.
Rodda, S. J., & McMahon, A. P. (2006). Distinct roles for Hedgehog and canonical Wnt signaling in specification, differentiation and maintenance of osteoblast progenitors. Development, 133, 3231–3244.
Kashiwagi, A., Fein, M. J., & Shimada, M. (2011). Calpain modulates cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27(Kip1)) in cells of the osteoblast lineage. Calcified Tissue International, 89, 36–42.
Bertoli, C., Copetti, T., Lam, E. W., Demarchi, F., & Schneider, C. (2009). Calpain small-1 modulates Akt/FoxO3A signaling and apoptosis through PP2A. Oncogene, 28, 721–733.
Gutzkow, K. B., Naderi, S., & Blomhoff, H. K. (2002). Forskolin-mediated G1 arrest in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells: Phosphorylated pRB sequesters E2Fs. Journal of Cell Science, 115, 1073–1082.
Parada, Y., Banerji, L., Glassford, J., Lea, N. C., Collado, M., Rivas, C., et al. (2001). BCR-ABL and interleukin 3 promote haematopoietic cell proliferation and survival through modulation of cyclin D2 and p27Kip1 expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 23572–23580.
Ishida, N., Hara, T., Kamura, T., Yoshida, M., Nakayama, K., & Nakayama, K. I. (2002). Phosphorylation of p27Kip1 on Serine 10 is required for its binding to CRM1 and Nuclear Exports. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 14355–14358.
Rodier, G., Montagnoli, A., Di Marcotullio, L., Coulombe, P., Draetta, G. F., Pagano, M., et al. (2001). p27 cytoplasmic localization is regulated by phosphorylation on Ser10 and is not a prerequisite for its proteolysis. EMBO Journal, 20, 6672–6682.
Delmas, C., Aragou, N., Poussard, S., Cottin, P., Darbon, J. M., & Manenti, S. (2003). MAP kinase-dependent degradation of p27Kip1 by calpains in choroidal melanoma cells. Requirement of p27Kip1 nuclear export. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 12443–12451.
Kashiwagi, A., Schipani, E., Fein, M. J., Greer, P. A., & Shimada, M. (2010). Targeted deletion of Capn4 in cells of the chondrocyte lineage impairs chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 30, 2799–2810.
Kashiwagi, A., Fein, M. J., & Shimada, M. (2011). A high fat diet-induced impaired glucose metabolism in mice with targeted deletion of calpain in osteoblasts. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 409, 235–240.
Onishi, T., & Hruska, K. (1997). Expression of p27Kip1 in osteoblast-like cells during differentiation with parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology, 138, 1995–2004.
Qin, L., Li, X., Ko, J. K., & Partridge, N. C. (2005). Parathyroid hormone uses multiple mechanisms to arrest the cell cycle progression of osteoblastic cells from G1 to S phase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 3104–3111.
Klopfleisch, R., & Gruber, A. D. (2009). Differential expression of cell cycle regulators p21, p27 and p53 in metastasizing canine mammary adenocarcinomas versus normal mammary glands. Research in Veterinary Science, 87, 91–96.
Klopfleisch, R., Schutze, M., & Gruber, A. D. (2010). Loss of p27 expression in canine mammary tumors and their metastases. Research in Veterinary Science, 88, 300–303.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Institutes of Health grants R01 DK072102 and P30 DK057521, the William F. Milton Fund, and the MGH interim support fund (to M. S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimada, M. Overview of Calpain-Mediated Regulation of Bone and Fat Mass in Osteoblasts. Cell Biochem Biophys 66, 23–28 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-012-9393-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-012-9393-7